CLE Q4
Padre Calungsod:
13 or 14 when he left PH IN 1668 to join Jesuit priests headed by Fr. Diego Luis de San Vitores in a mission expedition to the “Islas de los Ladrones” renamed “Marianas” or Guam.
declared Patron of the Filipino Youth and we celebrate his feast ordinarily on April 2.
St. Perpetua
One of the first women known as a martyr in the church
“the blood of martyrs is the seed of Christianity”
2 sources of faith: These sources form one sacred deposit of faith (Dei Verbum 10)
Sacred Scriptures
From the Gospels and Bible
Apostolic Tradition
Refers to the teachings and practices passed on to the church from the apostles.
What apostles practiced came from the scriptures therefore it is also considered a sacred tradition
Teachings of the apostles became the habit that was handed down to early Christians and handed to us but that tradition is not stagnant and is changing.
Must grow in our knowledge and appreciation not only for scriptures but also of our church’s tradition
Tradition: The way the people of God have transmitted and have lived the Scriptures
Church: Calls its members to participate in the “new evangelization because of the changing ways and thinking in our modern world.
Mission of the Church: talks about what happened to the followers, apostles, and church after the resurrection
Birth of the church (A.D 33 Pentecost event)
Pentecost: Happened 50 days after crucifixion
Apostles received the outpouring of the Holy Spirit in the form of tongues of fire and strong minds and initiated the first evangelization
Apostles started to speak in different languages and became more courageous to speak of Christ
Apostles clearly understood the mission Jesus gave them at the Last Suppe or institution of the Eucharist.
Found in ACTS 2
Considered the birthday of the church
Strong wind: God’s first breath of life into all creations
Fire: Manifest of God
Evangelization: Calls for reformation or renewal of the teachings
Acts of the Apostles and Apostolic Church (30-70 C.E)
Records the first 30 years of history and progress of the church
Records that about 3,000 people believed Peter’s Sermon and were baptized on the day of Pentecost
Considered as the 5th gospel written by St. Luke
Paul:
Responsible for the spread of the Church to the Gentiles (non-Jews)
The second half of the book (13-28) was written by Paul
Formerly called Saul was a Pharisee and had been a persecutor of Christians.
Was converted to Christianity when he encountered the Risen Christ on the road to Damascus
Became known as the “Apostle of the Gentiles”
Peter:
Started the evangelization, and helped the apostles to proclaim the Good News.
Wrote the first 12 chapters of the ACTS that narrate his works
The first pope of the Church
Peters Sermon: Tells the basic truths that he and other Apostles would proclaim about Jesus
Jesus died but rose from the dead
Therefore, Jesus is our Lord and Savior forever.
Peter and Paul: 2 outstanding figures in the age of the Apostolic Church
Antioch:
A new Christian community, where followers of Jesus were first called Christians
Early Church (70-312 C.E):
All the first Christians in Palestine were Jews and people looked down and them and they were considered “fallen-away Jews”
Persecution of the early church went on for several centuries, most of them happened during the rule of Nero (A.D 64-68) and Diocletian (A.D 303-305)
Roman Christian Empire (315-590 C.E):
Constantine:
One of the greatest rulers of the Roman Empire, formerly devoted to the cult of the Unconquered Sun, his views changed in 312 A.D when he was fighting Maxentius (leader of Italian soldiers) in Italy
Before the battle, he saw a cross superimposed on the sun with the inscription (In hoc Signo, Vinces or In this sign you shall win) he ordered his men to battle with the cross painted on their shields and defeated their enemies, and soldiers were also converted.
Roman persecution of Christians stopped when emperor Constantine granted religious freedom by signing the law known as EDICT OF MILAN in A.D 315 and Christians were finally able to openly believe and worship Jesus Christ
Emperor Theodosius: 380 A.D He eliminated paganism and made Christianity the official religion of the Roman Empire empowering the spreading of Christianity
Many Roman Christian churches were built
the liturgy was enriched and mass celebration was granted
Christianity was declared the official religion
early council of the church (Nicaea, Ephesus, Chalcedon) and the writing of the Fathers of the church played crucial roles in establishing important doctrines as responses to the confusion brought by the heresies of individuals or groups of Christians at that time.
Canon of the Sacred Scriptures:
In 382 C.E. the official list of inspired books of the bible, known as the Canon of the Scriptures first came to being. It is a formal definition of the Canon was proclaimed by the Council of Trent in the 16th Century
St. Jerome (342 A.D):
“Ignorance of scriptures is ignorance of Christ”
Gained a place in history with his Vulgata the only official translation of the Bible for the Catholic Church
Took 40 years to complete the translation from Hebrew (Old Testament) and Greek (New Testament) into Latin which was the language the people easily understood
He was born in Dalmatia in 342 he studied grammar and theology
He was called to Rome as secretary of the Pope
St. Augustine of Hippo:
Declared that it is only on the authority of the Roman Catholic Church that we accept any book of Scripture.
Heresies:
Opinions that do not follow church teachings.
A statement of belief or teaching that differs from or contradicts the official teachings of the church.
Heresies and ecumenical councils:
Nicaea (325) Proclaimed the divine nature of Jesus
Artanism: Initiated by Arius saying that Jesus was not God but only a man
Constantinople I (381) Define the nature of the Holy Spirit
Macedonianism: Denied divinity of the Holy Spirit
Ephesus (431) Mary is the mother of God
Nestorianism: Denied that Jesus is not God so therefore Mary is not the mother of God
Chalcedon (451) Jesus as one divine person with 2 natures (divine and human)
Monophysitism: Son of God but not a real man
Constantinople II (553)
Nestorianism: Erroneously divided Jesus into 2 persons
Constantinople III (680) Defined the doctrine for the two wills in the person of Christ
Monothelism
Nicaea II (787) Legitimacy of the veneration of images, specified that adoration was due to God alone while veneration is given for the saints.
Iconoclasts: (Image destroyers) Wanted to abolish all the icons and statues of saints.
Muslim:
In the religion of Islam, members are called Muslims
Mohammed:
The founder is Mohammed in Arabia in the year 622, a merchant of Mecca which is a house of prayer
Married to a rich widow who bore him 7 children
At age 40, received a vision from Allah, through the medium of the archangel Gabriel, the prophetic call which he wrote down in the Koran which is the scripture of Muslims
He started preaching the necessity of Holy war or Jihad against unbelievers. After the capture of Mecca, they conquered Arabia, the Middle East, North Africa, and Spain in 712.
Christians in Europe were trembling. Charles Martel the king of France stopped the Muslims’ advancement in the battle of Poitiers in 732
Defeated from France, they attacked Italy from the Mediterranean Sea at the walls of Rome the Muslims were defeated.
5 pillars by Muslims:
Professing of faith in Allah and in Mohammed as his prophet
5 daily prayers facing towards Mecca and public prayer in the Mosque on Fridays
Fasting during Ramadan month from daybreak to sunrise
Almsgiving
Pilgrimage to Mecca once in a lifetime to kiss the black stone in the Kabal which is a sign of baptism for Muslims
Medieval Church:
The Middle Ages, which stand between ancient and modern times, lasted for almost a millennium
In the 7th century, the Roman empire weakened due to the migration of northern tribes across Europe
Barbarian tribes (that practice idolatry/ black worshiping, non-believers) plundered city after city until Rome was taken.
Replaced by small kingdoms with strong warriors as rules
Civilization in Europe halted due to educational and government institutions
Church was establishing influence in that era of “cultural and moral darkness: where priests and other officials were not good examples, and were driven by corruption and greed
Dark ages in medieval:
Faded into darkness, demoralizing the spread of Christianity, and heresies grew persistent because of church leaders, and their corruption from their ranks (hierarchy, family appointing family)
Struggles of power between church and state
Division of great Schism and Christians left the area because they believed the church doesn’t give others the chance to follow Jesus
Schism: People are influenced by the religious denominations, the great separation between Eastern and Western due to migration in Europe
The separation between the Eastern Greek-speaking church and the Western Latin church in Rome
Crusades and inquisitions happened (war) they wanted to invade places of other groups to be recognized in the church and state
Pope Alexander Borgia the Sixth:
The worst pope in history and is known for his corruption (spends the money from the taxes of the people so that he can live in luxury)
Made cardinal at the age of 25 by his uncle Pope Calixtus III (corruption with rank)
Was elected pope in 1442 among those who elected him were his family
Made his son Cesare Borgia at the age of 18 or 20 a cardinal
His wife is also a pagan
“the greater the darkness the clearer the light” By Saint Paul in the time of the Apostles:
The Spirit who dwells in the church worked through various chosen people and groups to keep the Faith burning during the dark ages.
Pope Gregory VII:
Initiated monastic life, renewals, reforms
Saint Catherine of Siena:
Influenced by Pope Gregory
Used her wisdom, natural personal charm, and spiritual insights to become the people’s ambassador of peace among parties at war
St. Francis of Assissi:
Sent as the missionary who ministered to the spiritual needs of people
Born to a wealthy family left his wealth and committed to being a missionary
St. Dominic:
Patron Saint of Catholic schools
“Dominicans”
St. Thomas Aquinas:
Gave importance to living with pagans or barbarians (worship cults) and influence them slowly
A Dominican priest, outstanding preacher, philosopher, and theologian, harmonizing reason and faith, pagan philosophy with the scriptures
Black Death (1344):
Terrible death brought to Europe by bubonic plague-infected rats aboard a ship traveling from the black sea of Sicily.
it produced vomiting, mental disorganization, and delirium causing death within a few days
about 25 million people or 1/3 of the world’s population died
Reformation and Counter-reformation (1517-Vatican II)
Martin Luther
Augustinian monk
Scandalized by the church prelates who were more concerned with wealth and power than the spiritual needs of the people
Revolted against the catholic church
Nailed his 95 thesis that points to reform of the church on the door of Wittenberg castle church in 1517
he had no idea church action would lead to a whole new group of religious denominations known under the general title Protestantism
Counter-Reformation Movement: The Catholic Church’s Response to Luther’s Criticisms
General revival of religion
Saints such as St. Ignatius of Layola and their respective religious orders vigorously carried out reforms and spiritual writings and examples focused on interior conversion, keeping of prayer, and commitment to do God’s will in contrast to the external obedience to obligation.
Vigorous effort to reconquer lost territories in Europe and to extend dominions in Asia and South America
St. Francis Xavier went to the east and attempted to convert China and Japan.
King Philip II of Spain supported expeditions to new lands.
In 1521, Ferdinand Magellan arrived in the Phillippines Islands and brought us Christianity.
Holding of the Council of Trent
Pope Paul III called for a council to affirm and consolidate Catholic teachings and strengthen discipline.
Church in 16th, 17th, 18th, 19th centuries: Vatican I
Faced problems of Secularism, pluralism, totalitarianism, liberalism, tensions between governments, and internal dissent among Catholic intellectuals.
Rerum Novarum or On the Condition of the Working Classes in 1891
Pope Leo XIII produced the first formal church social document.
Pope Pius XI:
Vatican I was convened by Pope Pius XI to address the rising influence of rationalism, materialism, and liberalism.
Council was not formally closed because Italian troops occupied Rome in the summer of 1870
Vatican II in 20th century:
High point in the Christian faith.
Opened by St. John XXIII on October 11, 1962
Closed by St. Paul VI on December 7, 1965
Aimed for the renewal of the church for the sake of evangelization.
Aggiornamento: Sign of the times
Content of 2nd Vatican Council:
Denouncement of the nature of the church
A clear announcement or purpose on the needs of the church
Mission of the laity (us)
Most members of the church are laity
Religious freedom
To what extent can Christians express their religious freedom
Revision of the liturgy (how we celebrate the mass)
Use of the native language or Latin during mass and sacraments
For people to understand and participate better in mass
Important matters:
Empowering church unity
annual meeting of all religious denominations to improve unity, we are the church, just different teachings
common ground in certain issues with protestant churches and discuss the possibility of unity with the easter orthodox church
the council produced 16 documents complied in one book called Vatical II documents which is composed of moral issues and revisions in the liturgy that people neglect
Church at present times:
Popses that followed the closing of Vatican II up to the present have consistently taught that the heritage of the faith passed onto us by the early church must be preserved and communicated to the people of our present times in an understandable way
10 years after Vatical 11, in 1975 St. Paul VI wrote his apostolic exhortation entitled Evangelii Nuntiandi or Evangelization in the Modern World.
This laid the foundation and direction evangelization must take for our times.
This is the document where for the first time, the church emphasized that spreading the Gospel is the role of every Christian, not just priests, deacons, and professional staff of the church.
St. John Paul II:
coined the term “new evangelization” and popularized it. He wrote numerous letters and encyclicals and published the Universal Catechism of the Catholic Church (CCC)
Traveled over 100 countries preaching the Gospel. He promoted inner conversion to Christ.
Pope Benedict XVI:
Made new evangelization the central pillar of his pontificate.
In 2010, he institutionalized new evangelization by creating an office known as the Pontifical Council for the Promotion of the New Evangelization.
In 2010, he wrote Verbum Domini, or Word of God where he proclaims that God’s Word has not lost its relevance and vitality.
Pope Francis:
He is the 266th pops from the line of the apostle Peter.
He emphasizes the need for joyful proclamation of the Gospel especially to God’s “little ones” the poor.
His ideas on evangelization are found in his apostolic exhortation entitled Evangeli Gaudium or the Joy of the Gospel.
The challenge of the modern word - Found in Vatican II (1963-1965)- Second Plenary Council of the PH or PCP II (1991) by Pope John Paul II - Vission: Chuh as a community of disciples centered in Jesus Christ, a church of participation, communion, mission of the poor- Mission: Renewed integral evangelization (RIE)- Renewed Catechesis, renewed social apostolate, renewed worship
DNW: doctrine, meral, worship (dimensions of faith)
PCP II:
Produced own documents, proposing ways how we should move toward renewing our faith life in such a way that we can live the full life of the Gospel
From Pentecost to the present time, we see that the Church has gone through many successes and failures, lights and shadows, goodness and evil, glory and shame. But stood the test of time because of God’s constant support.
To study church history is to see the hand of God at work amid strife and sin. We see how the Holy Spirit reunites what sin and folly of men and women have divided.
No matter what the church will never die for we are built upon the foundation of the apostles and prophets with Christ as the capstone.
Titles of Jesus:
Kind of relationship with a person and how he mingled and reached out to the people
Evangelists and early Christians used certain titles when they preached Jesus to others. The New Testament repeats many of these titles to enlighten us on what Jesus did and who He is for us.
Lord
“Sir or master”
Greek translation, Kyrios was used to translate the Hebrew name of God, YHWH
Kyrios means Lord.
Son of God
Man of extraordinary power or goodness.
Shows a unique Relationship with god as a son-and-father relationship with God.
Proof of His Incarnation
Prophet
One who brings the truth
Truth and the word are Christ Himself, He is the voice of God.
Priest
mediator between God and people
“pontifex” or bridge builder
King
He is divine and king of all kings
He shows us a different kind of kingship, to serve and not to be served
Christ
Greek title meaning “anointed one” translating the Hebrew word messiah
As baptized Christians, we carry Christ’s name, anointed to share in His mission
Symbols of Jesus:
During the time of persecution, this is their way to continue their traditions. These can be seen in many religious paintings, altar carvings, church walls, mass vestments, sacred linens, and devotional objects.
Alpha and Omega

Alpha is the first letter while omega is the last letter of the Greek Alphabet
Jesus is the beginning and the end of human history
Chi Rho

P and x are the first two letters of the Greek word Christ
Commonly associated with healing miracles (Rx of doctors)
IHS

Latin for Iesus Hominum Salvator which means Savior of Mankind
Commonly seen in the Vestments of the priest
Fish
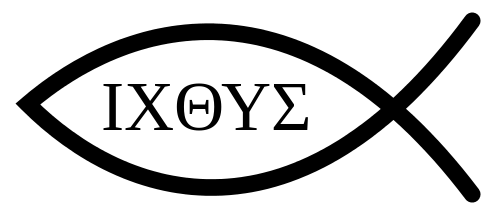
The Greek word for fish is Icthus and is an anagram for the first letters of the Greek phrase meaning Jesus Christ son of God, Savior
A common survival of early Christians
The teaching of early church councils on Jesus:
Apostles and convert believers
Clarified misleading doctrines
Magisterium or the teaching authority of the church
Vatical II ( to clarify matters and give direction to the church ministries)1962-1965
Early church council (heresies)
The church, people of God
Apostles Creed
The “mystery” of Incarnation, the mystery here does not mean something we can never understand, but something for which there is always more to understand.
Creeds and Doctrines: Have a long pastoral history behind them, and are products of centuries of searching for the truth about Christ.
Creeds are summary statements of the beliefs of the church
Basic statement creeds apostles made in preaching and recorded in New Testament
creeds in the form of Questions asked during the annual baptismal profession of faith at easter
conciliar creeds formulated by church councils. Examples are the Nicene-Constantinopolitan Creed and Constantinople I. These were used to correct the heresy by Arius who denied the divinity of Jesus.