macro molecules
Macro molecules = carbon based
carbon atom is the basic atom of organic compound
organic compound in living things 4
4 organic compounds
carbohydrates Ex. pizza bread pasta
protiens Ex. egg fish meat chicken
lipids Ex. oil butter cheese avocado
nucleic acid ( DNA and RNA)
small units are called monomer
large units are called polymer
property | monomers | polymers |
sugar = glucose amino acid fatty acids nucleotide | = carbohydrates = protiens =lipids = nuclieic acid |
monomers are connected to for polymers by using hydrogen bonds
carbon atom has unique properties
have 4 valence electrons can form up to 4 chemical bonds
can form:
straight c-c-c
branched -c-c
|
- c -
rings
bsic elements of organic compounds
monomer | polymer |
C,H,O -N | Carbohydrates Protiens Lipids Nucleic acid |
basic elements for all living things 95%
carbohydrates -
hydrogen -
oxygen -
nitrogen
phosphorus
sulfur
carbohydrates
monomer = monosaccharide
polymer = polysaccharide
elements = C,H & O
use: provide energy for living things
cell wall in plant cell made up of cellulose
examples:
monosaccharide Ex: glucose
disaccharide Ex: sucrose maltose
polysaccharide Ex: in plants → cellulose in animal → glycogen
Lipids
elements= C,H & O
non polar
use: store energy and provide insulation, as well as serving as structural components of cell membranes.
lipids:
Fats: glycerol and 3 fatty acids saturated
c-c-c-c
oils: unsaturated
c=c-c-c=c
lipids: fat/ oil/ wax hormones
protein
elements: C,H & O (N)
functions: enzymes ← biological catalysts/ speed up the rate opf chemical reaction
protein building up body structure
Ex: enzyme/ collagen/ homoglobin/ antibodies
→ monomer of protien amino acids link together by peptide bond
nucleic acid
DNA and RNA
monomer → nucleotide
function:
direct synthesis of protein
genetic code
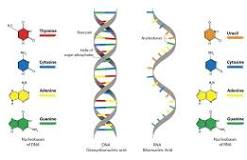
nucliotide:

enzymes
protien
speed up the rate of chemical reaction
Enzyme: biologival catalyst