9.2_Female_Reproductive_uterus
Female Reproductive System Overview
Key Components
Uterus
Vagina
Pelvic floor
Uterine Anatomy
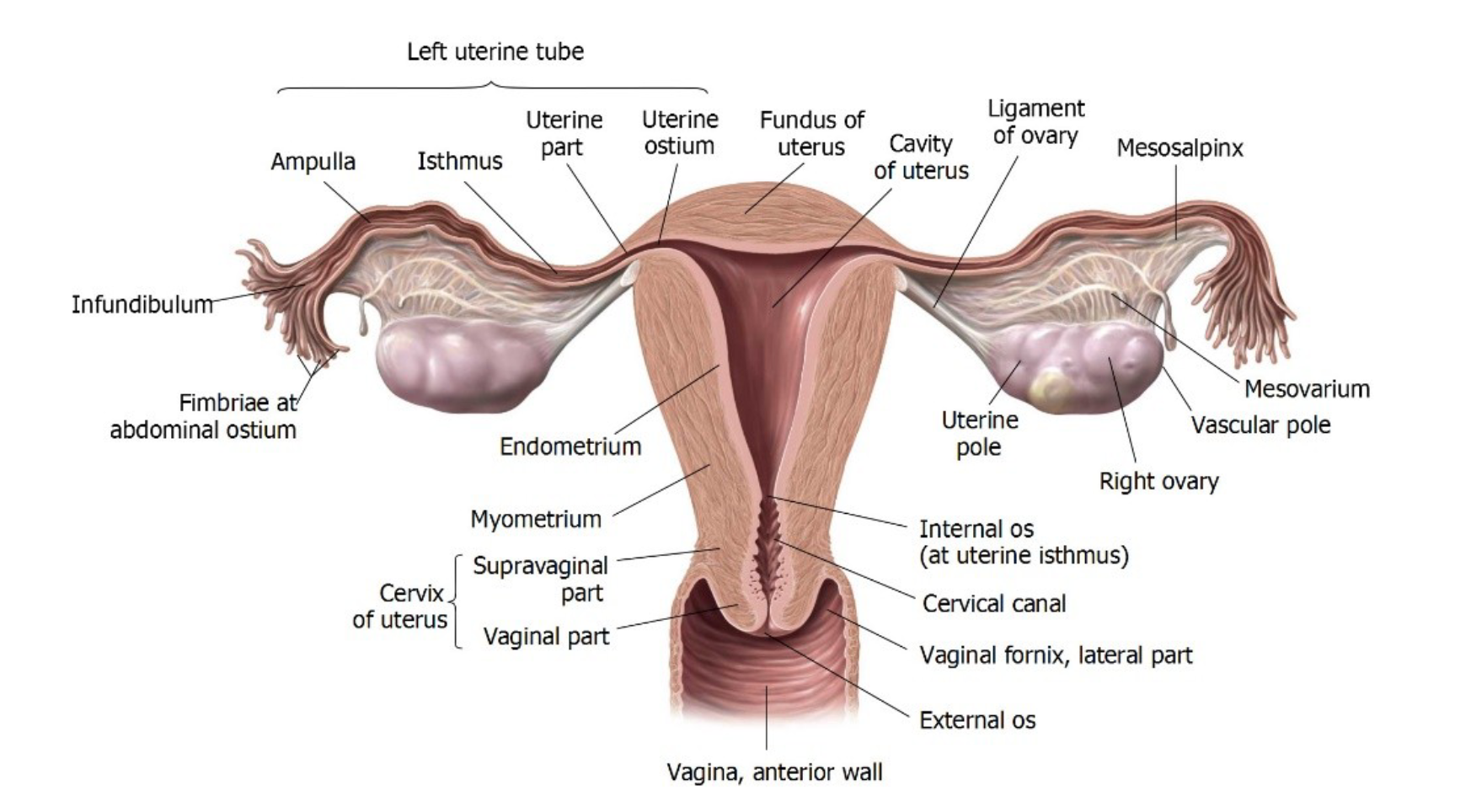
Uterine Tube (the whole thing)
Functions: Receives oocyte and site for fertilization
Sections:
Fimbriae
Infundibulum
Ampulla
Isthmus
Connects to the peritoneal cavity.
Uterus Functions
Development of embryo/fetus
Expulsion of fetus during childbirth
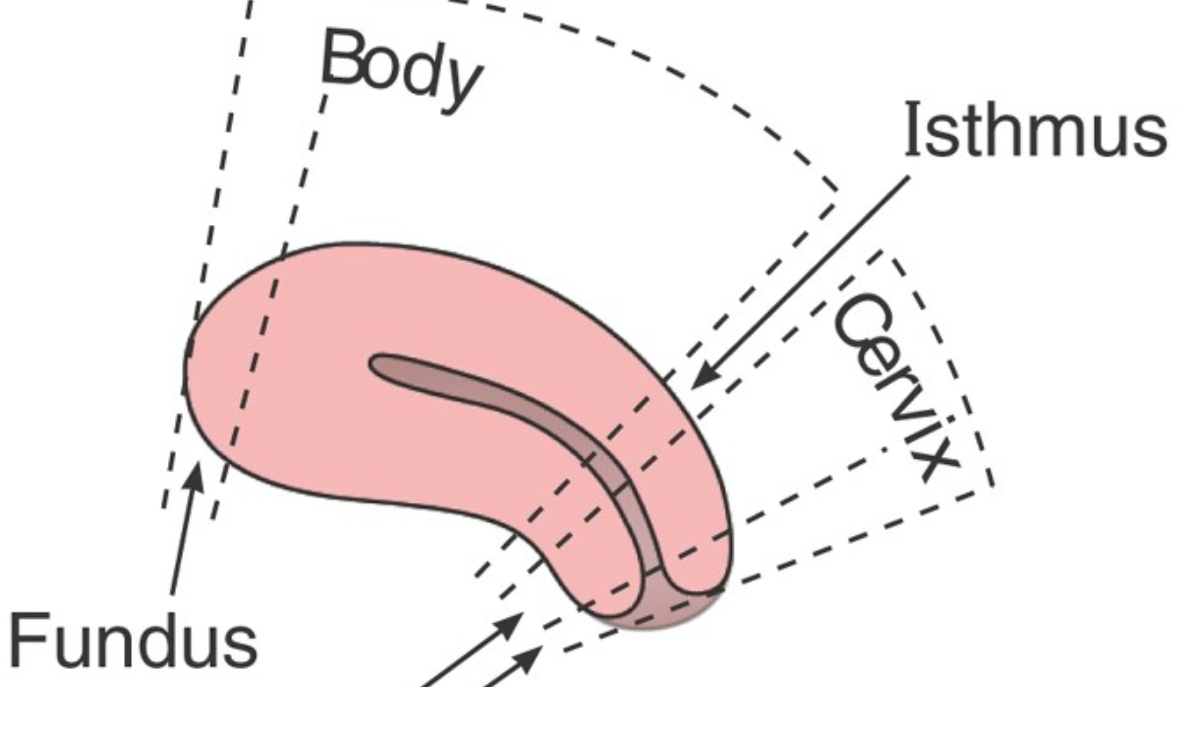
Major parts: Body, fundus, isthmus, cervix, and uterine tubes
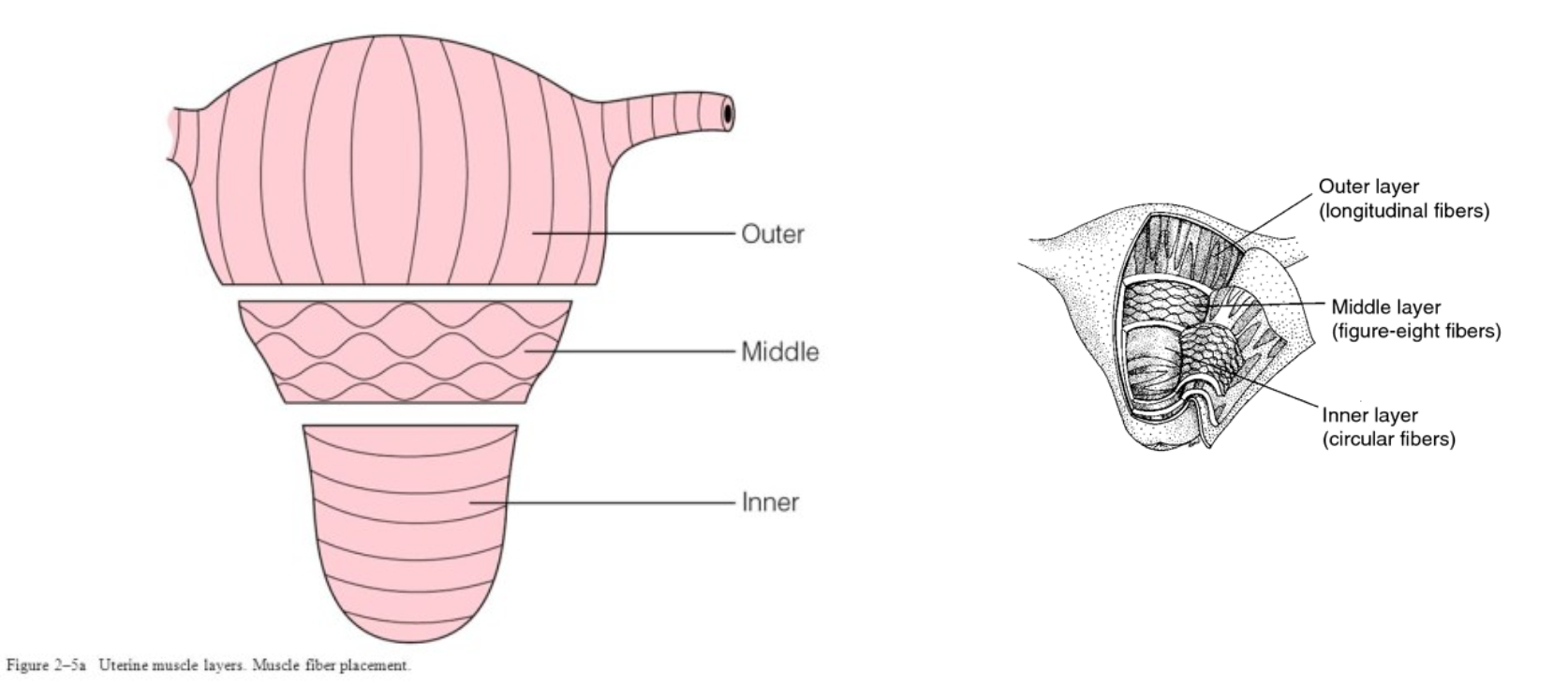
Uterine Wall Structure
Layers:
Endometrium: Inner lining; changes with hormonal cycles.
Myometrium:
Smooth muscle layer, consists of three layers:
Longitudinal (outer)
Circular (inner)
Oblique (middle)
Adventitia: Outer connective tissue layer
Changes in the Uterus
Monthly endometrial changes due to hormonal cycles.
Uterus enlarges during pregnancy (grows to support the fetus).
Fetal head engages in the pelvic cavity prior to labor ( "drops" before birth).
After menopause, lack of hormones leads to uterine atrophy (reduction in size and functionality).
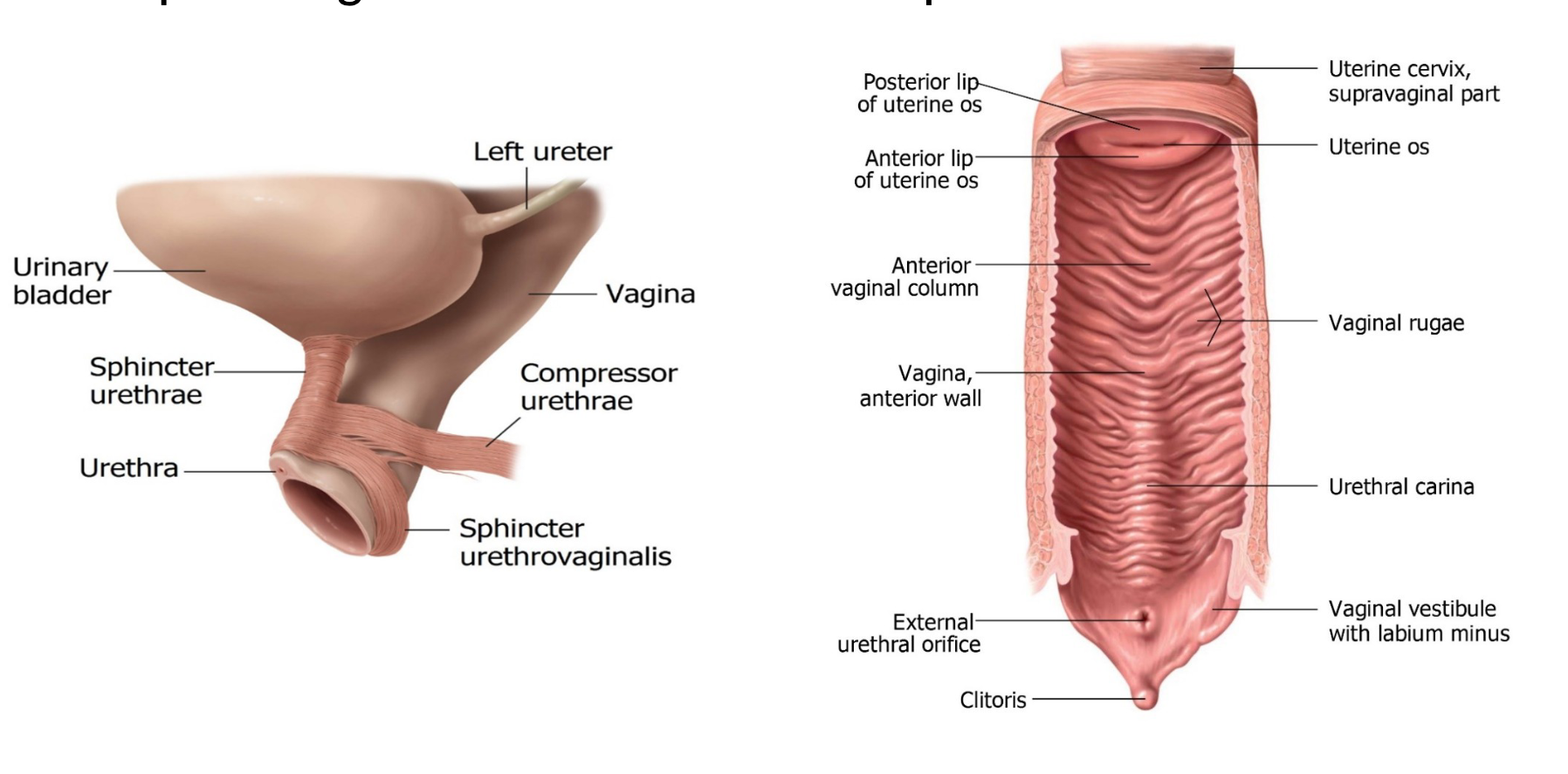
Vaginal Anatomy
Functions:
Passage for menstrual blood, fetus during childbirth, penis, and the ejaculate.
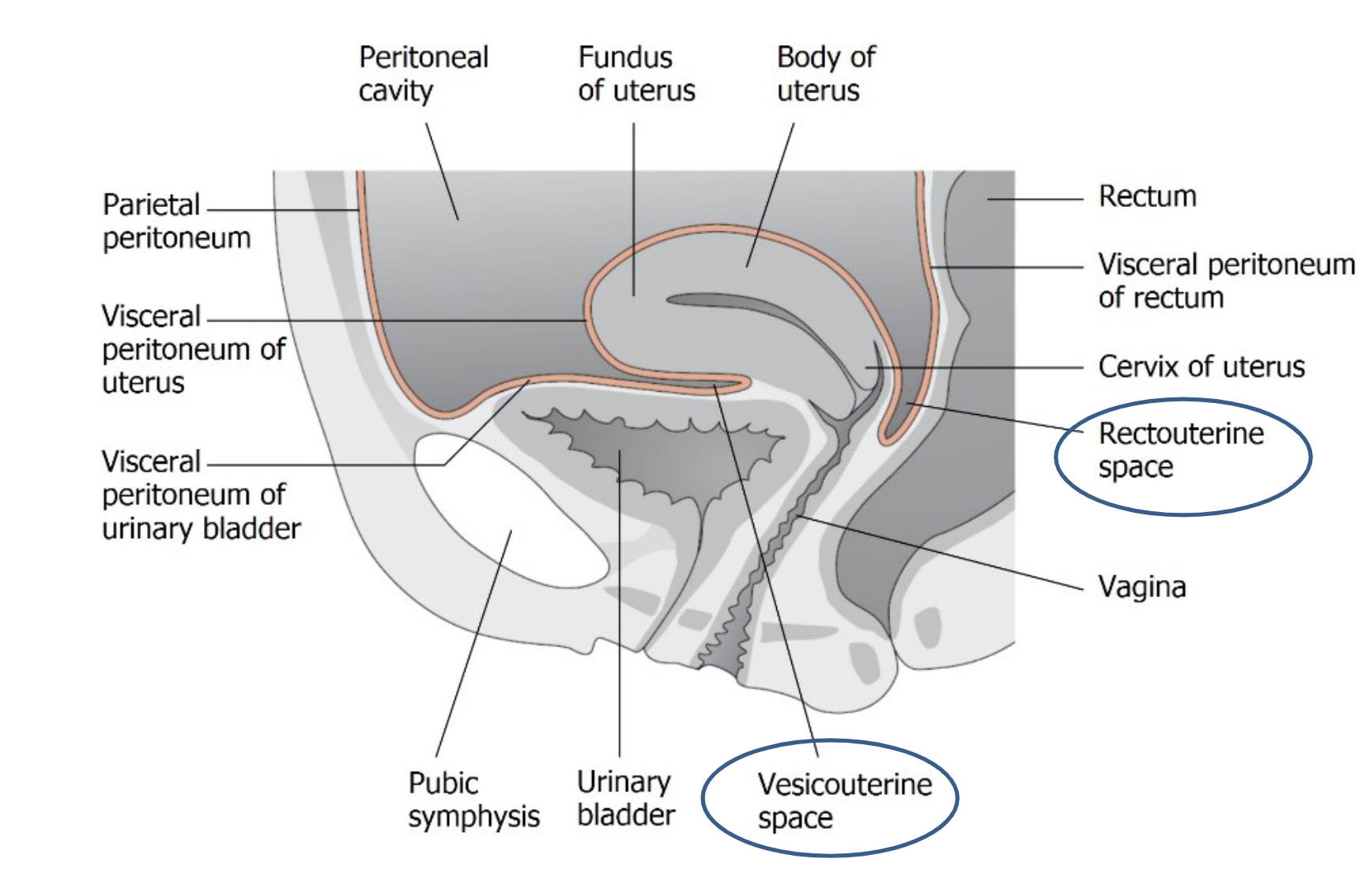
Connects the cervical canal from the internal to the external os.
Fornices:
Anterior fornix and posterior fornix act as arches supporting the vaginal wall.
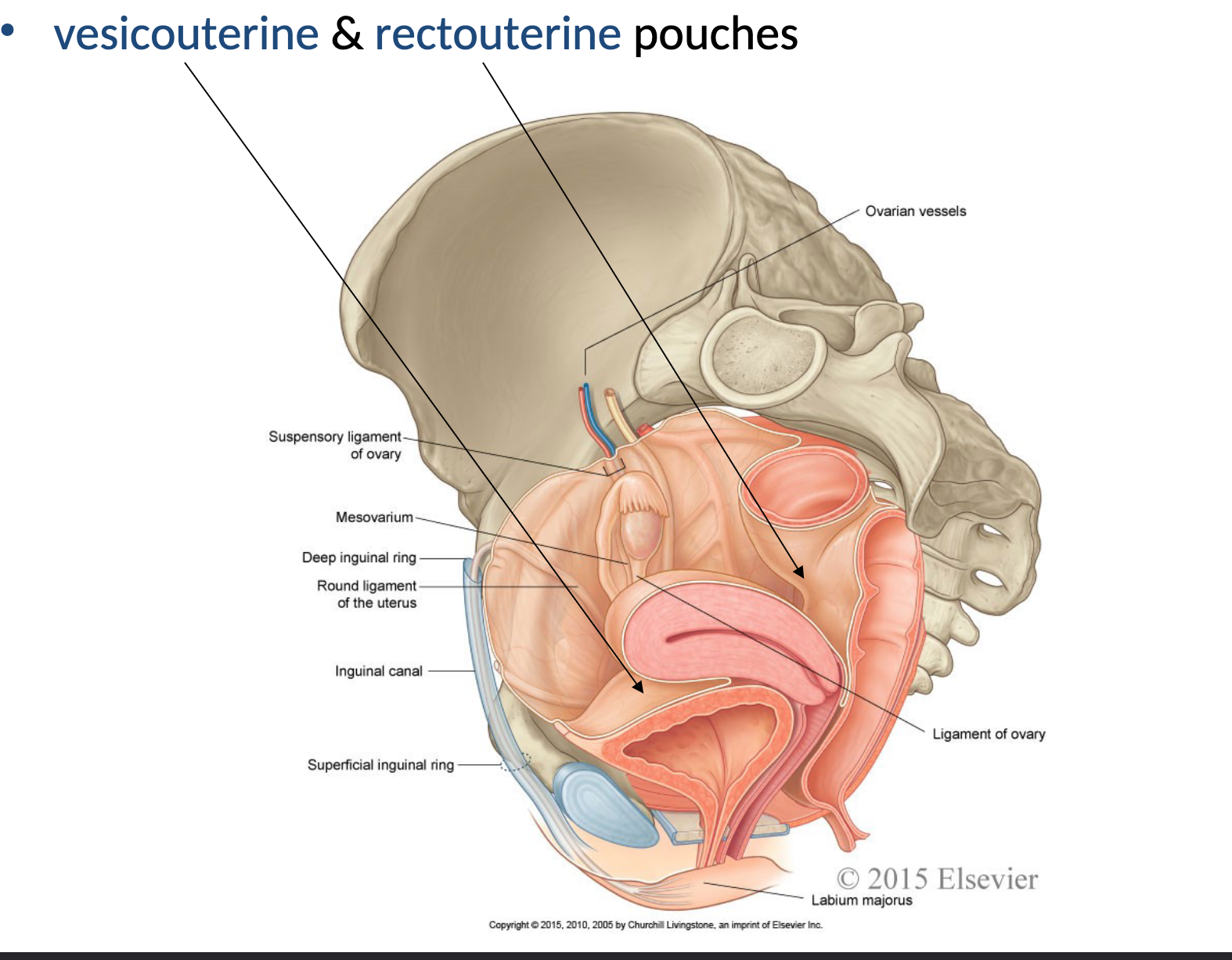
vesicouterine (anterior) & rectouterine (posterior) pouchs
Vaginal Wall Composition
Mucosa:
Stratified squamous epithelium(thin outer tissue) providing resistance to abrasion.
Muscularis Layer:
Smooth muscle facilitating contractions, especially during orgasm.
Adventitia:
Outermost connective tissue layer.
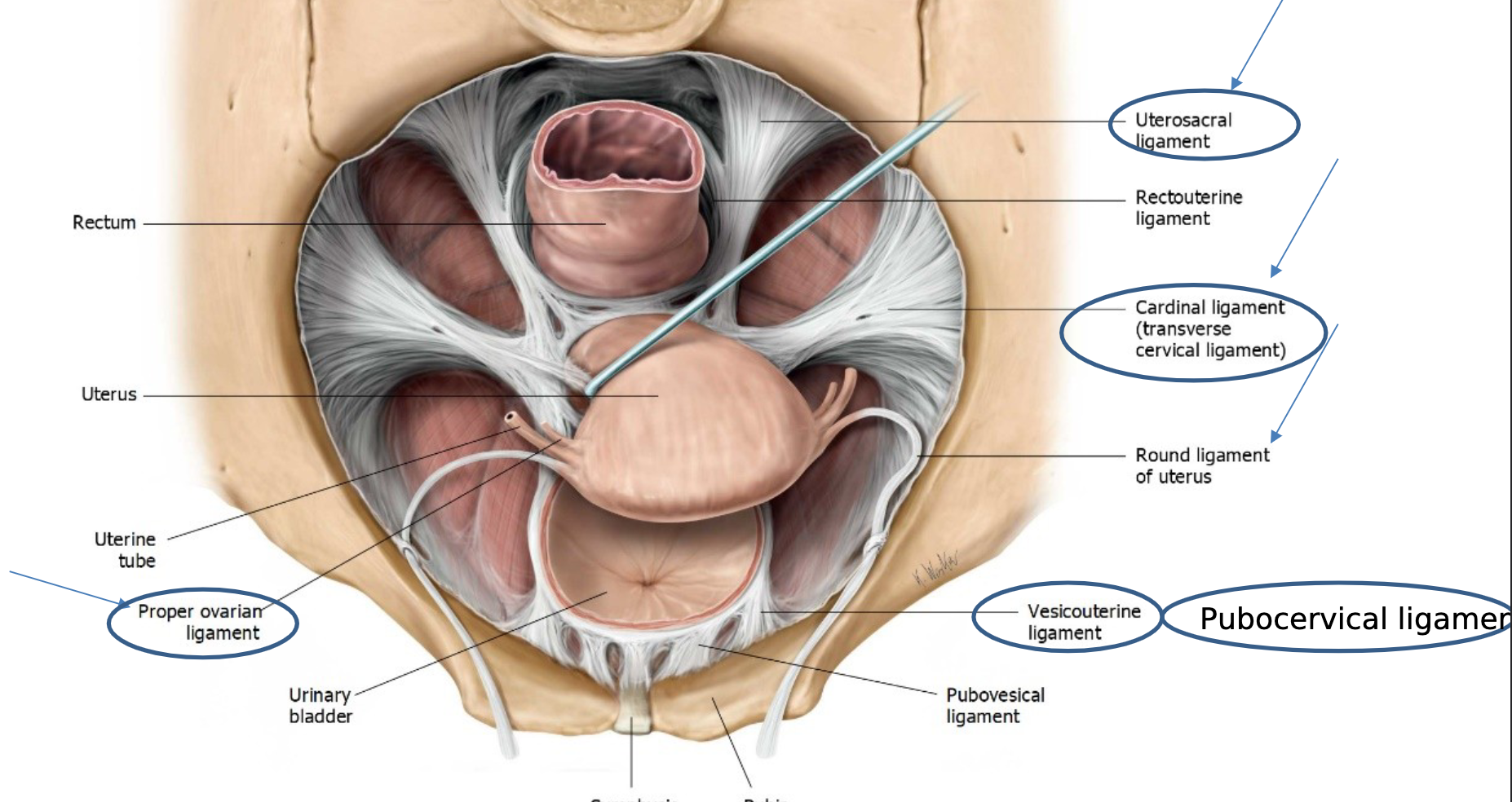
Ligaments of the Uterus
Suspensory Ligament of Ovary:
Contains ovarian artery and vein.
Broad Ligament: Encloses the uterine tubes, ovaries, and the uterus.
Round Ligament of Uterus: Connects the uterus to the labium majus.
Uterosacral and Cardinal Ligaments: Provide support to the uterus and pelvic organs.
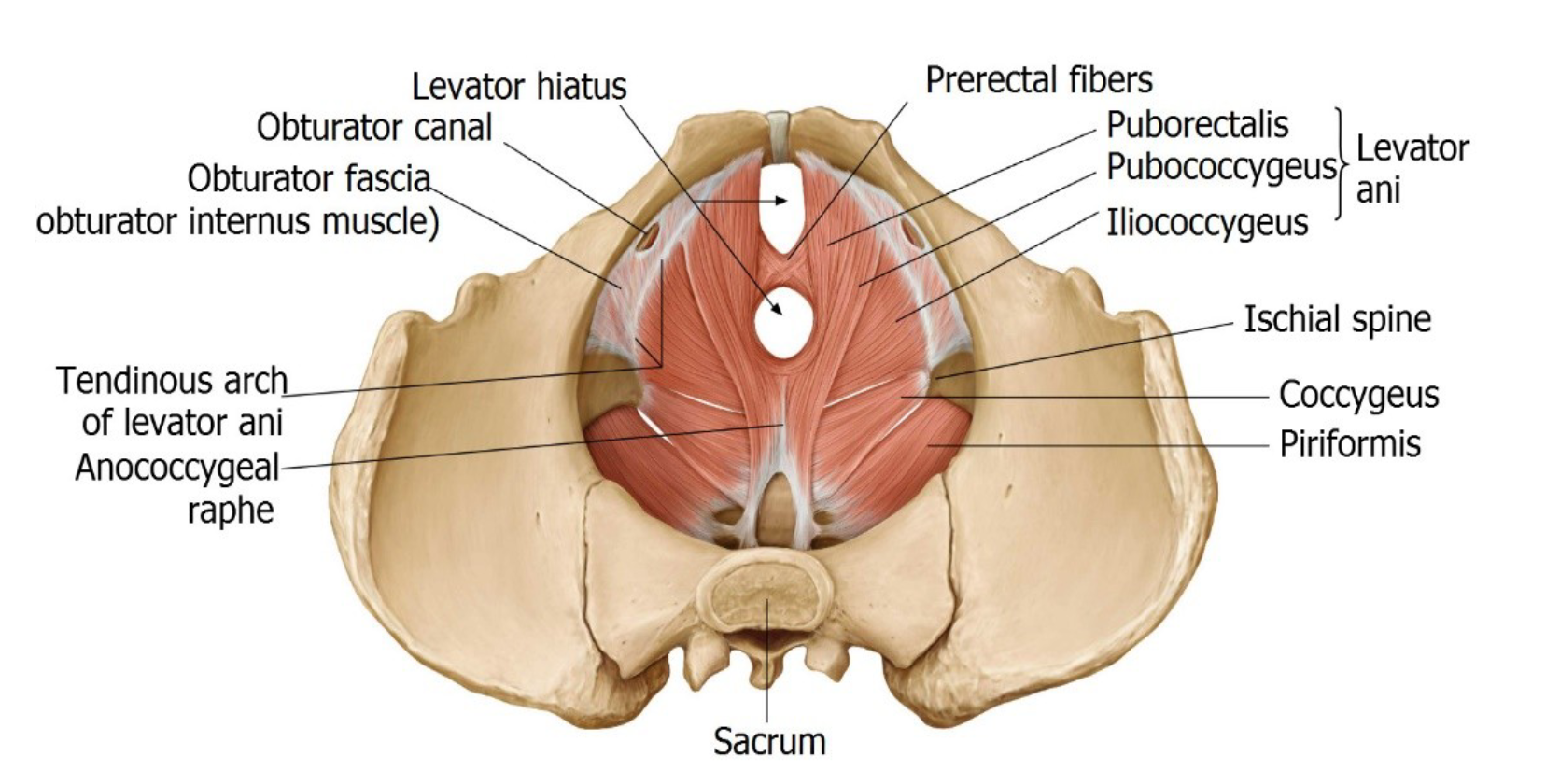
Muscles of the Pelvic Floor
Levator Ani Group:
Key muscles: Pubococcygeus, Iliococcygeus.
Coccygeus Muscle: Contributes to pelvic support.
The pelvic diaphragm contains openings for the rectum, vagina, and urethra.
Summary of Hormonal Influence and Changes
Menstrual Cycle:
Estrogen stimulates endometrial growth.
Progesterone promotes endometrial maintenance for implantation.
Menstruation occurs when progesterone levels drop, causing degeneration of the endometrium.
Pregnancy:
Myometrium hypertrophies to allow for contractions during childbirth.
Relaxin causes dilation of cervix and vagina for fetal passage.
Menopause:
Estrogen and progesterone levels decrease, leading to uterine atrophy.