Unit 1: Part 1: Biological Bases of Behavior
KEY
term: #4fb58c
key information: #c0f1e5
Heredity and Environment
Evolutionary Perspective
natural selection: adaption —> survival —> reproductive success
Charles Darwin: came up with natural selection
eugenics: how natural selection causes the best traits and processes to be expressed in humans
used in history to kill or sterilize large groups of people (eg: Hitler killing the Jews as the ‘inferior’ race)
Heredity: the traits our parents have are passed to us
nature vs nurture debate: are our traits hereditary or from experiences
studied through:
twin studies
identical twins: genetically the same
fraternal twins: from two separate eggs (not genetically identical)
family studies
adoption studies
Molecular genetics: studies the structure and function of our genes at a molecular level
Epigenetics: the study of changes in an organism caused by modifications in gene expression rather than changes in the actual genetic code
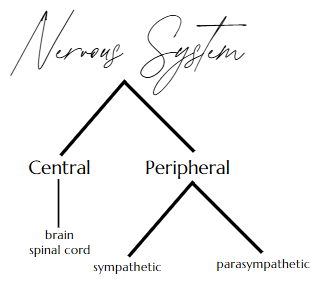
The Nervous System Structure
Nervous system
receives information about what is happening inside and outside the body
directs the body on how to respond
maintains homeostasis
Two systems:
Central Nervous System
brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System
nerves
two systems:
Somatic
controls voluntary actions
Autonomic
controls autonomic actions
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic
S: fight, flight, or freeze
speeds things up
being in love, seeing a bear, etc
heartrate increases, breathing increases, digestion slow down, pupils dilate, saliva production stops
P: rest and digest
pumps the breaks
normal heartrate, breathing, and digestion, pupils contract, saliva is produced
Reflex: a simple, automatic response to sensory stimulus (knee jerk response)
doesn’t reach the brain- only goes to the spinal cord
The Endocrine System
The Endocrine System sends hormone throughout the body
slower than