Coordination and Response
1. The Nervous System
Function: Detects and responds to changes in the environment (stimuli) to maintain homeostasis.
Key Components
Central Nervous System (CNS):
Brain and spinal cord.
Processes information and coordinates a response.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS):
Nerves that connect the CNS to the body.
Neurons
Sensory Neurons: Carry impulses from receptors to the CNS.
Relay Neurons: Connect sensory and motor neurons in the CNS.
Motor Neurons: Carry impulses from the CNS to effectors (muscles or glands).
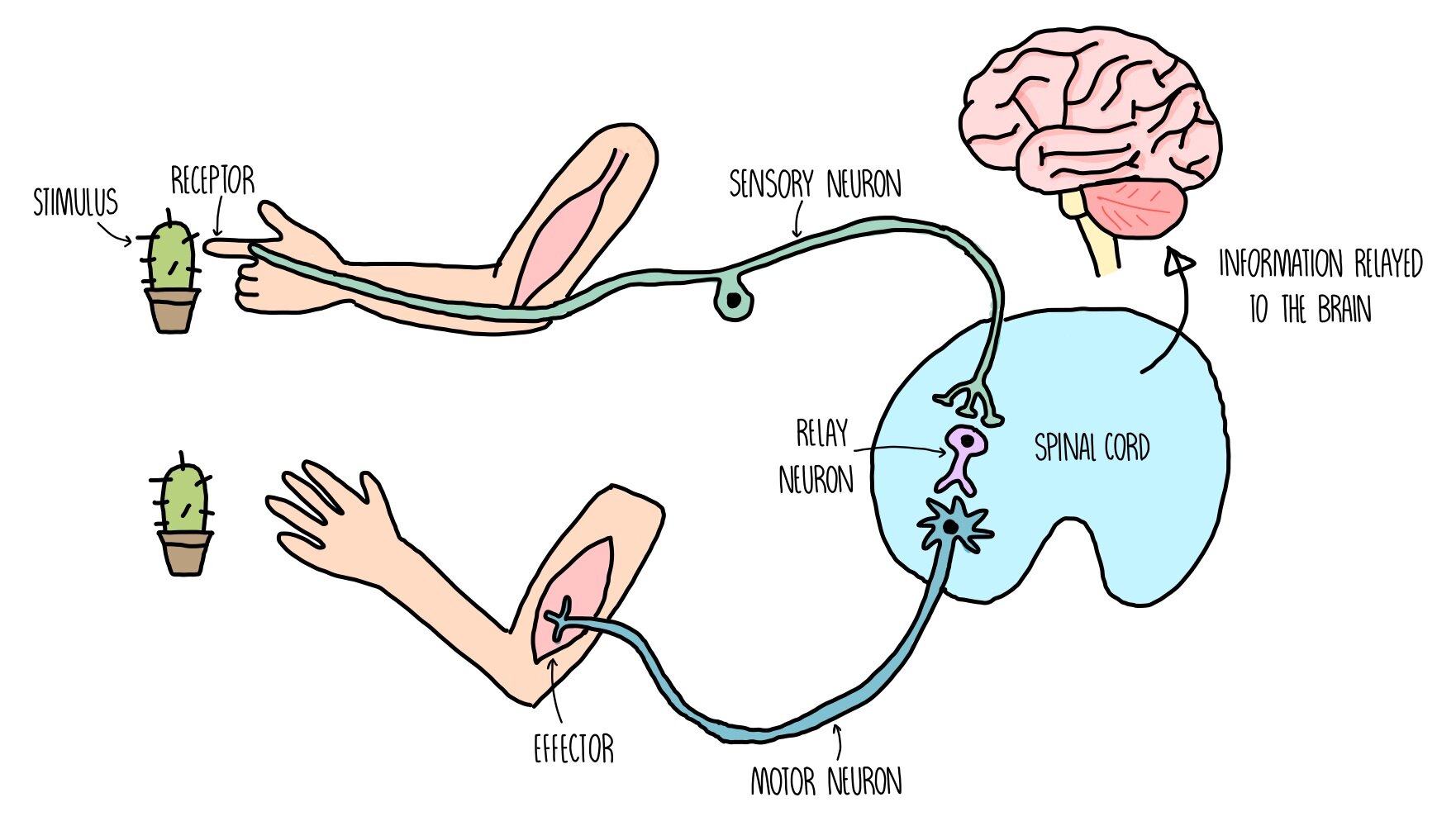
Reflex Arc
A quick, automatic response to a stimulus (e.g., withdrawing a hand from a hot object).
Stimulus → Receptor → Sensory Neuron → Relay Neuron → Motor Neuron → Effector → Response.
2. Hormonal System
Works alongside the nervous system but uses chemical messengers (hormones) transported in the blood.
Key Hormones
HormoneProduced ByTarget OrgansFunction | |||
Insulin | Pancreas | Liver | Reduces blood glucose levels. |
Adrenaline | Adrenal glands | Various | Prepares body for "fight or flight." |
Testosterone | Testes | Male body | Controls male secondary characteristics. |
Oestrogen | Ovaries | Female body | Controls menstrual cycle, secondary characteristics. |
3. The Eye
Structure and Function
PartFunction | |
Cornea | Refracts light into the eye. |
Iris | Controls the size of the pupil and light entry. |
Lens | Focuses light onto the retina. |
Retina | Contains light-sensitive cells (rods and cones). |
Optic Nerve | Sends visual information to the brain. |
Accommodation (Focusing):
Near Object:
Ciliary muscles contract.
Suspensory ligaments loosen.
Lens becomes thicker.
Distant Object:
Ciliary muscles relax.
Suspensory ligaments tighten.
Lens becomes thinner.
Pupil Reflex:
Bright Light: Pupil constricts (circular muscles contract).
Dim Light: Pupil dilates (radial muscles contract).

4. Coordination in Plants
Tropisms: Growth responses to stimuli.
Phototropism: Growth towards light (shoots).
Gravitropism (Geotropism): Growth towards gravity (roots).
Role of Auxins:
Plant hormones that regulate growth.
Uneven distribution causes cells to grow at different rates:
In shoots: Auxins promote cell elongation (towards light).
In roots: Auxins inhibit cell elongation (towards gravity).

5. Homeostasis
Maintaining a constant internal environment (e.g., temperature, water balance).
Thermoregulation:
Controlled by the hypothalamus.
Too Hot:
Sweat glands produce sweat.
Vasodilation: Blood vessels widen to increase heat loss.
Too Cold:
Shivering generates heat.
Vasoconstriction: Blood vessels narrow to reduce heat loss.
Osmoregulation:
Controlled by the kidneys.
ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone):
Regulates water reabsorption in the kidneys.