Bio Unit 8: Evolution
Have a working knowledge of Natural Selection, Hardy Weinberg Theory, Evolution of populations, Genetic Drift, Bottleneck Effect, Founder Effect, Gene Flow, Homologous and Vestigial Structures
Evolution:
occurs to a population not just an individual
4 steps:
Variation
Competition
Adaptations
Selection
Natural Selection:
mechanism of evolution (individuals with certain traits are more likely to survive and reproduce… NOT RANDOM)
survival of the finest —> occurs naturally in the environment
5 basic steps:
Variation
Inheritance
Selection
Time
Adaptation
unequal reproduction
some individuals don’t evolve
can amplify/diminish only heritable traits
evolution isn’t goal-directed
Hardy Winberg Theory:
𝑝 + 𝑞 = 1 (*alleles, dominant vs. recessive)
𝑝² + 2𝑝𝑞 + 𝑞² = 1 (*genotypes, homo dominant vs. hetero vs. homo recessive)
Assumptions:
no selection
no mutation
no migration
large population
random mating
Evolution of populations:
population: a group of organisms all the same species and can breed w/ each other
Genetic drift: change in frequency of an existing gene variant in the population due to random chance (more pronounced in smaller populations bc fewer contributing to next generation’s gene pool)
Founder effect:
small group of individuals breaks off (migrate) from a larger population to form a new population
the new population's gene pool may not represent the original population's genetic diversity
Bottle-neck effect:
significant reduction in population size (due to events like natural disasters) can lead to a genetic bottleneck, where the surviving population has reduced genetic diversity
Genetic drift vs. natural selection:
Aspect
Genetic Drift
Natural Selection
Process Type
Random
Non-random
Population Size
Effects more significant in small populations
Can occur in any population size
Role of Environment
No direct influence
Direct influence (selective pressures)
Effect on Allele Frequencies
Random fluctuations
Increases frequency of advantageous alleles
Genetic Variation
Can decrease genetic variation
Can maintain or increase genetic variation
Outcome
Potential loss of alleles or fixation by chance
Adaptation to the environment
Examples
Bottleneck effect, founder effect
Industrial melanism in peppered moths, antibiotic resistance in bacteria
Gene Flow:
any movement of individuals or genetic info they carry from one population to another (due to movement of individuals)
Homologous and Vestigial structures:
Homologous/divergent:
similarity in characters resulting from shared ancestry
different species but similar bc common ancestry
Vestigial:
“leftover” structures; served an important function in ancestors
analogous/convergent:
organs w/ similar functions (not ancestry related)
Define the terms Adaptation and Speciation.
Adaptation:
organisms experience change in their traits to be better suited for the environment
Speciation
the evolutionary process by which populations evolve to become distinct species (over time and possibly bc of isolation)
Understand the role of gene mutations and how they can only be passed on to the offspring if they occur in an organism’s sex cells.
mutations are the source of genetic variation
mutations in sex cells can be passed down to offspring
Explain why increased genetic diversity tends to improve the survival of a species.
increased variety of traits —> bigger likelihood of survival
decreased inbreeding —> less genetic disorders
interact in more stable and complex ways within ecosystems.
Explain the following examples of evolution in modern times in terms of the theory of natural selection: the peppered moth, insect resistance to insecticides, and bacterial resistance to antibiotics.
peppered moth:
in very polluted places, darker moths are favored bc blend in better
inesct resistance to insecticides:
as we use more insecticides, the insects that are able to withstand and survive the chemicals reproduce —> then more of the insects become immune to the pesticides (immunity passed down through reproduction)
bacterial resistance to antibiotics:
Overuse and misuse of antibiotics have accelerated the evolution of antibiotic-resistant bacteria
Resistant bacteria survive antibiotic treatment and reproduce so frequency of resistant bacteria increases, leading to the spread of antibiotic-resistant strains.
Define and understand the terms: heterozygote advantage, balancing selection, and frequency-dependent selection.
heterozygote advantage:
heterozygous genotype has relatively greater fitness than homozygous recessive/domninant
greater reproductvie success of heterozygous individuals
preserves variation in gene pool
Balancing selection:
a type of natural selection that maintains genetic variation within a population by favoring multiple alleles at a particular locus over time.
prevents any allele from being fixed
Frequency-dependent selection:
fitness of a genotype depends on proportion of individuals w/ certain genotypes in the population
Define and understand the following selection patterns: directional, disruptive, & stabilizing, and their impact on evolutionary fitness.
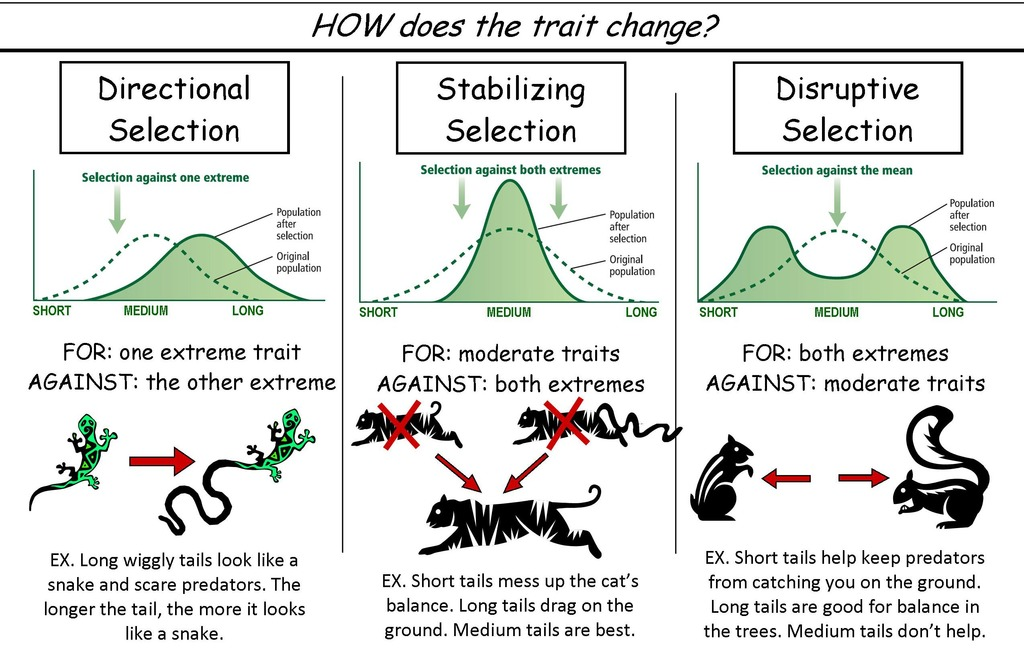 Understand key points associated with evidence of evolution.
Understand key points associated with evidence of evolution.
fossil record
comparative anatomy
molecular biology
biogeography
direct observation
comparative embryology
Reading cladograms
The main line of a cladogram represents the passage of time.
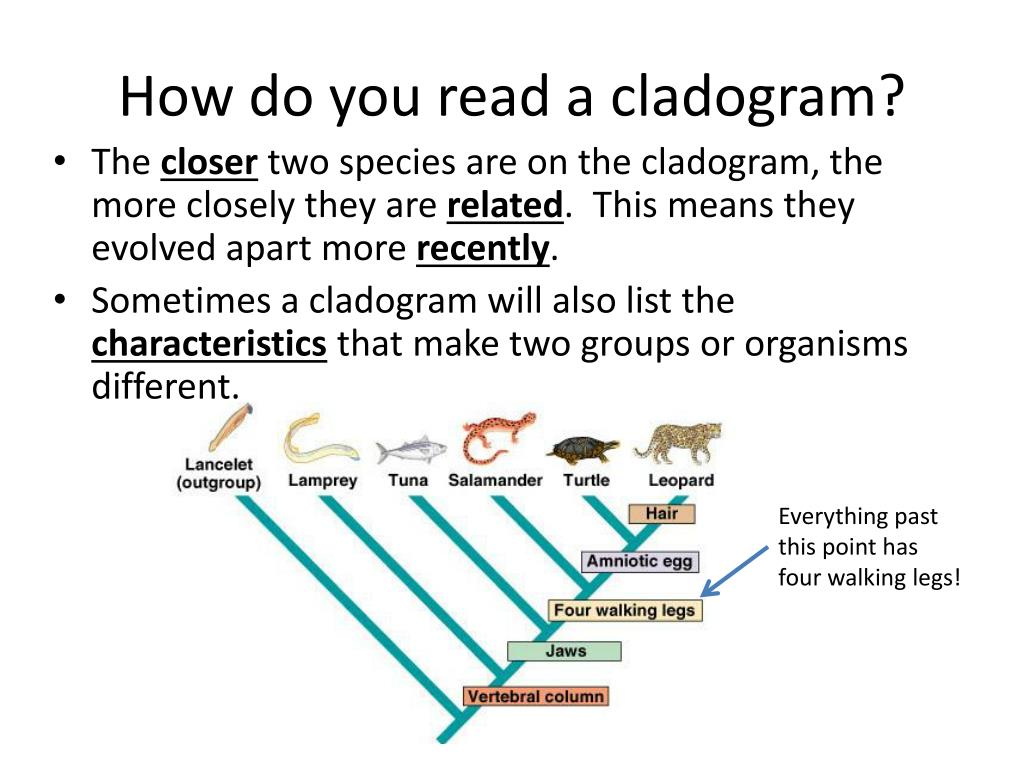
Additional Videos:
Evidence for evolution:
Direct observation
mutation happens by chance, passed on through natural selection
Homology
structural similarities (results of common ancestry)
Vestigial Structures
features that are not useful to an organism & must be remnants of ancestral features (ex. wisdom teeth)
molecular homology:
we can gauge how closely related species are by comparing their genomes
fossil record:
get an idea of what kind of organisms existed + when
Biogeography:
following change in geography helps us make fossil predictions
Factors that guide evolution:
genetic variation makes evolution possible
genetic drift: shows chance events gradually alter the gene pool
can alter allele frequencies and lead to loss of genetic variation
founder effect: deviations amount founders (smaller group) are statistically significant
bottleneck effect: original population—> catastrophic event —> survivors
deviations among survivors are statistically significant
gene flow: occurs to migration of fertile organisms
Sexual selection and sexual dimorphism:
adaptations that help organisms attract/select mate
intersexual selection:
one sex chooses which members of the opposite sex to mate w/
intrasexual selection:
members of the same sex compete for mates