12-08: Energy & Metabolism
Kinetic & Potential Energy
- Metabolism: the sum of all chemical reactions needed to sustain life
- Energy is the ability to do work (movement)
- Types of energy:
- Kinetic: motion
- Potential (chemical potential energy): energy contained/stored in chemical bonds within a molecule
- First law of thermodynamics: energy cannot be created or destroyed - it can only be converted from one form to another
- Some reactions produce or take up more energy than they require
Metabolism
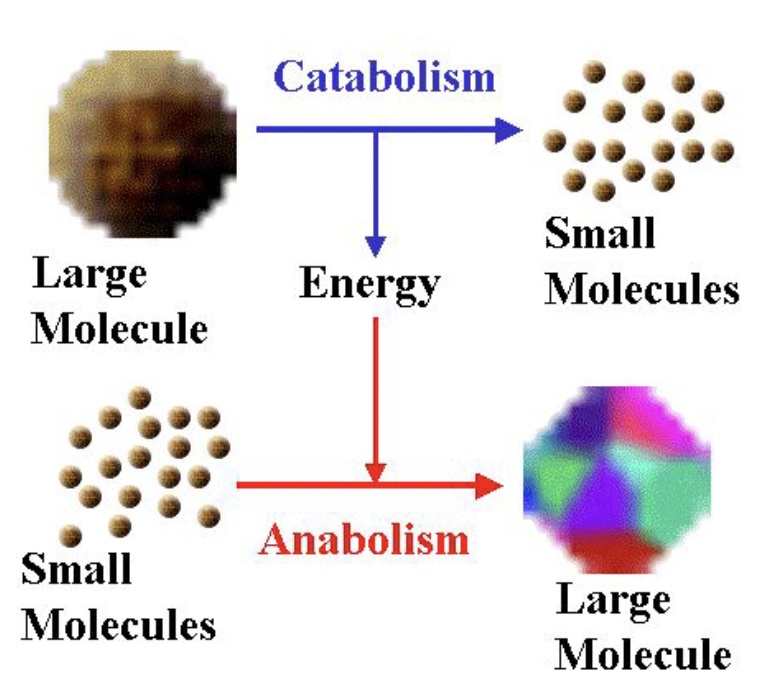
Metabolism = anabolism + catabolism
- Anabolism: builds up
- Catabolism: breaks down
- The sum of all chemical reactions
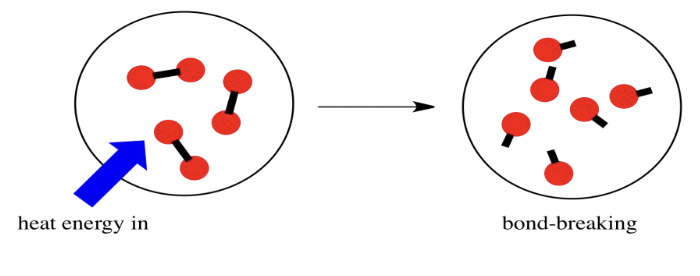
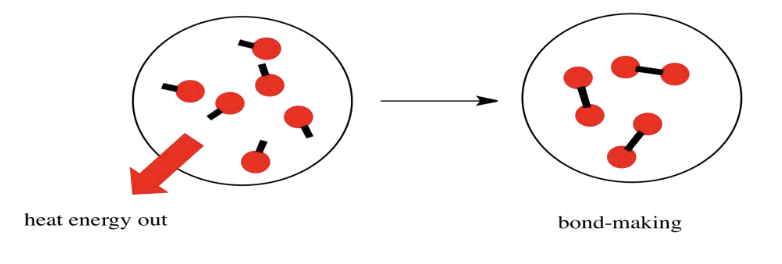
In a reaction, bonds between reactants are broken down and bonds between products are formed
- Energy is absorbed when reactant bonds break and energy is needed
- Energy is released when product bonds form
Anabolic Reactions
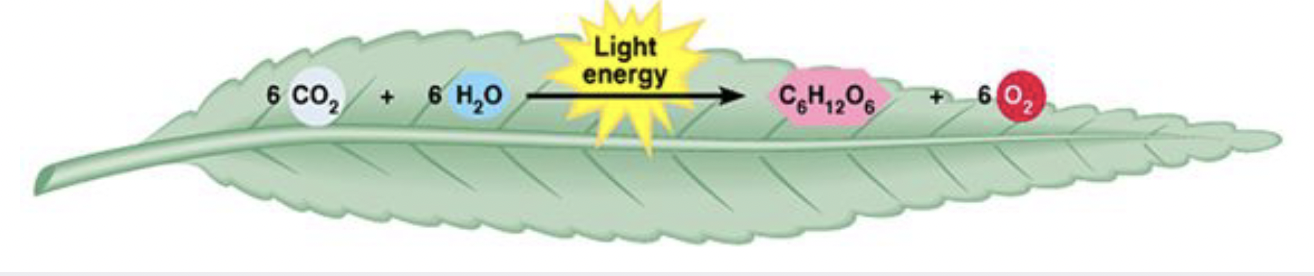
Build complex substances from smaller subunits
Overall require the input of energy to occur
Endergonic reactions: a need for energy
E.g. photosynthesis
Catabolic Reactions
Breakdown of complex substances
Overall release energy
Exergonic reactions: release of energy
Energy can be used for other jobs
E.g. cellular respiration

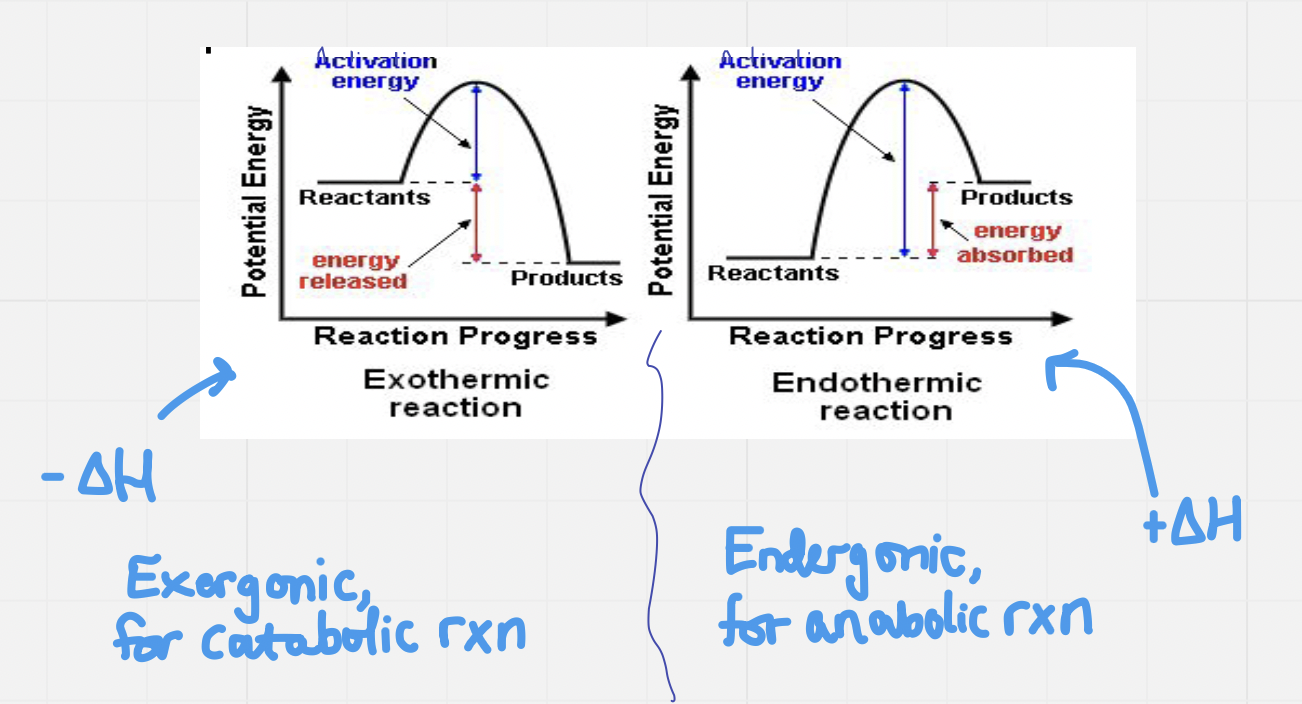
Exothermic vs. Endothermic
Enthalpy (∆H): a measure of the energy in a system, related to the amount of heat released or absorbed by a reaction
Exothermic reactions: ∆H < 0 (negative) – releases more thermal energy than they absorb
- Products have less potential energy than reactants
Endothermic reactions: ∆H > 0 (positive) – absorbs more thermal energy than it releases
Chemical reactions need activation energy for a reaction to happen
Energy Loss
- Second law of thermodynamics: in every energy conversion, some energy becomes unusable, thus increasing the entropy of the universe
- Heat is the typical form of loss of usual energy – it contributes to the increasing disorder in the surroundings
- Entropy (∆S): measure of randomness/disorder
- +∆S: more disorder
- -∆S: less disorder
Gibbs Free Energy
The most useful kind of energy
In a chemical change, since some energy is lost to entropy, the usable remainder is called Gibbs Free Energy
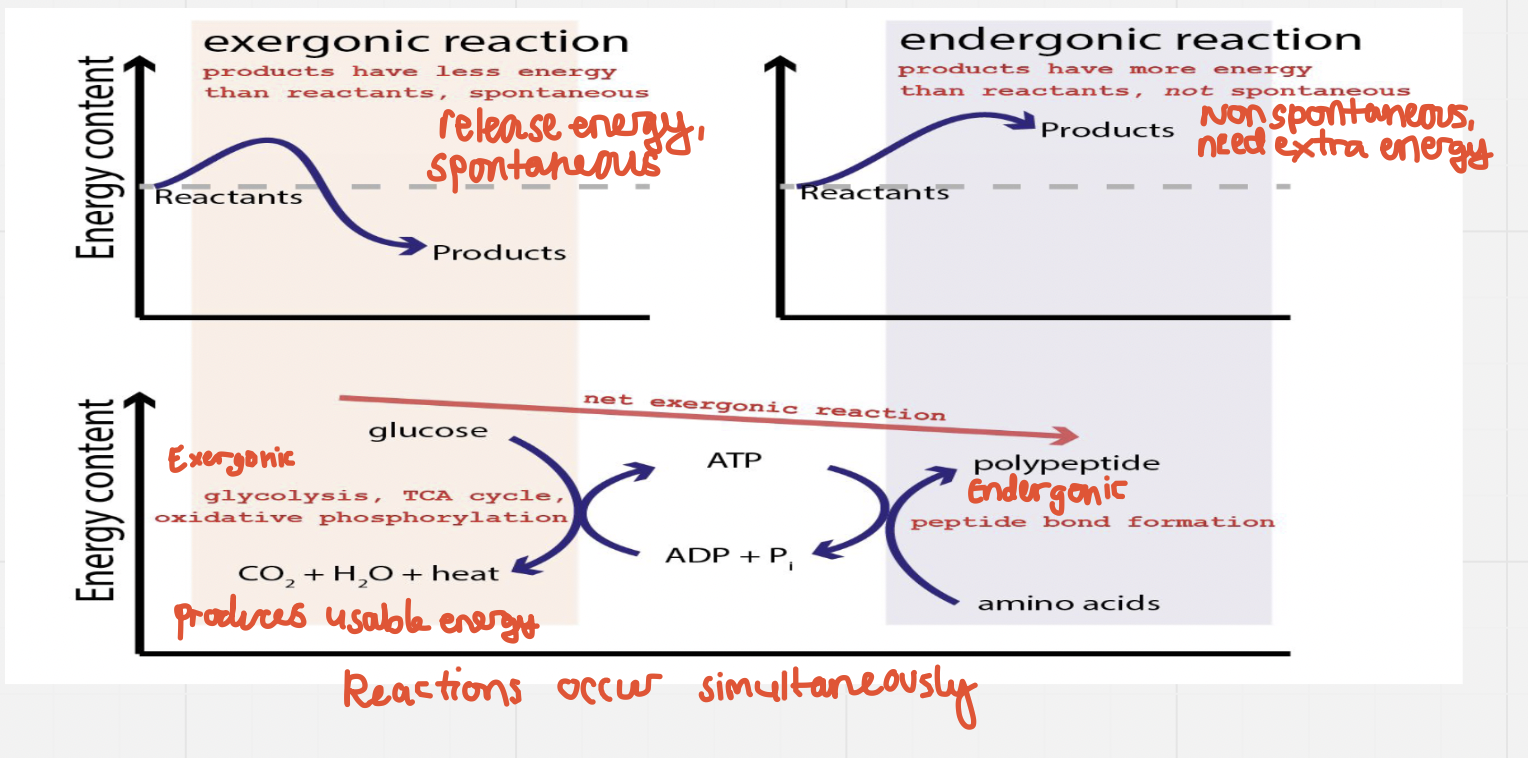
Exergonic reactions release free energy (-∆G) and are spontaneous – i.e. don’t need certain conditions to occur, will continue as long as there is sufficient reactant w/o a continuous input of free energy
Endergonic reactions absorb free energy (+∆G) and are not spontaneous – i.e. they absorb more free energy than it produces and it won’t happen with a continual source because of this
- Spontaneous: don’t need a continual source of energy, once they hit their activation energies they will occur (e.g. once the match is lit, the fire continues)
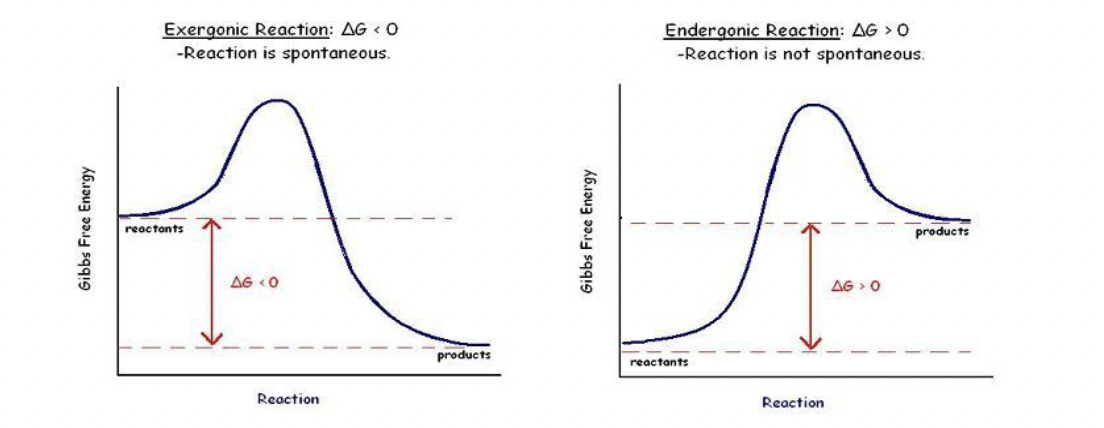
Spontaneous Reactions
Reactions that release free energy (-∆G) are spontaneous
Spontaneous reactions are those that will continue on their own once started (after activation energy)
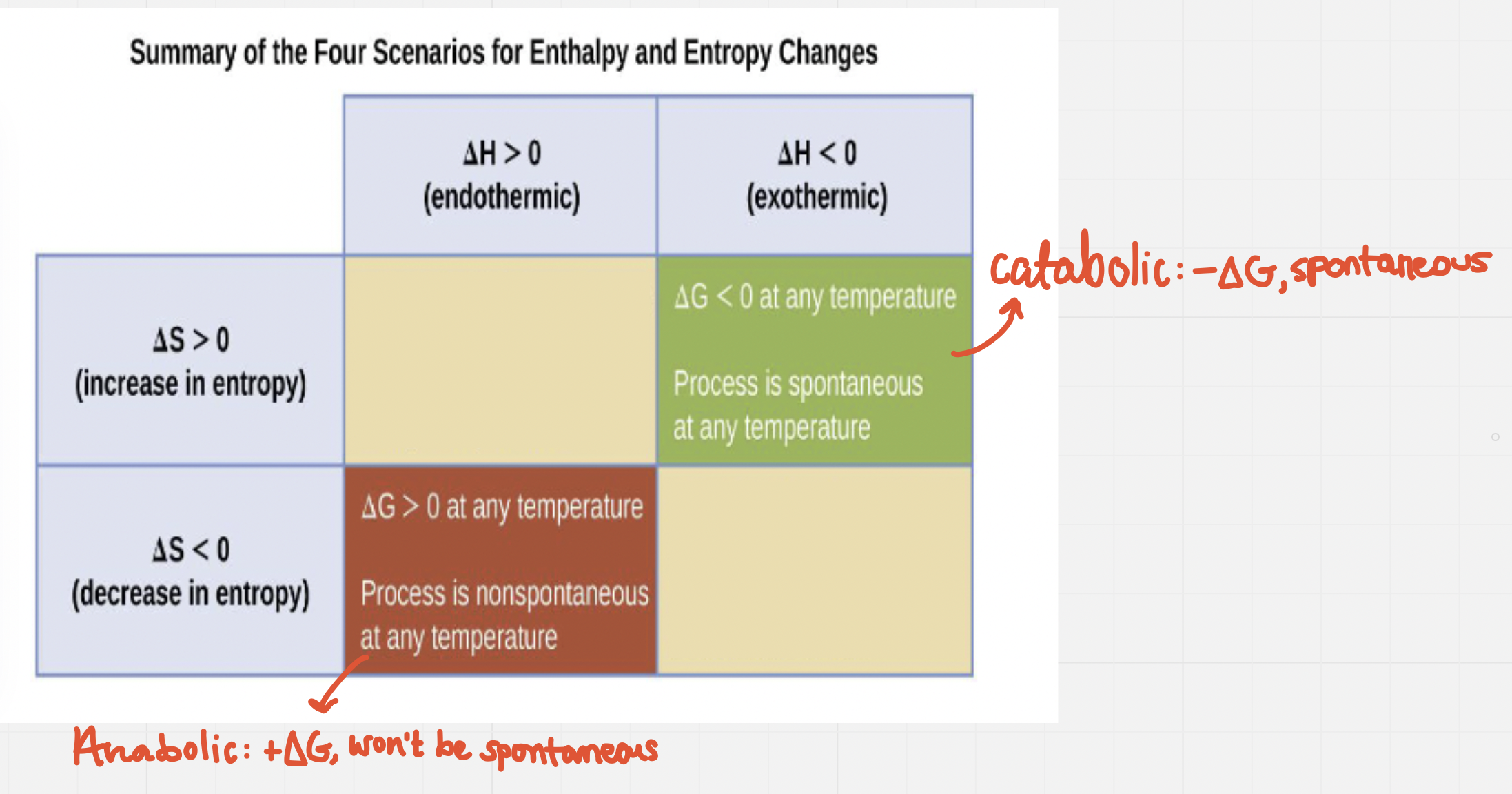
Total energy change/enthalpy(∆H) and total disorder change/entropy (∆S) both play a key role in determining whether or not a reaction will be spontaneous (along with temperature)
∆G = ∆H --- T∆S
Metabolic Pathways
Catabolic pathways
- Break down complex molecules into simple ones
- Release free energy – spontaneous (-∆G)
Anabolic pathways
- Build more complex molecules from simple ones
- Absorb free energy – non spontaneous (+∆G)
In order for non spontaneous reactions to occur, they must be coupled with spontaneous ones
ATP Hydrolysis
- Hydrolysis: breaking something down (catabolic)
Energy for endergonic reactions in cells is mostly provided by coupling the reaction with the hydrolysis of ATP
- When water reacts with it, it breaks it into ADP and the phosphate bonds to a reactant thus making it more reactive, provides energy
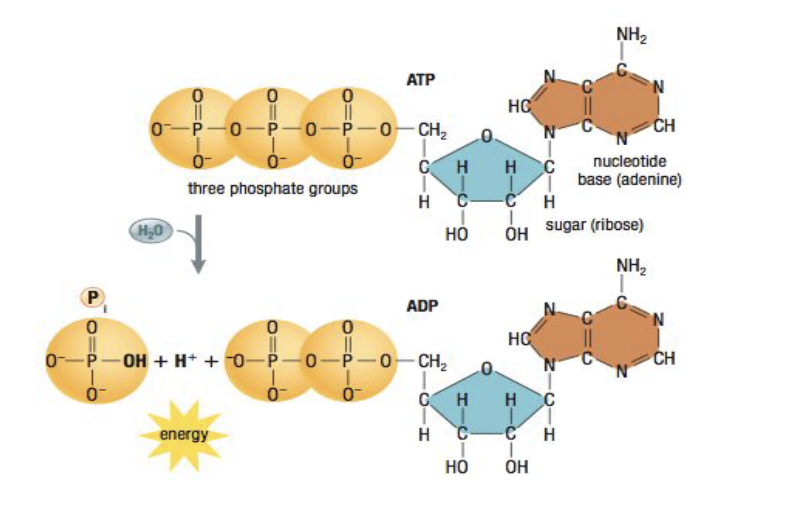
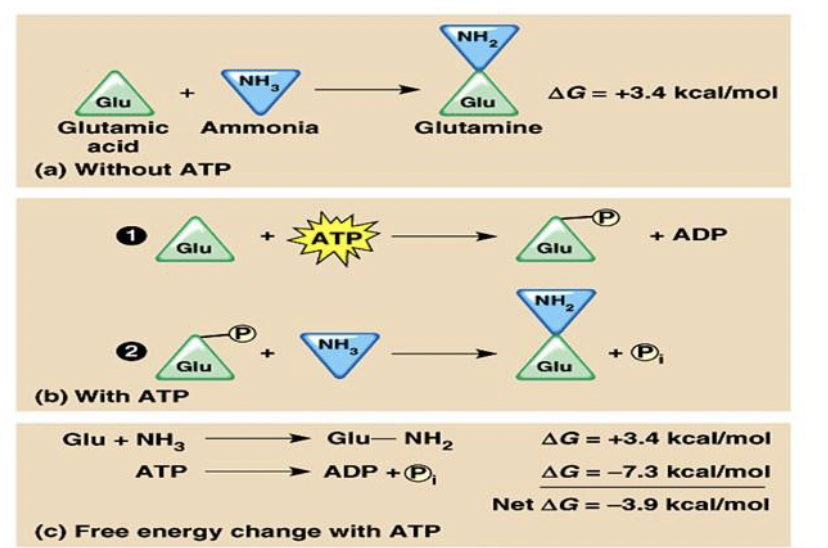
Coupled Reactions