Cardiac Anatomy and Physiology Notes
Cardiovascular System Overview
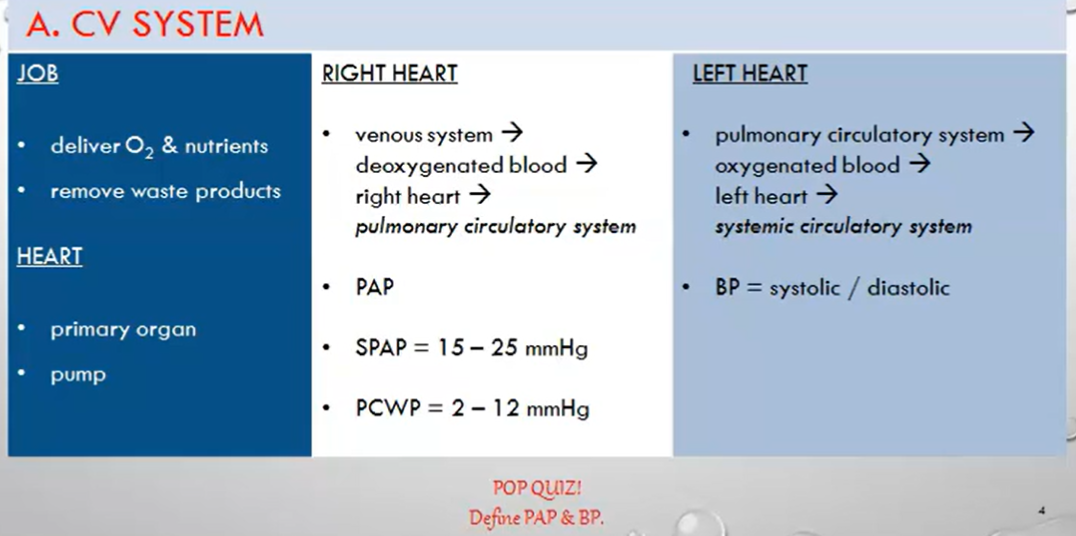
The cardiovascular (CV) system circulates blood to and from tissues, meeting the body's metabolic needs by:
Delivering oxygen and nutrients.
Removing waste products.
The CV system comprises:
The heart (primary organ).
The pulmonary circulatory system.
The systemic circulatory system.
The heart acts as the driving force (pump) for the entire system, ensuring continuous blood circulation.
The heart is a two-sided pump: the right heart and the left heart.
Right Heart and Pulmonary Circulation
The right heart is associated with the pulmonary circulatory system.
Characteristics of the right heart:
Low-pressure system.
Low resistance.
Low oxygen saturation (O2 sat rate of 75%).
Deoxygenated blood returns to the right heart via the venous system. This blood is:
Depleted of oxygen.
Burdened with carbon dioxide.
Venous and blue in color.
The right heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs, where:
Carbon dioxide is exchanged for oxygen.
Oxygen is acquired during inhalation.
Carbon dioxide is excreted during exhalation.
Oxygenated blood then travels through the pulmonary circulatory system and returns to the left heart via the four pulmonary veins.
Pulmonary Artery Pressure (PAP)
PAP is the pressure within the pulmonary arteries.
Normal systolic PAP (SPAP) at rest: 15-25 mmHg.
Elevated SPAP:
Greater than 25 mmHg at rest or greater than 30 mmHg with exercise signifies pulmonary hypertension (PH).
Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure (PCWP)
PCWP is the pressure measured when a pulmonary catheter with an inflated balloon is wedged into a pulmonary artery branch.
Normal PCWP: 2-12 mmHg.
PCWP is an indirect measurement of left atrial pressure.
Define PAP: Pulmonary Arterial Pressure
Define BP: Blood Pressure: The force exerted by circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels, typically measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and expressed as systolic over diastolic pressure.
Define MAP: Mean Arterial Pressure, calculated as the average pressure in a patient's arteries during one cardiac cycle, and is a critical indicator of perfusion.