Volcanic Hazards
Volcanic Hazards
- Volcanic hazard: a danger to people, property, or the environment created directly or indirectly by volcanic activity
- Types of volcanic hazards:
- Landslides
- Tsunamis
- Ash falls
- Hot ash flows
- Pyroclastic flows
- Mudslides
- Lava flows
- Release of gas
- Fiery clouds
- Nuée ardente
- Key terms
- Exposure: people and property at risk to volcanic phenomena
- Volcanic threat: the qualitative risk of a volcano to people and property
Mitigation Methods
- Identification of hazardous areas
- Monitoring of hazardous areas
- Development of emergency plans for people residing in hazardous areas
- Eg. evacuation
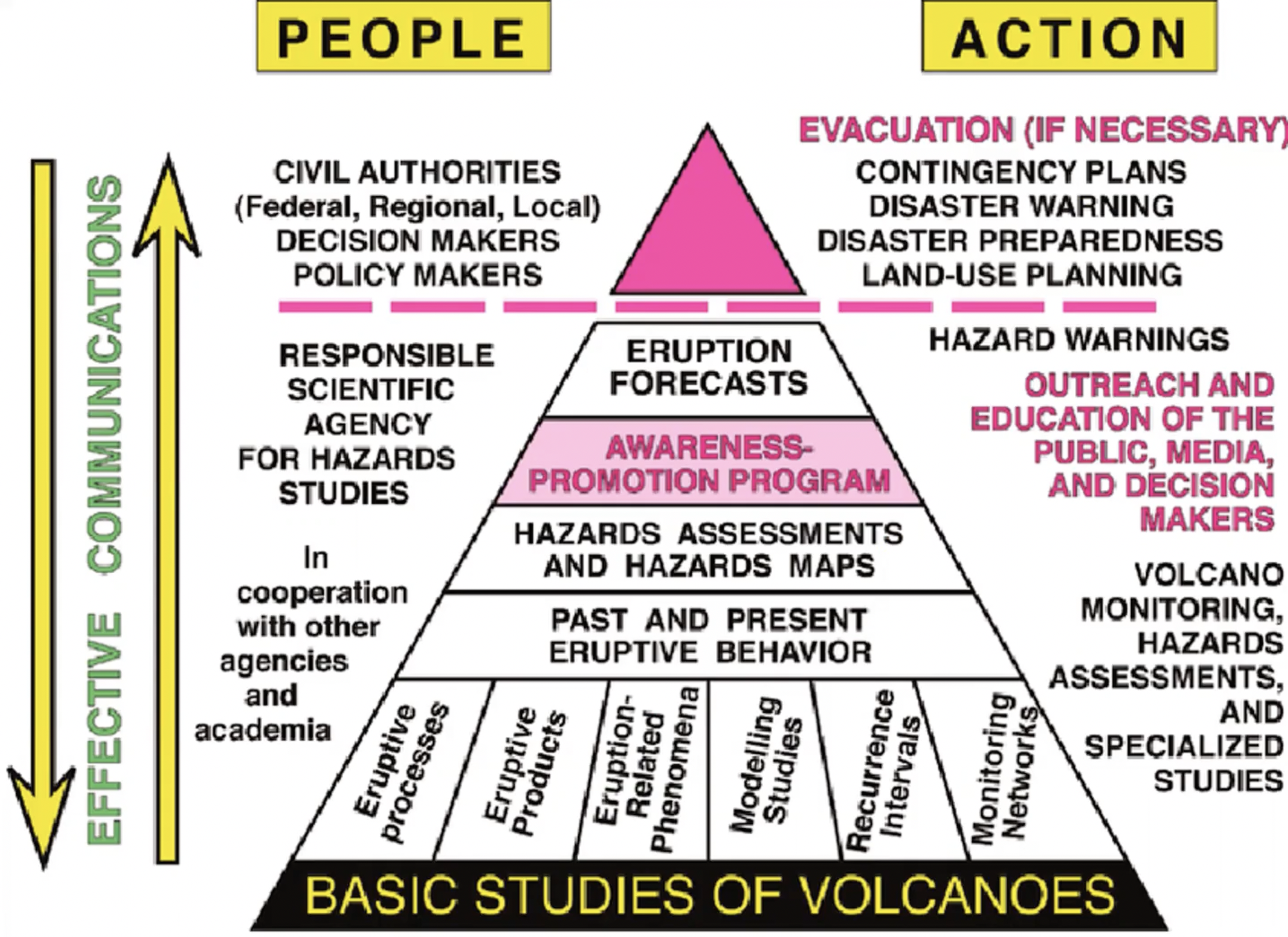
- Eg. evacuation
Common Precursors to Volcanic Hazards
- Rising earthquake swarms
- Ground surface movement
- Increased presence of [abnormal] gases in the atmosphere
- Variant temperatures
Collecting Information
Risk Knowledge
- Systemic collection of information and undertaking of risk assessments
- Are hazards and vulnerabilities well known?
- Do patterns and trends exist in these factors? If so, what are they?
- Are risk maps and data widely available?
Monitoring and Warning Services
- Development of hazard monitoring and early warning services for people residing in the affected area
- Which parameters are being monitored and why?
- Is there a sound scientific forecasting system?
- Can accurate and timely warnings be generated?
Dissemination and Communication
- Communication of risk information and dispersion of early warnings
- Do warnings quickly and effectively reach everyone at risk?
- Are the risks and warnings understood by those reached?
- Is warning information clear and applicable?
Response Capability
- Creation of national and community response capabilities
- Are response plans up-to-date and regularly tested?
- Are local capacities of knowledge utilized to their full extent?
- Are people prepared to react to warnings?