physics
Changes of State and the Particle Model
Particle Model: All matter is made up of tiny particles (atoms or molecules) that are in constant motion.
Solid: Particles vibrate in fixed positions.
Liquid: Particles are close together but can move past each other.
Gas: Particles are far apart and move freely at high speeds.
Changes of State:
Melting: Solid to liquid (energy is absorbed).
Freezing: Liquid to solid (energy is released).
Boiling/Evaporation: Liquid to gas (energy is absorbed).
Condensation: Gas to liquid (energy is released).
Sublimation: Solid to gas (direct change without going through liquid phase).
Energy and Changes of State:
When a substance changes state, the temperature doesn't change (during the phase change).
The energy is used to break or form the bonds between particles (e.g., during melting or boiling).
Internal Energy and Transfers
Internal Energy: The total energy of the particles in a substance, including both kinetic and potential energy.
- Kinetic Energy: Due to the motion of particles.
- Potential Energy: Due to the position of particles (how far apart they are).
Energy Transfers :
Mechanical Transfer: Energy is transferred by the action of a force moving an object (eg. pushing and pulling)
Electrical Transfer: Energy is transferred when an electric current flows through a circuit
Thermal Transfer: Energy is transferred from hotter objects (via conduction, convection, or radiation
Radiation Transfer: Energy is transferred in the form of electromagnetic waves (eg: light, infrared, radio waves)
Specific Heat Capacity:
Formula: Q = m × c × T
Where:
Q = Heat energy (J)
m = Mass (kg)
c = Specific heat capacity (J/kg°C)
T = Change in temperature (°C)
Particle Model and Pressure
Pressure: The force exerted by particles as they collide with the walls of a container.
Formula: P= F/A
Where:
P= Presseure (Pa)
F= Force (N)
A= Area (m²)
Gas Pressure and Temperature:
As the temperature of a gas increases, the particles move faster, leading to more collisions with the container walls. This increases pressure (if volume is constant).
Boyle's Law: For a fixed mass of gas at constant temperature, the pressure and volume are inversely proportional.
Formula: P1×V1 = P2×V2
Where:
P= Pressure (Pa)
V= Volume (L)
Charles's Law: For a fixed mass of gas at constant pressure, the volume of the gas is directly proportional to its temperature in Kelvin.
Formula: V1/T1 = V2/T2
Where:
V= Volume (L)
T= Temprature in Kelvin (K)
Atoms and Isotopes
Atoms: The smallest unit of an element that retains its chemical properties. Composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Protons: Positive charge, found in the nucleus.
Neutrons: No charge, found in the nucleus.
Electrons: Negative charge, orbit the nucleus in energy levels.
Atomic Number: The number of protons in the nucleus (determines the element).
Mass Number: The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus.
Formula: Mass Number = Protons + Neutrons
Isotopes: Atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons, resulting in different mass numbers.Example: Carbon-12 and Carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon.
Atoms and Nuclear Radiation
Nuclear Radiation: Emission of particles or electromagnetic waves from the nucleus of an atom.
Alpha Radiation (α): Helium nucleus (2 protons, 2 neutrons), low penetration (can be stopped by paper).
Beta Radiation (β): High-energy electron, medium penetration (can be stopped by a sheet of metal).
Gamma Radiation (γ): High-frequency electromagnetic wave, very high penetration (can only be stopped by thick lead or concrete).
Radioactive Decay: The process by which an unstable nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation.
During decay, the atomic number or mass number changes, transforming the atom into a different element or isotope.
Half-Life: The time taken for half of the radioactive nuclei in a sample to decay.
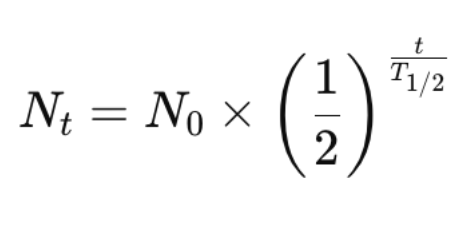
Nt = Remaining nuclei
N0 = Initial nuclei
t = Time elapsed
T1/2 = Half-life of the substance
Uses of Radioactive Materials:
Medical: Tracers, cancer treatment, radiography.
Industrial: Thickness gauges, monitoring equipment.