Chapter 22- Primates
Arboreal: living in trees
Brachiation: Swinging from limb to limb in trees
Prehensile tail: one that can be used like an arm or leg for grasping and holding on
Quadrupedal movement: moving on all four limbs
Stereoscopic vision: seeing an object at the same time with both eyes in the same plane with slightly different perspective gives depth perception, width, height, etc.
Objective One
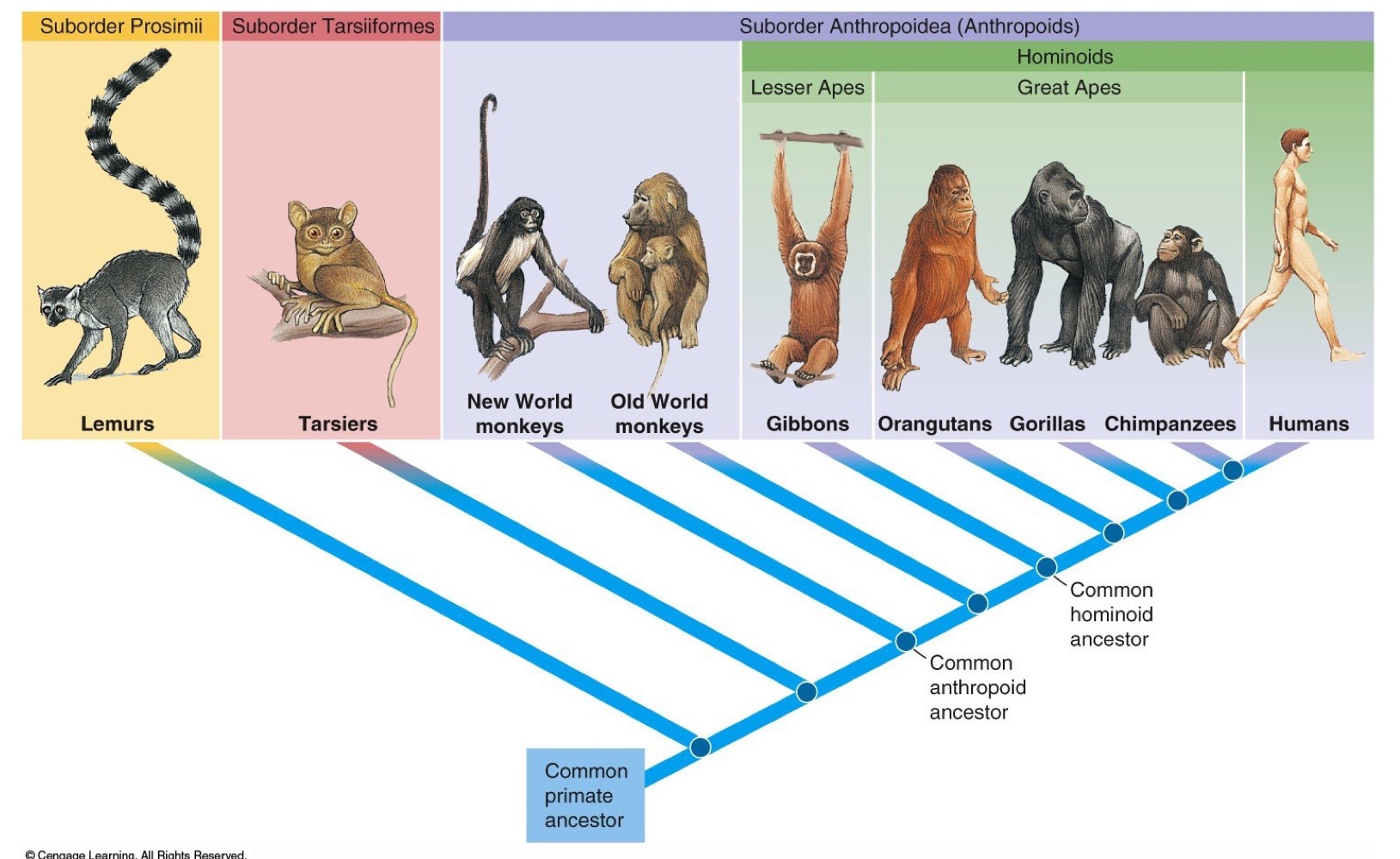
Reconstruct the cladogram for primate evolution; name and give examples of the three suborders of primates; distinguish among anthropoids, hominoids, and hominins
Primate Cladogram
Three suborders
Prosimii
Trarsiiformes
Anthropodiea
Humans and humanoid ancestors are Hominins
Objective 2
Describe locomotion in hominoids (remembering/understanding)
Hominoid Locomotion
Brachiation (gibbons and organutans)
swinging from limb to limb
tree dwellers
ex: monkey bars
Knuckle walking (chimpanzees and gorillas)
use arms to assist in quadrupedal waling
Upright (hominini including current humans)
humans
Objective 3
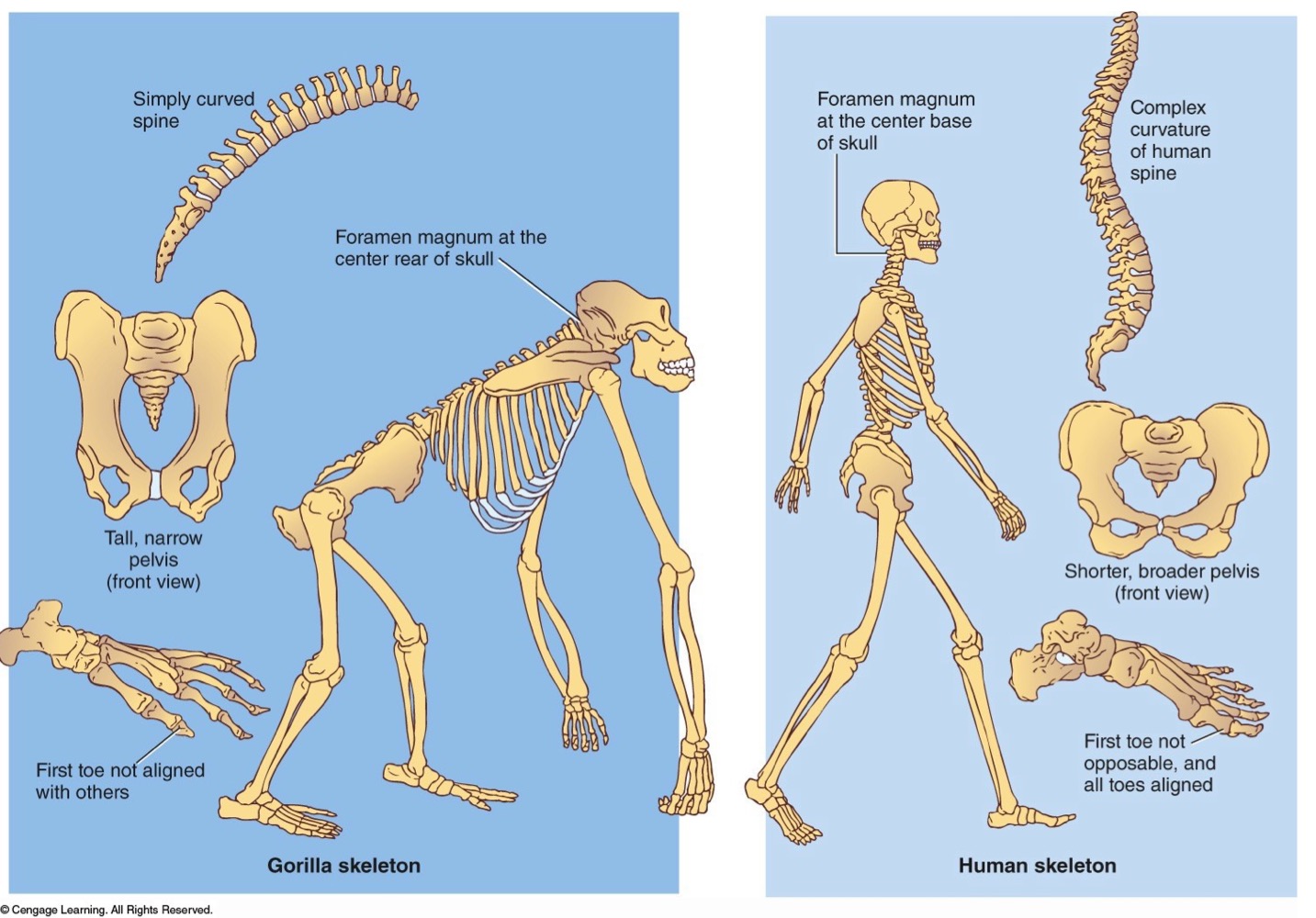
Describe the skeletal and skull difference between apes and hominini
Skeletal differences between humans and gorillas
Toe alignment
Humans- first toe aligned and not opposable
Gorillas- first toe not aligned and is opposable
Pelvis
Humans- short, broad
Gorillas- long, oval
Vertebral column
Humans- base of skull
Gorillas- long, oval
Foramen magnum
Humans- 4 curves
Gorillas- one simple curve
Jaw
Humans- u-shaped
Gorillas- rectangular
Pronounced facial feature
human-chin
gorillas- supraorbital ridge
Objective 4
List and describe differences between Old World and New World monkeys
Comparision of Old World and New World Monkeys
Tail
OW- no prehensile tail
NW- prehensile tail
Nose
OW- narrow, with downward nostrils
NW- flat, widespread nostrils
Terrestrial vs aboreal
OW- both
NW- arboreal
Quadrupedal movement
OW- yes
NW- new
Objective 5
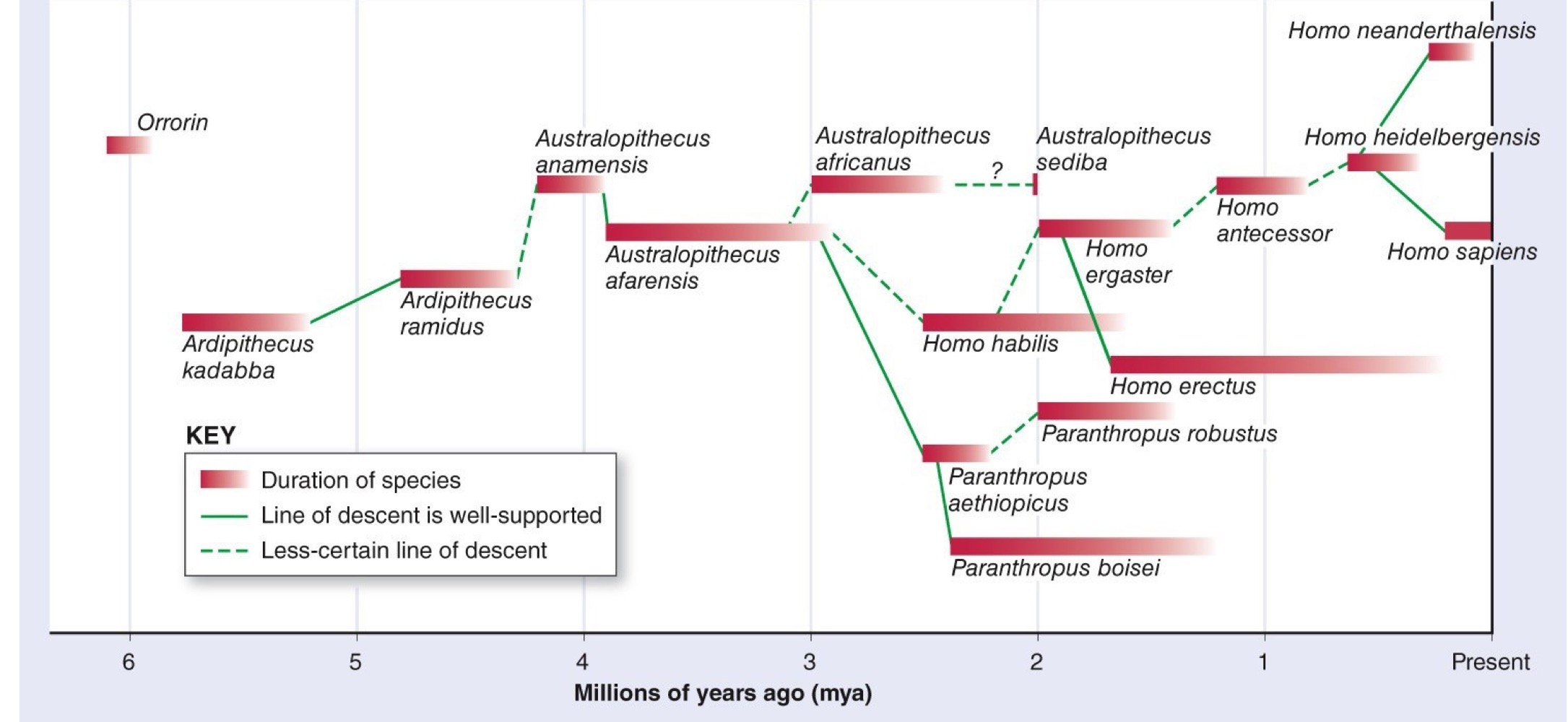
Understand that there were many species in the hominoid line and that at time more than one species simultaneously. Name the three most recent species of hominids
 Knowt
Knowt