Chapter 7: Intelligence
What do we think about?
Cognition
Latin root: “to think”
the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses
Thoughts as Concepts
Concept - Mental category that groups by common properties
Ex. Arabian, Quarter, Thoroughbred, Clydesdale, Mustang
Basic Concept - Concepts that have a moderate number of instances that make it easier to acquire
Prototype - Representation of a category, averaging all members together
Prototype for dogs?
Ears
Eyes
Snout
Height
Length
Exemplar - Your specific member representing your category
Ex. Sports. What sport comes to mind? Why?
Theories against theories
Theories - Using concepts as the framework of theories
Ex. Difference between dog and squirrel (in class example)
Schemas - Integrated mental network of knowledge, beliefs, and expectations concerning a particular topic or aspect of the world
Ex. First thought of a firefighter being a man or a nurse being a female
Solving Problems
Problem - Situation in which a current state is separated from an ideal state by obstacles
Problem Solving - Use of information to meet a specific goal
Evaluating the success of various strategy
Understand the Problem
Concept of how you interpret your problem
Ex. Gaining weight after having a baby
Is it the outcome of pregnancy or is my scale broken?
Functional Fixedness: tendency to see objects as only working in a particular way
Ex. Can’t open bottles without bottle opener so you can’t open it
Make a Plan
Algorithm - Precise step-by-step of rules that will reliability generate a solution to the problem
Ex. Doctor diagnosing you in the Emergency Room
Heuristic - Shortcut in problem-solving
Availability heuristic: frequency of event’s occurrence is predicted by the ease in which an event is brought to mind
Ex. Shark Attacks
Shark Week and Media Exposure of Sharks
Actual Likelihood: 1.625 in a million
Having an extra finger or toe: 1 in 500
Acceptance into Harvard: 1 in 100
Injured from a toilet: 96.4 in 100,000
Getting struck by lightning 94 in a million
Representativeness heuristic: stimuli similar to the prototype are believed to be more likely
Recognition heuristic: higher value is placed on the more easily alternative
Ex. What to eat in the cafeteria - Hamburger and salad or new Hungarian cuisine
Affect heuristic: we choose between alternative based on emotional or “gut” reactions
Ex. proposal
Utility Theory - Comput the expected outcome by multiplying measures of the usefulness of the outcome by its expected probability
Ex. Buying a car
Language
Language - System that combines meaningless elements such as sounds or gestures to form a structured form of communication that conveys meaning
Building blocks of language - Humans produce more than 500 phonemes (speech sounds)
Ex. the c sound in cat
Morphemes - Smallest components of speech that carry meaning
Prefixes: preschool
Ending: walked
Language Disorders
Damage to the left hemisphere
Aphasia: Loss of ability to speak or understand language
Broca's aphasia: Damage to the left frontal lobe, causing slow and simple syllables
No inflection in the words
Wernicke’s aphasia: they can speak but their words are not organized
How do we learn language?
Exposure - Seeing and hearing other people talk
Intelligence
Intelligence - Individuals ability to understand complex ideas, adapt effectively to the environment, learn from experience, engage in reason, and overcome obstacles
Assessing Intelligence - Alfred Binet and Theodore Simon looked into “mental age”
Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale created by Lewis Terman
Intelligence quotient (IQ): measure of an individual intelligence relative to a statistical normal curve
Mental Age/Chronological Age x 100
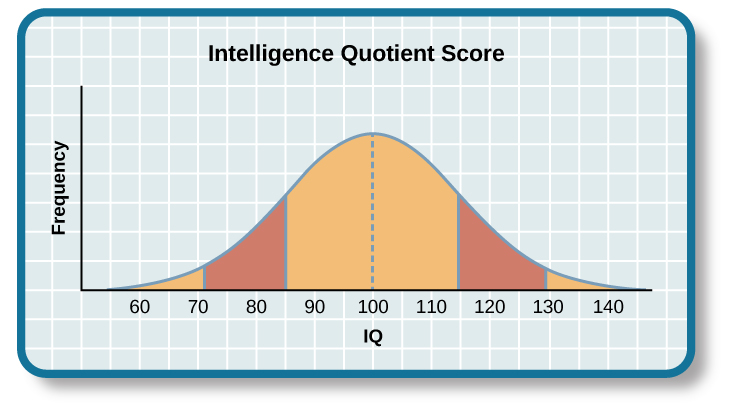
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) - more accurate for individuals with high and low intelligence as well as elderly and individuals with language difficulties
Type of Intelligence
General Intelligence - individual’s overall intelligence as opposed to specific abilities
Fluid Intelligence - the ability to think logically without the need to use learned knowledge
Ex. Uses for a tire
Crystalized intelligence: ability to think logically using specific learned knowledge
Ex. Multiplication table