HOMEWORK 2
It is possible through trade for a country to consume a combination of goods that lies beyond its production possibilities frontier. Through trade, a country can specialize in producing goods for which it has a comparative advantage and trade for goods that would be more costly to produce domestically. This allows the country to consume beyond its production possibilities frontier (PPF) by accessing a greater variety and quantity of goods than it could produce on its own.
Production possibilities frontiers (PPFs) can shift both outward and inward.
Outward shifts occur due to factors like technological advancements, increases in resources (labor, capital, land), or improved education and training.
Inward shifts can happen due to events like natural disasters, war, depletion of resources, or economic downturns that reduce a country's productive capacity.
In a PPF graph of goods X and Y, points that lie beyond (to the right of) the PPF represent combinations of the two goods that are currently unattainable. Points that lie beyond (to the right of) the PPF represent combinations of goods that are currently unattainable given the available resources and technology. A country or economy cannot produce these combinations unless there is an outward shift in the PPF due to factors like technological advancements, increased resources, or improved efficiency.
A decrease in the quantity of resources available would cause the PPF to shift inward, rather than just a movement along the curve. A movement along the same PPF occurs when there is a reallocation of resources between the two goods, but if resources decrease, the entire frontier contracts, reducing the economy's overall production capacity.
Productive efficiency means that an economy is producing goods in the most efficient way possible, using all available resources. On a PPF, this implies that all resources are fully utilized.
If an economy is operating on the PPF and wants to increase production of good X, it must reduce production of good Y due to the scarcity of resources—this is known as the opportunity cost.
Productive efficiency implies that it is impossible to obtain gains in one area without losses in another. When an economy is productively efficient, it means that all resources are being used in the best possible way. As a result, producing more of one good requires reducing the production of another due to limited resources—this is the concept of opportunity cost.
Any point on the PPF curve represents productive efficiency, while points inside the curve indicate inefficiency.
A PPF is a straight line as a result of Constant opportunity costs. A PPF is a straight line when the opportunity cost of producing one good in terms of another remains constant. This means resources are equally efficient in producing both goods, so shifting production from one good to another results in a constant trade-off.
In contrast, a bowed-out (concave) PPF represents increasing opportunity costs, which occurs when resources are not equally adaptable to producing both goods.
Productive inefficiency implies that it is possible to obtain gains in one area without losses in another. Productive inefficiency means that an economy is not using all of its resources efficiently. This means it is producing at a point inside the production possibilities frontier (PPF), rather than on the curve.
Since resources are underutilized, the economy can increase production of one good without sacrificing the production of another, simply by making better use of available / resources.
An increase in the quantity of resources available Shifts the PPF outward. An increase in the quantity of resources (such as more labor, capital, or natural resources) allows an economy to produce more of both goods. This causes the production possibilities frontier (PPF) to shift outward, representing economic growth and an expanded capacity to produce goods and services.
Jose has one evening in which to prepare for two exams and can employ one of two possible strategies.
Strategy | Score in Economics | Score in Statistics |
1 | 93 | 81 |
2 | 77 | 92 |
The opportunity cost of receiving a 93 on the economics exam is __________ points on the statistics exam. 11 points
An economy is productive-efficient if it produces maximum output with given resources and technology. An economy is productive-efficient if it is producing the maximum possible output with its available resources and technology. This means that no resources are wasted, and the economy is operating on its production possibilities frontier (PPF).
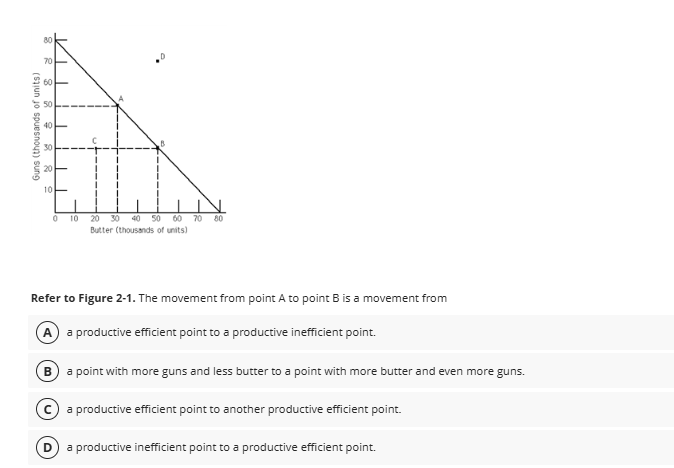
Option C: Correct. Since both A and B are on the PPF, the movement represents a shift from one efficient point to another.
Suppose the economy goes from a point on its production possibilities frontier (PPF) to a point directly to the left of it. Assuming that the PPF has not shifted, this could be due to The implementation of a new law that interferes with productive efficiency. If a law or policy restricts how resources are used (such as new regulations, trade barriers, or inefficient government controls), the economy may produce below its potential, causing a movement from a point on the PPF to a point inside (to the left of) it.
Points that lie inside (or below) the PPF are Attainable and productive inefficient –These points are within the economy’s capability to produce but indicate inefficiency, such as unemployment or misallocation of resources.
Productive efficiency implies the impossibility of gains in one area without losses in another.
If an economy is on the PPF, producing more of one good requires sacrificing some of another good, meaning there are trade-offs.
If there is always a 4-for-1 tradeoff between producing good X and good Y, it follows that the opportunity cost of X (in terms of Y) Is always the same and the PPF for these two goods is a straight line. Since the tradeoff is constant (4-for-1), the opportunity cost of X in terms of Y is always the same, and the PPF is a straight line.
In the production possibilities framework, economic growth is depicted by the PPF Shifting outward (away from the origin). Economic growth increases an economy’s ability to produce, expanding the PPF outward.
If the economy is producing at a point on its production possibilities frontier (PPF), the economy is Productive-efficient. When the economy is on the PPF, it is fully utilizing its resources, meaning it is operating productively efficiently.

Remains constant." – Correct. A straight-line PPF represents constant opportunity costs, meaning the same amount of copies is sacrificed for each additional fax machine produced.
If Luke can bake bread at a lower opportunity cost than Jason, and Jason can produce paintings at a lower opportunity cost than Luke, it follows that Luke has a comparative advantage in baking bread and Jason has a comparative advantage in producing paintings." This matches the definition of comparative advantage.
 Knowt
Knowt