Unit 4: Transoceanic Interconnections (c. 1450–c. 1750)
4.1 TECHNOLOGY IN SEA BASED EMPIRES
I. Magnetic Compass
Made in China
For directions
II. Astrolabe
Used for navigation by measuring the altitude of stars
Developed in the Islamic Golden Age
Important tool for sailors in the Age of Exploration
III. Lanteen Sails
Triagular shaped sail
Takes wind either side
IIII. Astronomical Charts
Diagrams of Stars and Conselations are essential for navigation, allowing sailors to determine their position at sea and chart their course effectively.
1. Caravel: A small, highly maneuverable sailing ship developed in the 15th century, ideal for exploration and trade routes (PORTUGAL)
2. Carrack: A large, ocean-going sailing ship used in the 15th to 17th centuries, known for its capacity to carry cargo and passengers, often utilized by European powers for long-distance exploration and trade (PORTUGAL)
3. Fluyt: A Dutch type of sailing vessel developed in the 16th century, designed primarily for cargo transport, featuring a wide hull and shallow draft, making it efficient for trade in shallow waters.
4.2 CAUSES OF EUROPEAN EXPLORATION
Huge motivation for states sponsoring maritime exploration was desire for Asian and Southeast Asian spices, most notably Pepper.
European wanted them but land based empires like Mughal, Manchu, Safavid and Ottoman controled land based routes since they were land based empires.
Portugal Trading Post Empire
Prince Henry the Navigator sponsored 1st attempts for all water route into Indian Ocean.
Motivations; Their motivations were Technology development, Economy like spices and Trans-Saharan Gold and spreading Christianity.
They put trading posts around Africa and Asia
Vasco de Gama established them in western and eastern coasts and discovered Calicut as they had a reward for those who participated in the Indian Ocean Network.
Later owned that network due to Caravals and Carracks having lots of space for big guns to take over.
Spain
King and Queen of Spain, Ferdinand and Isabella wanted a piece in the action once the heard.
Later, Christopher Columbus presented an idea that it be easier to travel to the west to reach the Spice Empire but was rejected by Portugal. He presented this idea to Ferdinand and Isabella to which they agreed to pay.
Instead he foud North and South America
Spain also sponsored Ferdinand Magellan who sailed across South America to Pacific to the Actual East Indies.
Spain began conquering every space they could explore and discover which led to the transatlantic trade.
Other European States
Other European empires began sponsoring maritime exploration for four reasons
Rivalry
Envy
Desire for wealth
Need for alternatives route to Asia
France | England | Dutch |
Sought for Westward Passage to Indian Ocean | Were late due to their booming textile industry making $ for investors | 1579, gained freedom from Spain |
Access to Fur Trade 1608, Samuel de Champlain established Quebec Also established their presence from Trading Posts | After Queen Elizabeth 1 defeated Spain attempt to invade England, she threw support for Westward Exploration Sent Walter Reight and established 1st colony which is Virginia Also established Jamestown in 1607 | Compete control for trading posts around Africa Dethrone Portugal from King of Indian Ocean Trade 1608, Henry Hudson discovered and claimed New Hampshire (NYC) |
4.3 COLUMBIAN EXCHANGE
Columbian Exchange: Transfer of new diseases, foods, plants and animals between Eastern and Western Hemisphere.
Transfer of Diseases
Malaria
Measles
Smallpox
Since the people in Eurasia were familiar of each other diseases due to frequent exchanges and visitations they developed immunnity to it but unfortuantly the indigenous people haven’t.
The exchanges of diets and food were from the European bringing wheat, grape, olives, banana and sugar into the western hemisphere the Indigenous sent back maize, potatoes and manoic. This increased lifespan, diet diversity and population boom.
However, coerced labor (forced labor) was used in order to be able to cash croping (Method of agriculture where food is grown primarly for exports) in order to do this.
Europeans also brought cattle, pigs and sheeps which was nice but ultimately put strain on indigenous farmers. BUT brought horses to indigenous which made them valuable as they could be used as transportation and hunt larger preys.
4.4 Sea-Based EMPIRES ESTABLISHED
Motives for Europe:
Gold
Glory
God
The Spanish set up operation bases in the Phillipines. They ran their colonies in America with taxation, coerced labor, and tribute systems.
England set up trading posts along the corners of Mughal EMpire which build up to colonial rulings in India. The Dutch did this too in Indonesia)
There was a continuity in trade during this period such as:
Middle Eastern, S. Asian, E. Asian and SE Asian merchants still using the trade network even after Europe uses it.
Merchnats like the Gujaratis in Mughal Empire increasing their profit and their wealth even with Europe controlling almost ever bit.
Tokugawa, Japan
However there was still resistance such as:
The shogun, Tokugawa, was chill when the
Europeans meddled in that was until they
decided to try and conver people there to
Christianity which angered him as it
disrupted the unification and order. He
burned the missionaries and expelled them.
Ming, China
Main motive for the voyages of Zheng He was main control of the maritime trade in which the Indian Ocean Trade would be processed through China.
This failed and later secret Portuguese
secelty traded and bribed unril authorities
found out and banished them and isolate themselves.
Asanta Empire and the Kingdom of Kongo were also huge parts of this transaction. The Asante Empire were high factored trading partners of Portugal and England by providing gold, ivory and enslaved laborers.
This made them rich, expand, and consolidate their power. They used that to their advantage as they repelled the British from colonizing their region.
Kingdom of Kongo: Meanwhile, they made strong diplomatic ties with Portuguese traders. Kongo provided gold, ivory, and endslaved laborers.
The Europeans made sure that the America colonial system was from agriculture and used existing and new labor systems for this.
| New | |
Mit’a System: Subjects of the empire were required for labor for a certain amount of time of numbers for days per year. | Chattel Slavery: System in which individuals were considered to be seen as property to be bought and sold. This developed hereditary slavery. | |
Indentured Slavery: People worked for 7 years without pay which were then paid for to be brought to a new location. Encomienda System: Spanish used this to coercise Indigenous people to work for Colonial authorities. Forced to work for protection and food. Hacienda System: Haciendas were large agriculture estates owned by Spanish Elites. Indigenous were forced to work in these fields for export. |
ENCOMIENDA VS HACIENDA
Encomienda focuses more on population. Hacienda focuses more on the economy
Development in Slavery
Continuity
African Slave Trade: Has always been a thing even before the Clumbian Exchange
Cultural Assimilation
Domestic Work
African slaves became domestic servants with high demand for African women.
Slaves held power
Enslaved people could hold political or military positions
Change
Agricultural Work
African males were purchases. 2:1 left a demographic change in Africa
Transatlantic trade larger
Racial Prejudice
Slavery became identified with blackness which led to justification of brutal slavery.
4.5 THE ECONOMICS OF EMPIRE BUILDING
Economies Strategies to consolidate to Remain Power were:
Mercantilism: State driven economic that emphasizes on a build up of gold and silver wealth by maintaining a favorable balance of trade.
Mercantalist economies strove to maintain a favorable balance of trade
Wanted more exports than imports
Joint-Stock companies: Limited liability (could only lose money they invested into their business) business, charted by state (Governments had to approve of thia to make sure it granted trade monopolies in various regions) of investors
States used merchants to expand its influence acrosss in off far lands while merchants relied on states to keep their interests and their activities safe while granting them monopolies in many regions.
Dutch East India Company: Charted in 1602 by dutch, whom granted the company a monopaly on trade in Indian Ocean. As they edge out Portuguese two things happened:
The company investors got mad rich
Dutch imparial government was able to expand and influence across many places through Indian Ocean.
Network of Trade Changes

CHANGE
Atlantic System
The movement of goods, wealth and laborers between the eastern and western hemispheres
Importance of Sugar
Silver was King
Coerced labor
CONTINUITY
Afro-Eurasian Markets Thrived
Regional markets across Afro-Eurasia continued to flourush and icrease their reach
Asian Land Routes
Overland routes like the Silk Road almost entirely controlled by Asian land-based powers, notably Ming China and then Qing Dynasty
Peasant and Artisans Labor
Artisans were laborers who made goods by hand.
4.6 Challenges to the State Power
Local Resistance:
1st Resistance: Fronde
Happened in France. Lous XIV was the posterboy for absolutism. Absolutism means that monarchs consolidated all power to themselves. And so several new edicts were passed to increase taxation among French Subjects, and so The French nobility, whose power had been under threat from the growing power of the monarchs led peasents into rebellion, Causing the Fronde.
2nd Resistance: Queen Ana Nzinga Resistance
Happened in Africa. Matamba and Dnongo grew concerned as Portugal enrochment ocurred in Africa. She allied with the Dutch and Kingdom of Kongo to fight back as she won.
3rd Resistance: Pueblo Revolt
Happened in America. Suffered terrible abuse from compressive Spanish system as they had been in coerced labor and suffered effects of disease; organize a revolt under Pope and killed as many spanish conquistadores.
Slave Rebellions
Maroon Societies: In Caribbean and Brazil. Escaped africans ran away and join these to fight for freedom. Prescence of this served as endless enticement for their workers to abandon their work. In Jaimaca, British tried to crush them but they fought back. Treaty was signed to acknolwedge the freedom of this community.
4.7 CHANGING SOCIAL HIERARCHIES
Responses to Diversity Ethnic
Expulsion | Tolerance | |
Jews in Spain and Portugal: 1492 Spain completed the renconquista to rib the iberian oeninsula from muslim rules. Saw who posed a threat to conversion of Christianity. Qing Rpression of Han people and made the men wear quebec hairstyle to show submission to the Qing Dynasty. | Jews in the Ottoman Empire: With the news of the expulsion of Jews in Spain, the Ottoman leader, Sultan Mehmed II, opened his empire. But were requiered to pay the Jizya tax since they werent muslims. Mughal Acceptance: AKHBAR THE GREAT refused too implament the jizya but built churched, mosques, and temples | |
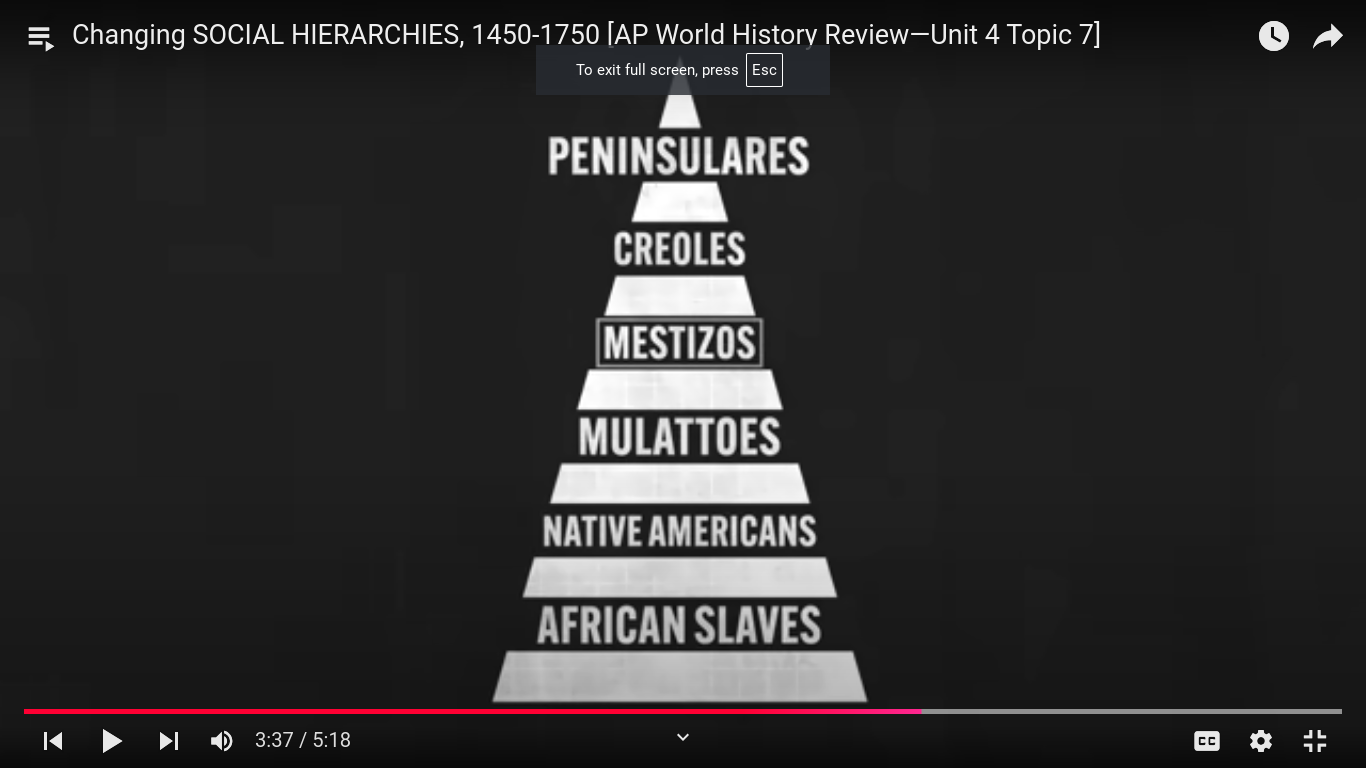
SPAIN CASTA SYSTEM