Knowledge Representation
Basic Definitions
Taxonomy:
Derived from Greek words "taxis" (arrangement) and "nomos" (law). A taxonomy is a classification or categorization of a complex system.
Examples include the ACM Computing Classification System and the Mathematics Subject Classification.
Knowledgebase (KB):
A technology used to store complex structured and unstructured information for use by a computer system.
In effort to move away from just keyword matching, search engines added AI techniques
Distinguished from a regular database.
A knowledge-based system consists of:
A knowledgebase representing facts about the world.
An inference engine that can reason about these facts, deduce new ones, or highlight inconsistencies using rules and logic.
Examples include Freebase, Google's Knowledge Graph, Apple's Siri, and IBM's Watson.
Google's Knowledge Graph accused of taking away traffic from Wikipedia, as it often provided direct answers that users previously had to click through to Wikipedia to find.
Inference Engine
Component of system that applied logical rules to KB to deduce new info
Dynamic and ongoing — each new fact can trigger new rules across engine
Works in 2 modes:
Forward chaining: starts with known facts and asserts new facts
Most common
“P implied Q”
Backward chaining: start with goals and words backward to determine what facts must be asserted so goal can be achieved
Cycles through 3 sequential steps: match rules, select rules, execute rules
Rule execution can result in new facts or goals added to KB, which will trigger cycle to repeat.
Cycle continues until no new rules can be matches
Binary Relations & Instances
Binary relations with type signature:
hasAdvisor: Person x Person
bornOn: Person x Date
Instances of above binary relations
hasAdvisor(Jim, Mike)
bornOn(Maya, 2000-02-02)
Knowledgebases and Search Engines
Search engines use knowledgebases to enhance the display of search results, moving beyond simple keyword matching.
The representation of knowledge in a knowledgebase is based on an object model.
Object Model: objects/concepts are organized into classes, which are arranged in a generalized hierarchy.The most generic concept is at the top; the most specific is at the bottom.
Includes classes, subclasses, and instances.
A taxonomy is a hierarchy of concepts with parent/child (subClass/superClass, or broader/narrower) relationships.
Parent/child is the only relation between concepts
Knowledgebases can express arbitrary complex relations between concepts (e.g., X marriedTo Y, A worksFor B, C locatedIn D).
Search engines use linked, structured data to:
Provide direct answers to queries.
Create enhanced displays in engaging visual formats (i.e. Person summary box on Wikipedia)
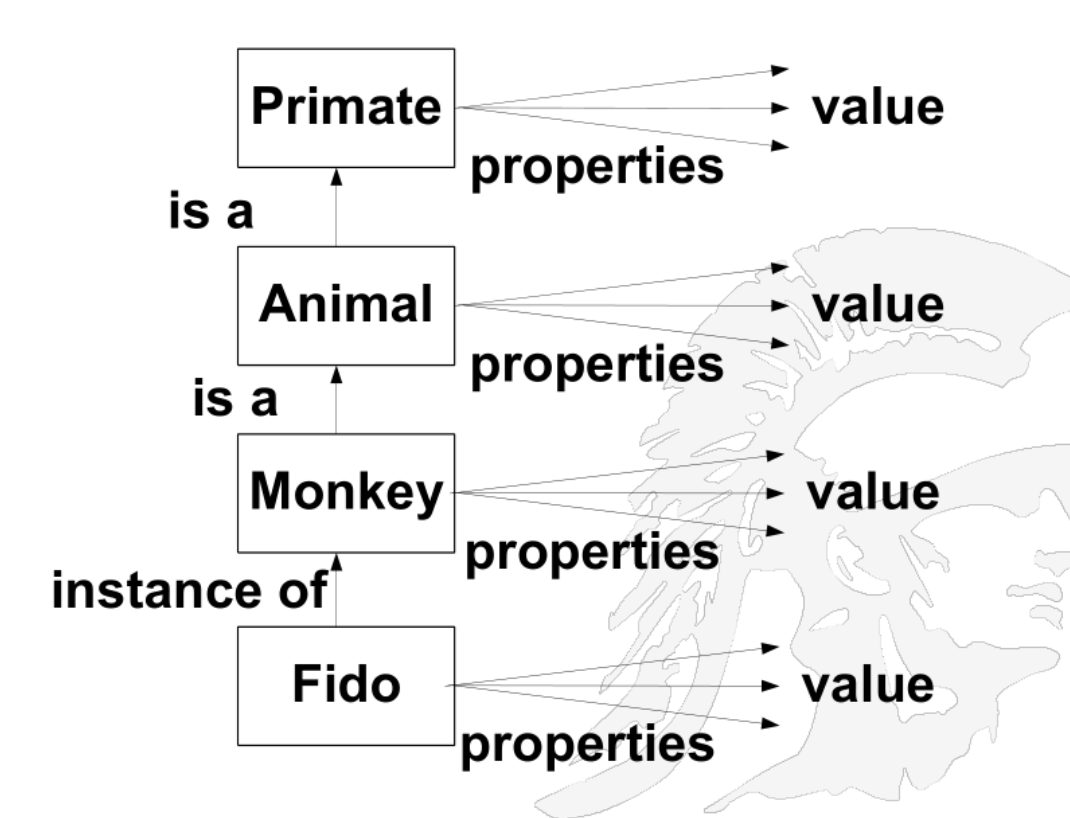
Inheritance
Inheritance is a key feature of knowledge representation, organizing knowledge into class hierarchies.
Through Inheritance:
An individual assumes the properties of its class.
Properties of a class are passed on to its subclasses.
Objects/concepts are organized into classes, which are arranged in a generalized hierarchy.
The most generic concept is at the top; the most specific is at the bottom.
Advantages:
Natural mechanism for representing taxonomically structured knowledge
provides means of expressing properties of class of objects/concepts
guarantees all members of class inherit properties — ensures consistency within class definition
reduced size of knowledge base since properties are defined for most general and more specific is nested within
Different Notations for a KnowledgeBase
Resource Description Format (RDF):
Is a W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) standard model for data interchange on the Web.
It provides a framework for describing and linking resources on the web, making it easier to integrate data from different sources.
Used for creating ontologies, which are formal representations of knowledge within a domain.
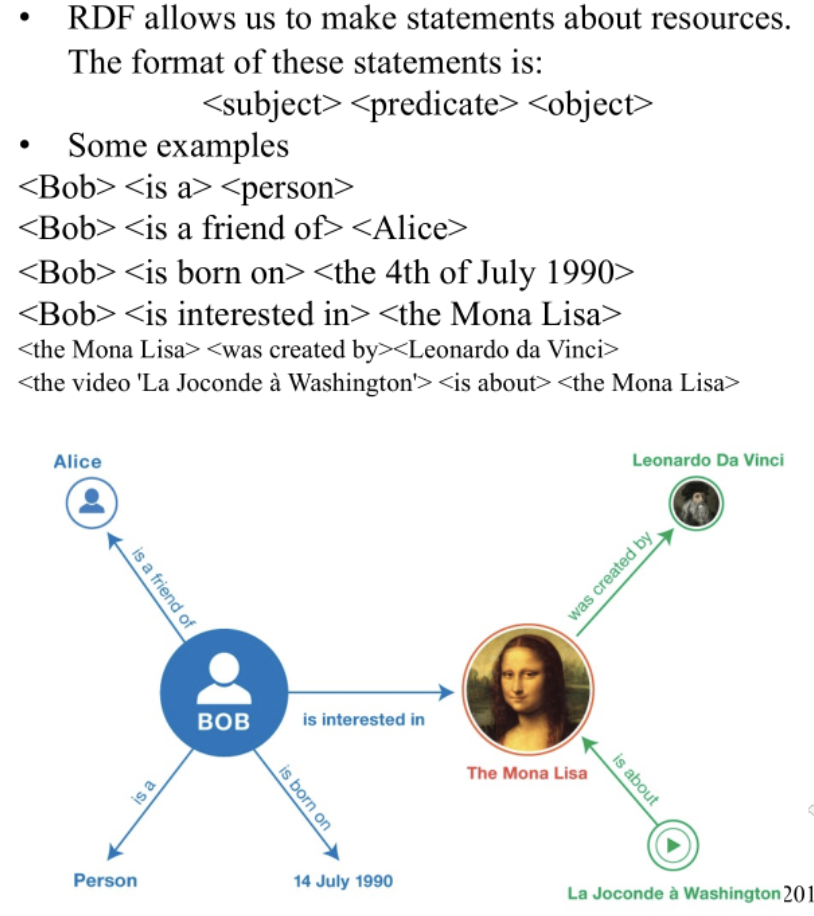
RDF is based on the idea of making statements about resources in the form of triples.
Sometimes, the terms "RDF Ontology" and "KnowledgeBase (KB)" are used synonymously, although an RDF ontology is a specific type of knowledge base that uses RDF as its underlying data model.
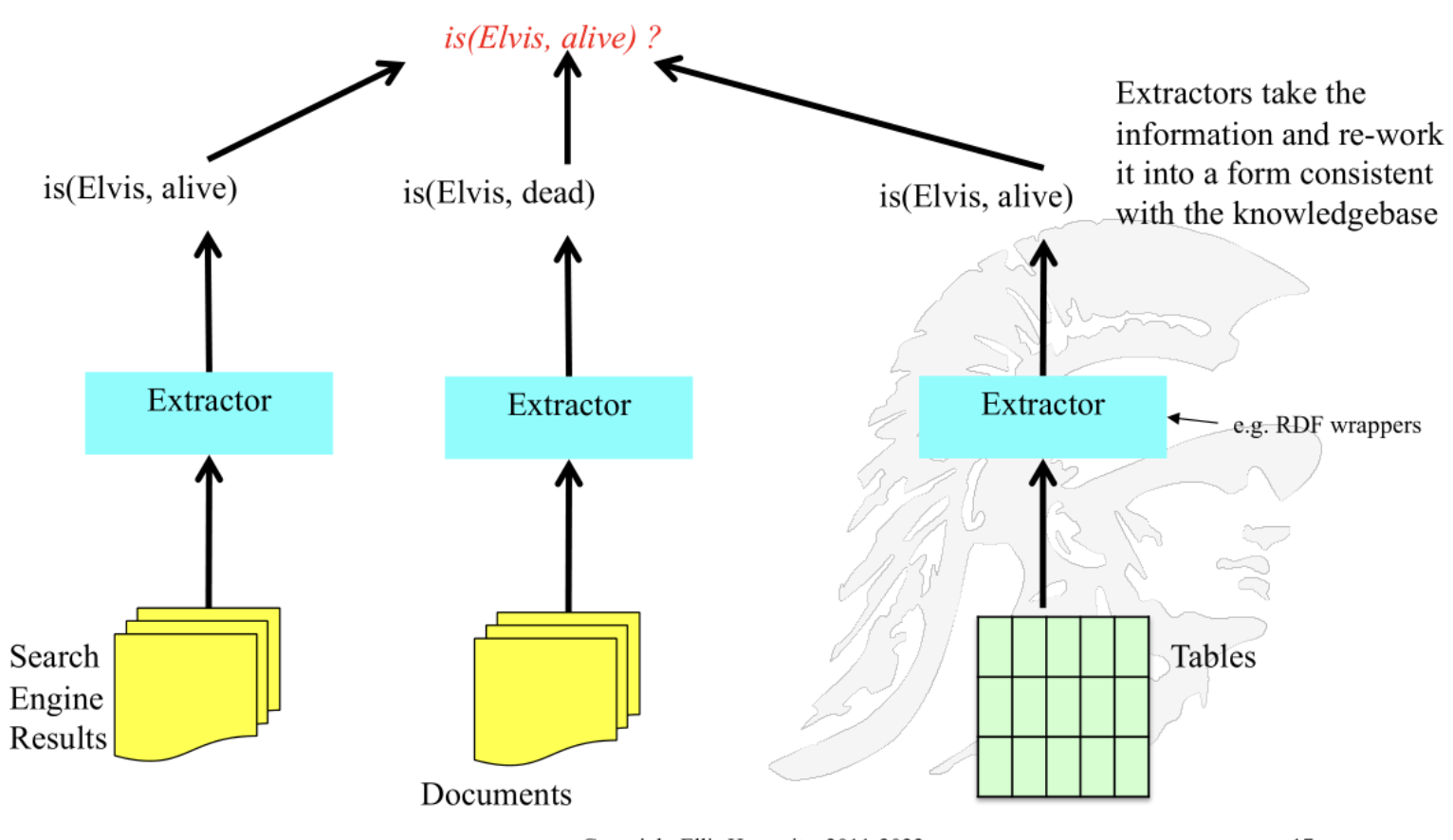
combined information from multiple sources with extractors
extractors take information and re-work it to form consistency within KB
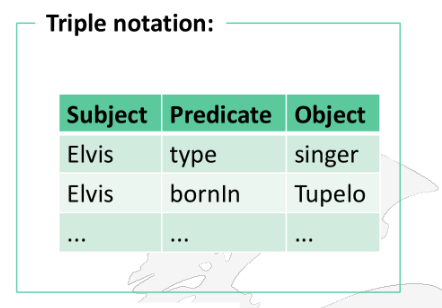
Triple Notation:
Subject Predicate Object
Examples: "Elvis type singer":
Subject: Elvis (the individual)
Predicate: type (the relationship indicating categorization)
Object: singer (the category or class)
It breaks down information into simple, self-contained statements.
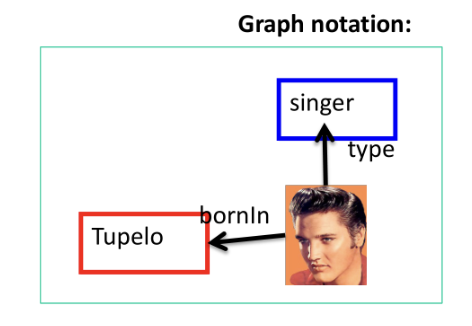
Graph Notation:
Knowledge is represented using a visual graph structure of nodes and edges
Each node represents ideas and concepts (i.e. subjects and objects) that can be related to one another by edges, which signify the relationships between these concepts.
Can represent concrete objects like a specific person, place, or thing
Can also represent abstract concepts like a category or class
URI (Uniform Resource Identifier) = a literal value
Nodes represent subjects and objects, identified by URIs (Uniform Resource Identifiers) or literal values. URIs denote resources or concepts.
Edges, labeled with URIs, show relationships between nodes; the URI specifies the type of relationship
Logical Notation: Uses logical statements to represent facts and relationships.
Follows a structured syntax
Key Components:
Predicates: Define the relationships or properties.
Arguments: Represent the entities or values involved in the relationship.
type (Elvis, singer): This statement asserts that Elvis is of type singer.
bornin (Elvis, Tupelo): This statement asserts that Elvis was born in Tupelo.

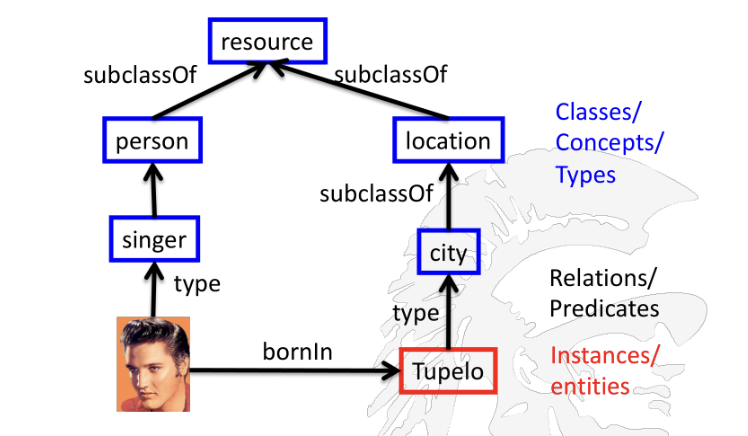
KnowledgeBases as Labeled MultiGraphs
Knowledgebases can be represented as directed labeled multigraphs.
Nodes are entities.
Edges are relations.
Labels: Attributes or types assigned to nodes and edges that specify their properties or relationship types.
Useful for explicit, structured knowledge representations, such as ontologies, data graphs, or knowledge schemas.
Can model complex relationships and multiple relations between entities
Facilitates computational reasoning through graph algorithms
A multigraph is a graph that permits multiple edges between the same nodes.
Semantic Network
A semantic network is a knowledge representation scheme that represents knowledge as a graph.
Nodes are concepts or facts.
Arcs are relations or associations between concepts.
Labels: types of semantic relationships with explicit labels (like "is a", "part of", "related to").
Both nodes and arcs are labeled.
is-A link is most important since it is used to establish inheritance
Labeled MultiGraphs vs Semantic Networks
Labeled MultiGraphs are a general graph-based formalism that can represent complex, layered relationships with multiple types of edges and rich labels.
Semantic Networks are a specialized form of labeled graph focused on meaning, concepts, and their relationships, often used in cognitive and linguistic contexts.
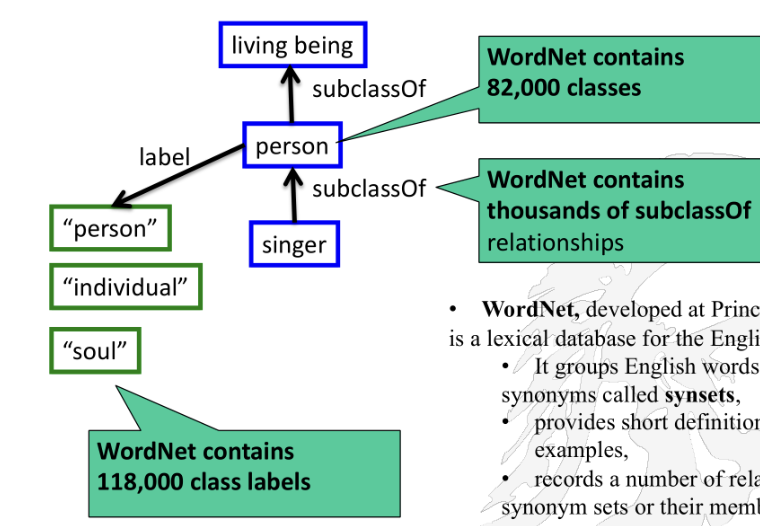
WordNet: Example of Semantic Network
WordNet is a lexical database developed at Princeton University for the English language.
It groups English words into sets of synonyms called synsets.
Provides short definitions and usage examples.
Records relations among synonym sets or their members.
WordNet contains:
82,000 classes
118,000 class labels
Thousands of subclassOf relationships
Use Cases:
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Used for word sense disambiguation, information retrieval, and text analysis.
Lexical Semantics: Provides a structured resource for studying word meanings and relationships.
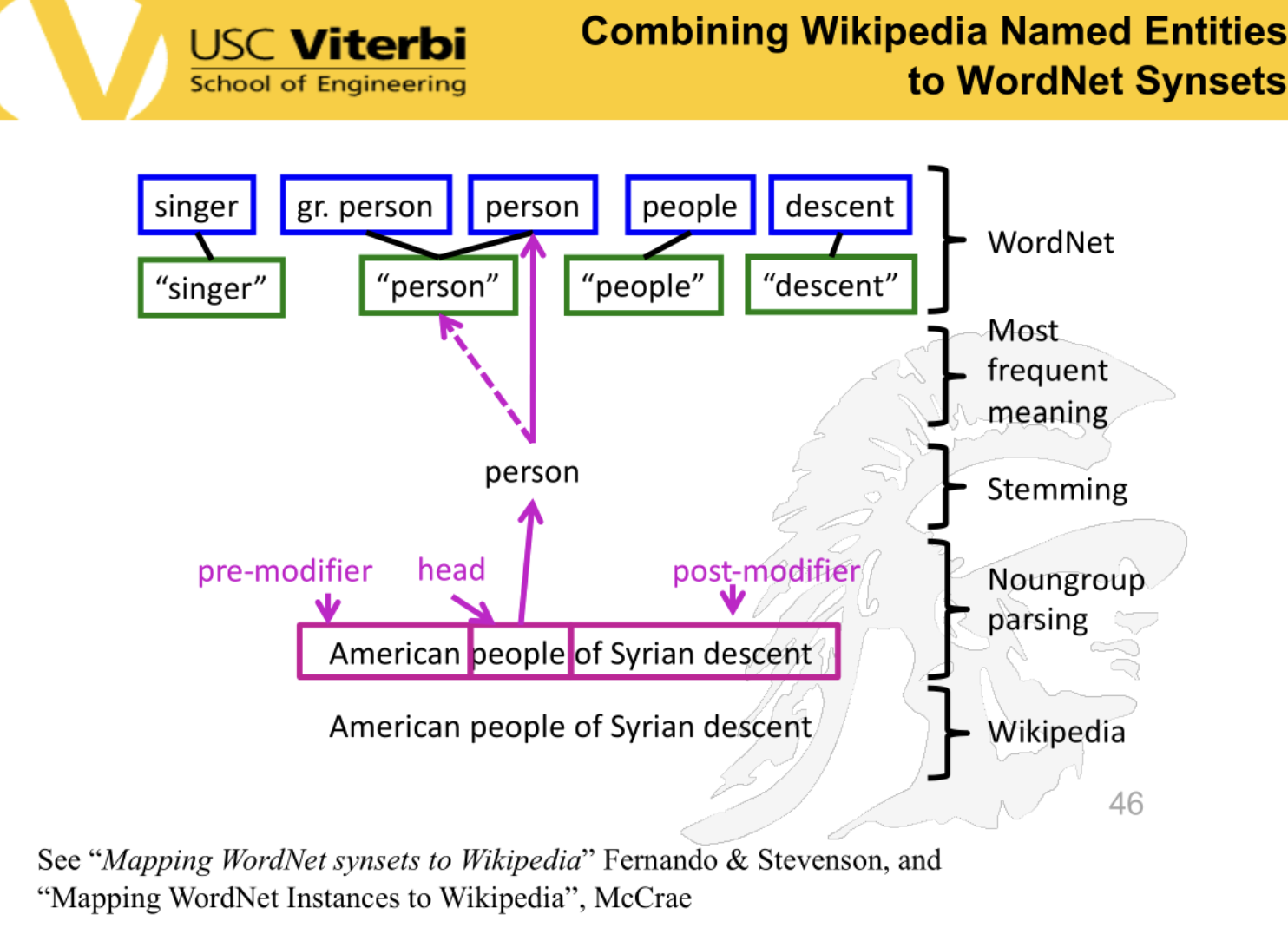
Wikipedia and WikiData
Wikipedia's original mission: To share the sum of all human knowledge for free, in every language.
WikiData is an effort to convert Wikipedia data into a knowledgebase.
WikiData aims to create a free, RDF-like KB about the world that can be read/edited by humans and machines.
Wikidata clients use the repository to:
Populate Web pages with structured data.
Enhance Wikipedia infoboxes by providing data that can be automatically updated and maintained.
Support data analysis by providing a structured dataset that can be queried and analyzed.
WikiData increases the quality and lowers the maintenance costs of Wikipedia and related projects.
An infobox is a structured table or panel commonly found on websites like Wikipedia. It summarizes key facts and data about the
5 Pillars of Wikipedia:
Encyclopedia (notable topics, no original research (NOR) )
Neutral POV (NPOV)
Free content (anyone can edit, no copyright)
Be civil
No firm rules
Structure
Links types:
Article Links: Connect to standard encyclopedia entries, providing in-depth information on specific topics.
Category Links: Organize articles into thematic categories, aiding in browsing and discovery of related content.
Interlingual Links: Link articles to their counterparts in different languages, facilitating multilingual access to information.
Types of Special Pages:
Redirect Pages: Automatically forward users from one page to another, typically used for alternative names or related terms.
Disambiguation Pages: List multiple pages with similar titles, helping users select the intended article when there are ambiguous terms.
type of special pages: redirect pages, disambiguation pages
Wikidata Multilingual Coverage
Each item in Wikidata can have labels, descriptions, and aliases in multiple languages, facilitating understanding and use by diverse linguistic communities.
Statements and properties are also designed to be language-neutral, allowing data to be used and interpreted consistently across different languages.
if entity dies:
adjust relationships
page recentering
property updates
Google Knowledge Graph
Introduced in 2012 with the Hummingbird update.
Powered in part by Freebase.
KnowledgeGraph was accused of taking away traffic from Wikipedia.
Knowledge panels are information boxes for entities (person, place, organization, event, etc).
Information sources include Wikipedia, LinkedIn, Crunchbase, Reuters, and Bloomberg.
Google's slogan: "things, not strings".
How Google Knowledge Graph Enhances Google Search
Improves variety of search results
Provides diverse interpretations by considering multiple meanings of query terms.
Example: For the query "apple," it distinguishes between the tech company and the fruit, offering varied results to match user intent.
Combines knowledge graph with Google Search’s documentation index
Integrates with Google Search’s index to refine results for specific entities.
Recognizes which entity a user seeks and focuses search around it, increasing efficiency and directing users to the correct information quickly.
Provide deeper, broader results, typically in an infobox. These infoboxes offer a structured overview of key facts, figures, and related information about the entity in question.
Give best summary
KB exploits best relationships amongst entities to summarize relevant content around a topic:
To effectively summarize content, the Knowledge Graph:
Analyzes Relationships: Examines the network of relationships between entities to identify the most relevant connections.
Prioritizes Key Information: Focuses on the most important aspects of the topic, such as key facts, figures, and events.
Contextualizes Content: Provides context by relating the topic to other entities and concepts in the Knowledge Graph.
Google Search
Combines document index with Knowledge Graph.
Employs Named Entity Recognition (NER) and Data Mining.
NER involves identifying and categorizing named entities within text, such as: People (e.g., Barack Obama), Organizations (e.g., Google), Locations (e.g., New York City), Dates and times (e.g., January 1, 2020), Quantities (e.g., 100 kg).
NER enables the Knowledge Graph to understand the context and meaning of search queries by recognizing the key entities mentioned.
Data mining involves extracting useful patterns and knowledge from large datasets. This includes discovering relationships, associations, and anomalies within the data.
Uses Query-Processor (Rankbrain, MUM & BERT).
Query-Processor: Refers to the components and algorithms used to understand and process search queries. Crucial for interpreting user intent and retrieving relevant information.
Key Functions:
Parsing: Breaking down the query into its constituent parts.
Semantic Analysis: Understanding the meaning and context of the query.
Query Transformation: Rewriting the query to improve search effectiveness.
Rankbrain: A machine learning-based component of Google’s search algorithm.
Uses deep learning to better understand the intent behind search queries.
Improves search accuracy by learning from user interactions and feedback.
MUM (Multitask Unified Model): A more advanced AI model that can understand information across different formats, including text, images, and video.
BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers): transformer-based model for NLP
Bidirectionatiol training al training allows BERT to consider the context of a word based on all surrounding words in a sentence, enhancing its understanding of nuance and meaning.
Includes an Entity API:
Provides programmatic access to entities and their associated information within the Knowledge Graph.
Enables developers to integrate Knowledge Graph data into their applications and services.
Supports various use cases, such as entity recognition, disambiguation, and information retrieval.
Uses Relevance-Scoring & E-A-T Evaluation:
Relevance-Scoring: Assigns a score to each search result based on its relevance to the query.
E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) Evaluation: Assesses the quality and reliability of content to ensure that search results are trustworthy and accurate.
E-A-T signals are used to rank results, giving priority to content from sources with high expertise, authority, and trustworthiness.
Ranks results using a Scoring-Engine (Hummingbird):
Hummingbird: The name of Google’s scoring engine that ranks search results based on various factors, including relevance, quality, and user experience.
Considers a wide range of signals to determine the best results for a given query.
Utilizes a Cleaning-Engine and Personalization:
Cleaning-Engine: Removes spam, irrelevant, and low-quality content from search results.
Personalization: Customizes search results based on a user’s search history, location, and other factors.
Enhances the relevance and usefulness of search results for individual users.
Focuses search around entities recorded in the KnowledgeGraph when recognized in the search query:
Leverages the Knowledge Graph to understand the entities mentioned in a search query and provide more targeted results.
When a user searches for a specific entity (e.g., “Barack Obama”), Google Search focuses on providing information about that entity.
Includes direct answers, knowledge panels, and links to relevant sources.