Study manual week 1
Week 1 - Lung infections + healthy aging

PT anamnesis - ICF
Request for help: be less short of breath during ADLs
Impairments
feeling unwell for years
short of breath
Diagnosis: Pneumonia, GP prescribes antibiotics
Activity
during extortion
walking: 300 m in 7 minutes - catch the bus (walking to the bus station)
feeling extortion after and during coughing
Participation:
- — -
Personal factors:
41 years old, male
PT didn’t exercise for years
smokes cigarette (10 x day, for 20 years) tried to stop but failed
gained 5 kg
problem sleeping → smokes
coughed phlegm after taking his antibiotics
in his free time, he writes children’s stories
Body weight: 90 kg, height 165 cm
Environmental factors
support system → wife
works in an accountant firm
Clinical measurements
BORG dyspnoea: 6
BORG fatigue: 7
NPRS: 2 when coughing
In class - friday, 2nd class
Hypotheses
1) smoking induced lung damage
2) physical deconditionong
3) obesity related difficulties
4) Potential early stage COPD
5) Residual pneumonia effect
assessment → look into chapter 6 for ASSESSMENT
1) ascultation, saturation
2) 6 minute walk test (endurance test)
3) BMI, body fat percentage, waist circumference
4) Spirometry, CAT, CCQ
Treatment
Goals
1) improve respiratory function
2) Increase physical fitness
3) Support stop smoking
4) Enhance overall qualitty of life
Means (aka how?)
anamesis it’s important too
how? breathing techniques exercuses
Supervised cardiovascular exercises
how? gradual exercsie rehab
MB preparation
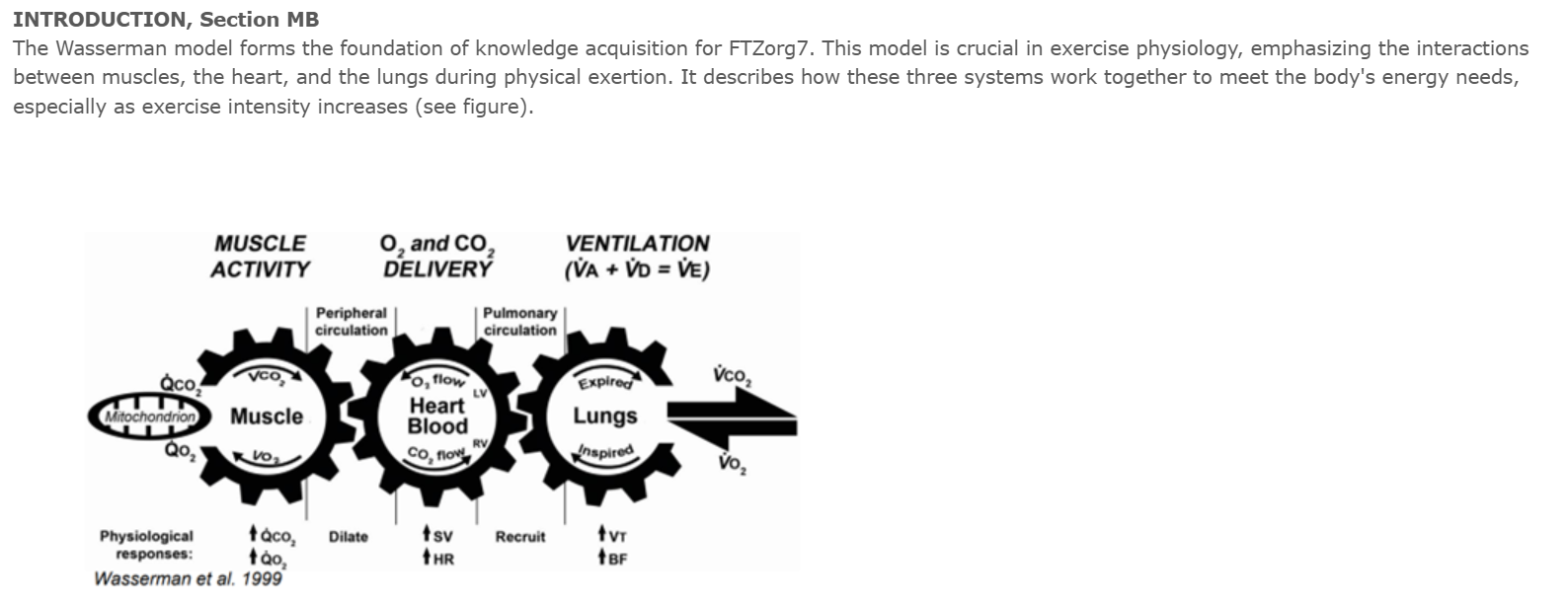
Wasserman model: interaction between the 3 Systems: muscles, heart, and lungs during physical exertion to maintain body homeostasis and adapt to the body's changes in energy demands
How do these systems work together?
Roles of Each System and Their Interconnections:

System 1: Muscles
it’s the peripheral component
They demand energy to create movement, this energy comes from the nutrients that are sent to them via aerobic and anaerobic processes
Muscles use oxygen when at rest, the oxygen is obtained by “aerobic metabolism“, when in exertion, the anaerobic metabolism is used and there is a production of lactate
Lactated it’s a bioproduct of the anaerobic metabolism (when oxygen is limited), the lactate goes again into the bloodstream and other organs (liver/heart) convert it into energy

System 2: Heart
it’s the central component
The heart pumps blood and delivers oxygen and nutrients to the muscles, it gets rid of carbon dioxide and lactate
HR and stroke volume increase with greater exercise intensity → = Higher cardiac output
The heart takes care of the oxygenation process, the heart sends the blood to the lungs, in the lungs the blood gets oxygen and it’s pumped to the muscles, the muscles give as a bioproduct CD and lactate, the blood rich in carbon dioxide and lactate returns to heart and heart sends it back to lungs
The function of the heart is regulated with a combo of neuro and hormonal signals, they respond to the muscle’s energy demands

System 3: Lung
it’s the ventilatory component
The main role is the gas exchange, to remove CD from blood
During exercise, Breath frequency and volume increase to meet the demand for oxygen and expel excess CD,
Ventilatory Threshold (VT) → point that marks the transition where ventilation rises to remove the larger quantities of CD (due to exercise)
lactate buffering: when L accumulates in the blood, there is more CD → It further stimulates breathing to expel the excess
How do they work together?

Summary:
1) System integration: the systems work together to meet body energy demands during exercise. It’s a cycle, the muscles require more oxygen and expel bioproducts, and the heart and lungs work faster and harder to supply oxygen and expel bioproducts
2) Feedback: there is constant communication between the systems and they respond to each other needs
3) Efficiency and performance: if one of the systems is not working, it affects the overall efficiency and performance
Notes in another file:


PT preparations

Core concepts PT


Study task 1 → done
Study task 2 → done
Study task 3

Study task 4:
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that causes inflammation in the air sacs (alveoli). The alveoli may fill with fluid or pus, leading to symptoms such as coughing, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or, in some cases, inhalation of harmful substances. It ranges from mild to severe, with severity depending on the cause, the person's age, and overall health.
Study task 5: BRUCE TEST
The BRUCE test, or Bruce Protocol, is a commonly used graded exercise test to assess cardiovascular fitness and determine maximum oxygen consumption (VO₂ max). It is often performed on a treadmill and consists of progressively increasing stages of intensity.
Key Features of the Bruce Test:
Protocol Stages:
The treadmill speed and incline increase every 3 minutes.
The starting point is usually a speed of 2.7 km/h (1.7 mph) and a 10% incline.
Each stage gets progressively harder, challenging the heart, lungs, and muscles.
Purpose:
Assess aerobic capacity (VO₂ max).
Monitor cardiovascular response (e.g., heart rate, blood pressure, ECG) during exercise.
Diagnose or monitor conditions like coronary artery disease or exercise-induced symptoms.
End of Test:
It continues until the subject reaches exhaustion, experiences symptoms (e.g., chest pain, dizziness), or the tester terminates it for safety reasons.
The total time or stage reached is used to estimate VO₂ max.
Study task 6:

BC preparations

Key words to know


Moos & Scaefer Illness processes

 Knowt
Knowt