Exam 3 Review
More definition based questions
KNOW THE ORDER
True false questions
matching questions
labeling diagrams
Fewer word problems
Chapters covered 20-31
No translocation types and no robertsonian vs reciprocal
includes up to genetic code
No molocular process details- ex no A, P, and E sites of ribosomes
No hershey and chase experiment
Major Topics
Chromosomal mutations
DNA experiments
Dna structure and organization
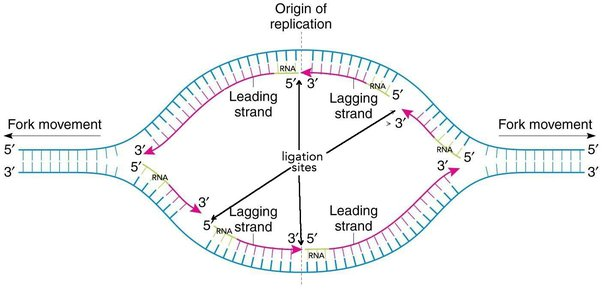
DNA replication (in bacteria mostly)
Mutation basic types, causes, repair mechanisms
Transcription (in bacteria and eukaryotes)
RNA processing
Translation (proteins, basics,
Practice Question 1:
What would happen if DNased type S filtrate was mixed with live type R and is injected into a mouse?
Yes the mouse would Die
No the mouse would live
More information needed
Practice Question 2:
An inversion occurs in a chromosomes changing the gene order. Is the in version paracentric or pericentric?
Og: ABCD*EFGH
Inverted: ABCDFE* DH
Paracentric: centromere is not included
Pericentric: centromere is included making this mutation Pericentric
What Would be the Effects of this chromosomal mutation on inversion carrier (heterozygotes)?
partial sterility bc large deletions and duplication
partaial sterility bc dicentric and acentric chromosomes resulting in large deletions
Pericentric causeless Large deletions and duplication - partial sterility
Paracentric causes large deletions that causes nonviable gametes bc dicent
SI Session
4.8.24
Topics to expect:
HEAVY on transcription and translocation questions
Simple questions about DNA repair
KNOW whats in bold on the slides for transcription and translation
Know the differences between particularly initiation and elongation in prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Know the Wobble and its just translating
Practice Question 1
DNA: 5’ CAGGAATTGC 3’ - __coding___ strand
3’ GTCCTTAACG 5’- ___template___ strand
mRNA: 5’ CAGGAAUUGC 3’
Template strand: what mRNA is being coded from directly
Jeopardy Game
Replication:
What Protein initiates DNA replication in prokaryotes? Where does this occur?
DnaA proteins will bind to the OriC of the prokaryotic DNA
DnaA helps recognize the origin site
DnaB acts as the helicase
DnaC inhibits unwinding
Dna And Gene Structures
Differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic gene structure includes:
existence of TATA Box
Introns and exons
Different type of promoter-
prokaryotes are the -35 and -10 which is where the sigma subunit will bind
Eukaryotes will start transcription at the +1 site
The 5’ UTR region is the region before the start codon that doesn’t get translated
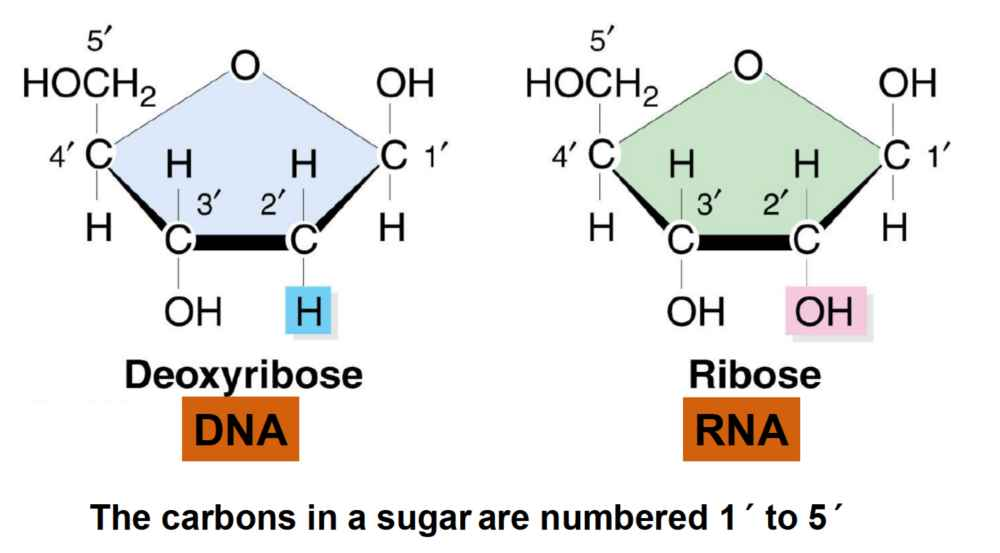
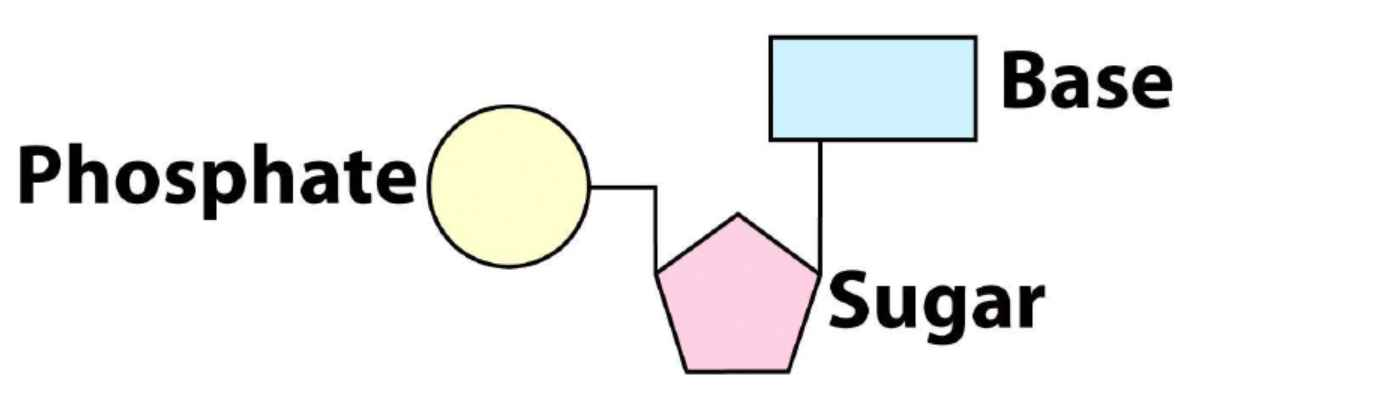
Draw out the structure of a nucleotide?
On the 1’ carbon of Deoxyribose, the base attaches. On the 3’ carbon is where the next bond forms and the 5’ is what holds the phosphate group.
Mutations and Repair
How do germ line mutations differ from somatic mutations?
Germ-line mutations can be passed down to offspring, while somatic mutations cannot
What is the NER? What is it going to repair?
NER= Nucleotide Excision Repair
NER will remove the strand segment containing DNA damage and replacement by new DNA synthesis used to repair UV damage and DNA helix distortions
BER fixes point mutations and mismatch repair
Be familiar with non-homologous end-joining
Transcription
True or false- in prokaryotic transcription the sigma factor is only needed for elongation
False- the sigma factor is needed for recognition and initiation. After the start of elongation, the sigma factor dissociates, leaving the core enzyme to complete the rest of transcription
Describe how eukaryotic transcription recognition and initiation occurs?
Eukaryotes- TBP (component of the TFIID) binds to the TATA box (core promoter) other transcription factors are recruits to the complex. TFIIB will recruit RNAPII and more transcription factors, including TBIIG (helicase) which will activate RNAPII by phosphorylation of the CTD tail.
Good Idea to memorize what each TF factor does- especially TBP
Don’t have to know the differences between RNA pol I and II.
Just know what transcription factors are and what they do.
RNA Processing and Translation
What is the Wobble Base?
The wobble base is the third base of the codon, which can leave you with variability of what amino acid will be added to the polypeptide chain.
Describe/ draw the structure of a polypeptide chain?
N-terminus is the amine group on the 5’ end at the start of the polypeptide chain
The Carboxyl group is at the 3’ end of the polypeptide chain
In Summary
Transcription
Translation
Diff. between Prokaryotes and eukaryotes
specifically between initiation and elongation
Be able to differentiate between transcription and translation proteins
Maybe know the different levels of DNA condensation??