Chapter 1: Organs, Organ Systems, and Body Organization
Anatomy
Anatomy - study of body structure
Gross / Macroscopic - No Microscope
Regional - Area to Area
Systemic - system by system
Surface - External form and relation to deeper structures
Microscopic - seen w/ Microscope
Cytology - Cellular anatomy
Histology - Study of Tissues
Physiology - Study of Functions/Processes
Cell Physiology - processes in cells
Neurophysiology - nervous System processes
Cardiovascular - processes in Heart, blood, blood vessels
Tissue - Group of cells w/ similar Structure
Humans have over 200 cell types
Organ - collection of 2 or more tissues to perform a function
4 General Types of Animal Tissue
Epithelial Tissue
Skin
Connective Tissue
Cartilage
Bone
Nervous Tissue
Brain
Nerves
Muscle
organ/Visceral
Heart
Skeletal
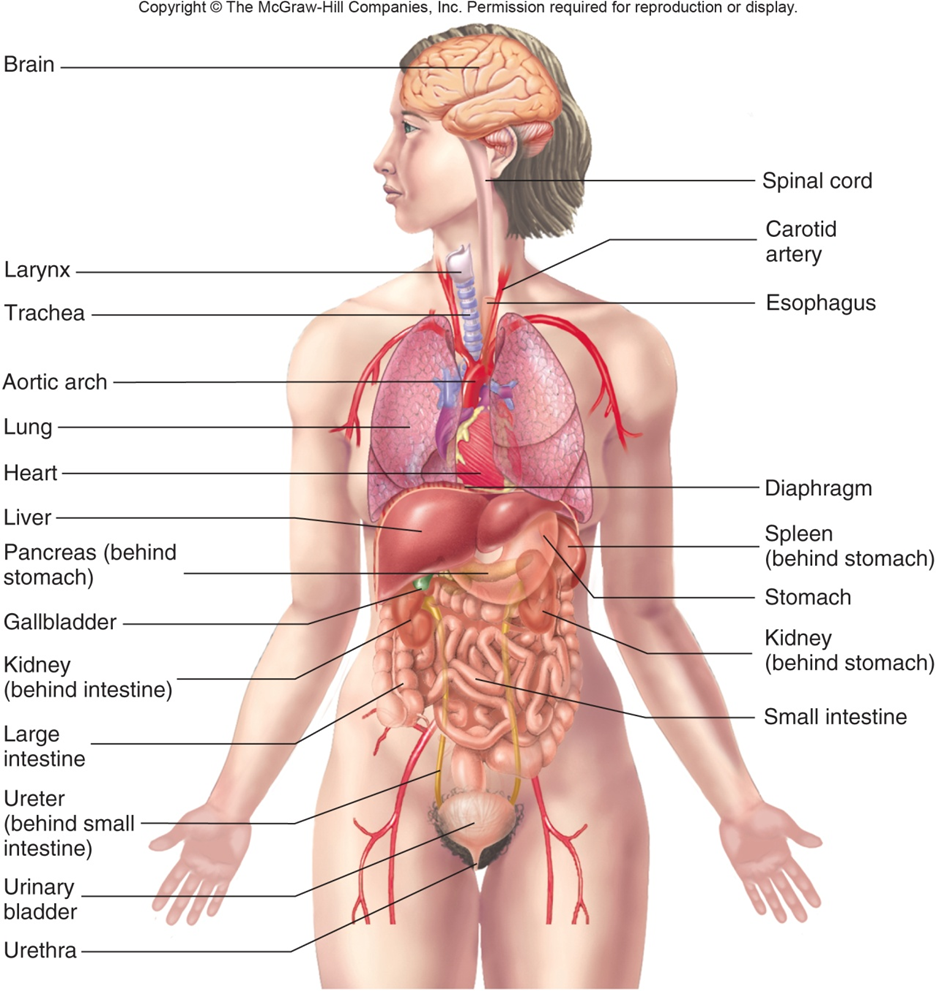
Organs
https://www.geoguessr.com/vgp/3801
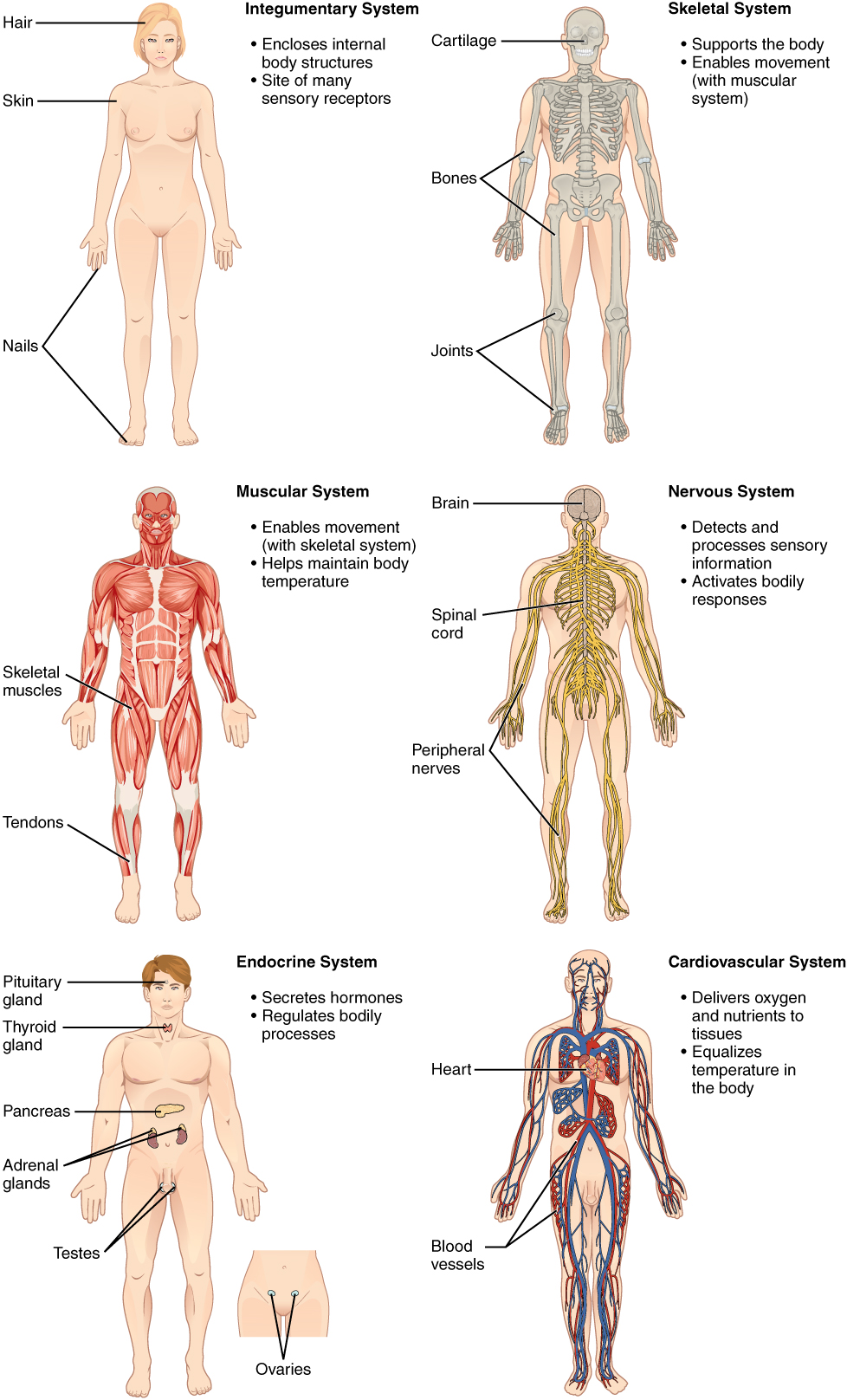
Organ Systems
Integumentary System - Encloses Internal Body Structures: Site of many sensory receptors: Prevents Water Loss: Produce vitamin D
Skin
Hair
Nails
Sweat Glands
Skeletal System - Supports body: Enables movement w/ muscular system: Produces Blood Cells: Stores minerals and Fats: Bones, Cartilage, Ligaments, Joints
Skull
Clavicle
Sternum
Ribs
Humorous
Vertebral Column
Radius
Ulna
Pelvis
Femur
Tibia
Fibula
Muscular System - Enables movement: Helps maintain body temperature: Maintains posture: Produces body heat: Muscles attached to skeleton by tendons
Temporalis
Pectoralis Major
Biceps Brachii
Rectus Abdominis
Sartorius
Quadriceps Femoris
Gastrocnemius
Nervous System - Detects and process sensory information: Activates bodily Responses: Controls movements, Physiological Processes, and intellectual functions: Brain, Spinal Cord, Nerves, Sensory Receptors
Brain
Spinal Cord
Nerve
Cauda Equina
Endocrine System - Secretes Hormones: Regulates body processes: Influences metabolism, growth, reproduction, etc.: Glands, Pituitary glad
Hypothalamus
Pituitary
Pineal Gland
Thyroid
Thymus
Adrenals
Parathyroids (posterior part of thyroid)
Pancreas (islets)
Testes (male)
Ovaries (female)
Cardiovascular System - Delivers oxygen and nutrients to tissues: Equalizes body temperature: Transports Waste, Gases and Hormones: Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood
Carotid Artery
Jugular Vein
Superior Vena Cava
Heart
Pulmonary Trunk
Brachial Artery
Aorta
Inferior Vena Cava
Femoral Artery and Vein
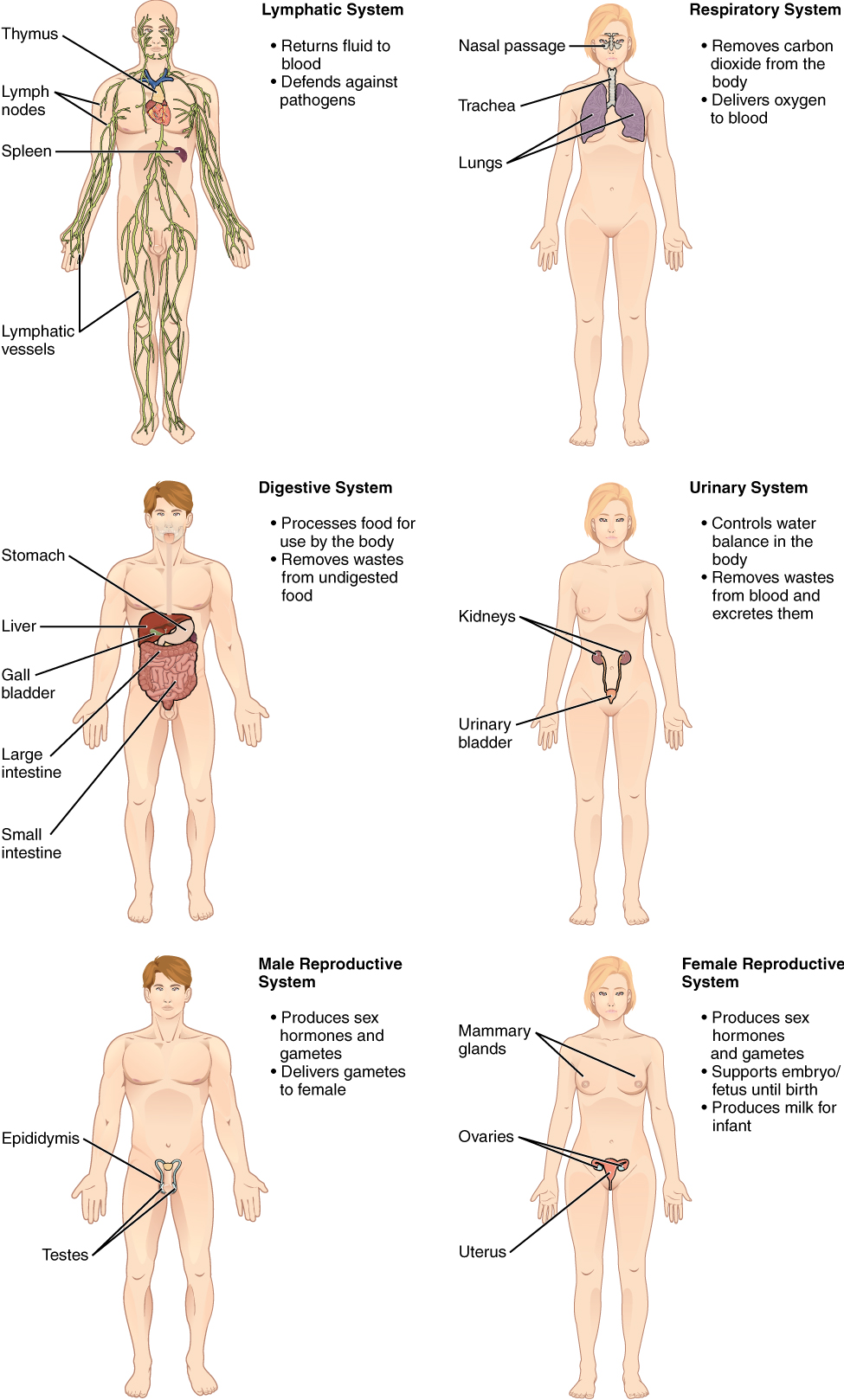
Lymphatic System - Returns fluid to blood: Defends against pathogens: Removes foreign substances form blood and lymph: Absorbs fats form digestive tract: Lymphatic Vessels, Lymph nodes, Lymphatic Organs
Tonsils
Cervical Lymph node
Mammary Plexus
Thymus
Axillary Lymph node
Lymphatic Vessel
Thoracic duct
spleen
Inguinal Lymph node
Respiratory System - Removes Carbon dioxide from the body: Delivers oxygen to blood: Regulates blood pH: Lungs and Respiratory Passages
Nose
Nasal cavity
Pharynx (throat)
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchi
Lungs
Digestive System - Processes food for use by the body: Removes waste from undigested food: Mechanical and chemical Digestion: Mouth, Esophagus, Stomach, Intestines, Accessory Organs
Pharynx
Oral Cavity
Salvatory Glands
Esophagus
Stomach
Pancreas
Liver
Gallbladder
Small Intestine
Large Intestine
Appendix
Rectum
Anus
Urinary System - Controls water balance in the body: Removes wastes from blood and excretes them: Regulates blood pH: Ion balance: Kidneys, Urinary Bladder, Ducts that carry urine
Kidney
Ureter
Urinary Bladder
Urethra
Female Reproductive System - Produces sex hormones and gametes: Supports embryo/fetus until birth: Produces milk: Ovaries, Vagina, Uterus, Mammary glands, Associated structures
Mammary Gland (breast)
Uterine tube
Ovary
Uterus
Vagina
Male Reproductive System - Produces sex hormones and gametes: Delivers gametes (sperm) to female: Testis, Accessory structures, Ducts, Penis
Seminal Vesicles
Prostate Gland
Testis
Ducts Deferens
Epididymis
Penis
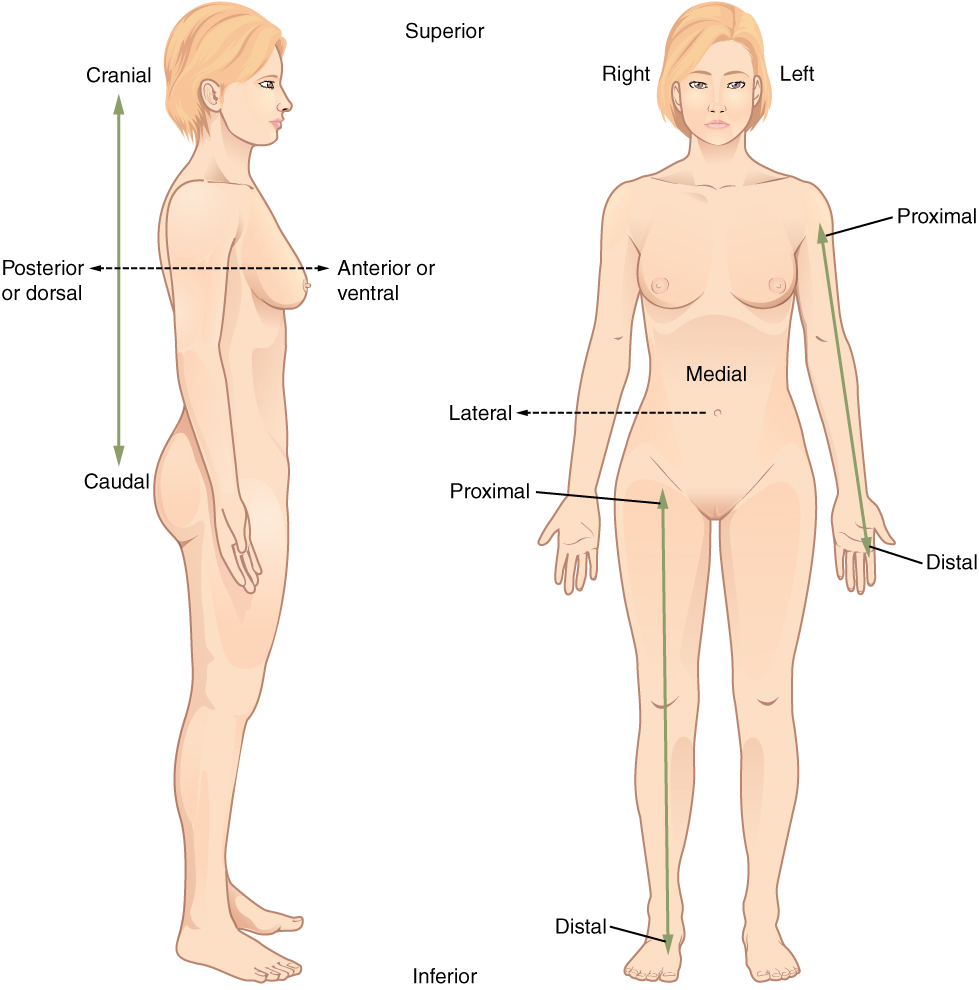
Anatomical Position
Anatomical Position - Erect, face forward, feet together, Palms forward
Supine - Face up
Prone - Face down
Superior/Cephalic - Towards head
Inferior/Caudal - Towards feet
Medial - Towards center
Lateral - Away from center
Proximal - Closer to
Distal - Away from
Superficial - Surface
Deep - Deep
Anterior/Ventral - Front
Posterior/Dorsal - Back
Body Parts and Regions
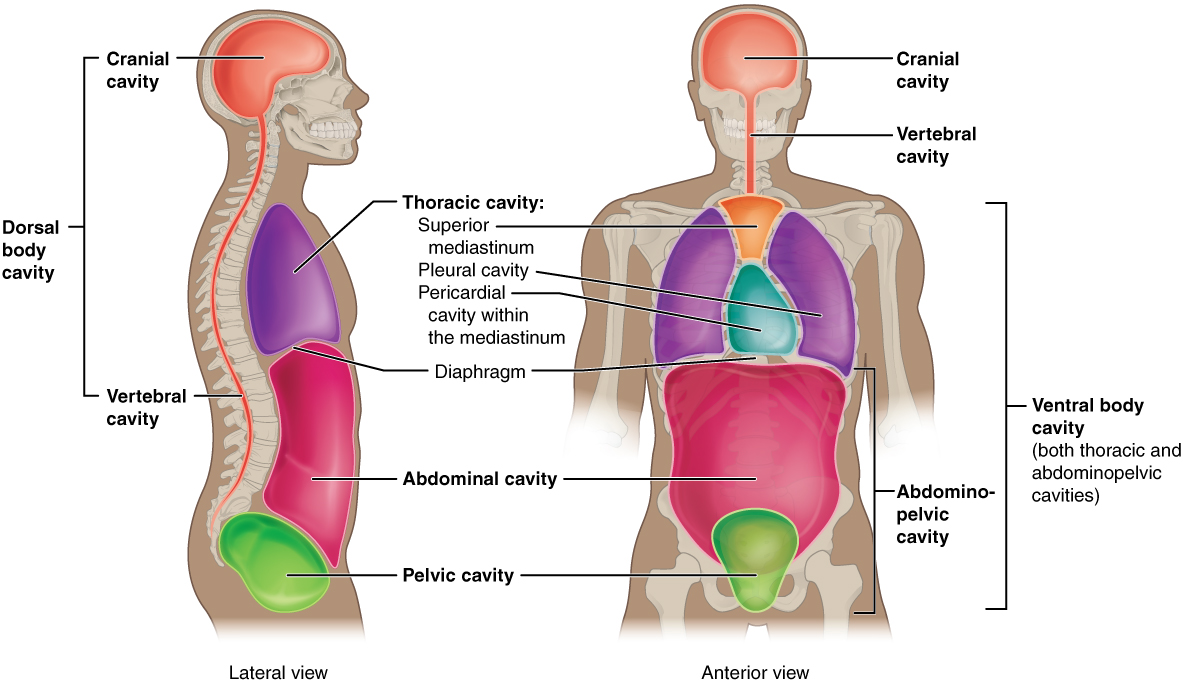
Body Cavities - Fluid filled Space
Diaphragm - Divides Thoracic and Abdominopelvic cavity
Mediastinum - Contains all structures of Thoracic cavity
not lungs
Trunk Cavities
Thoracic
Abdominal
Pelvic
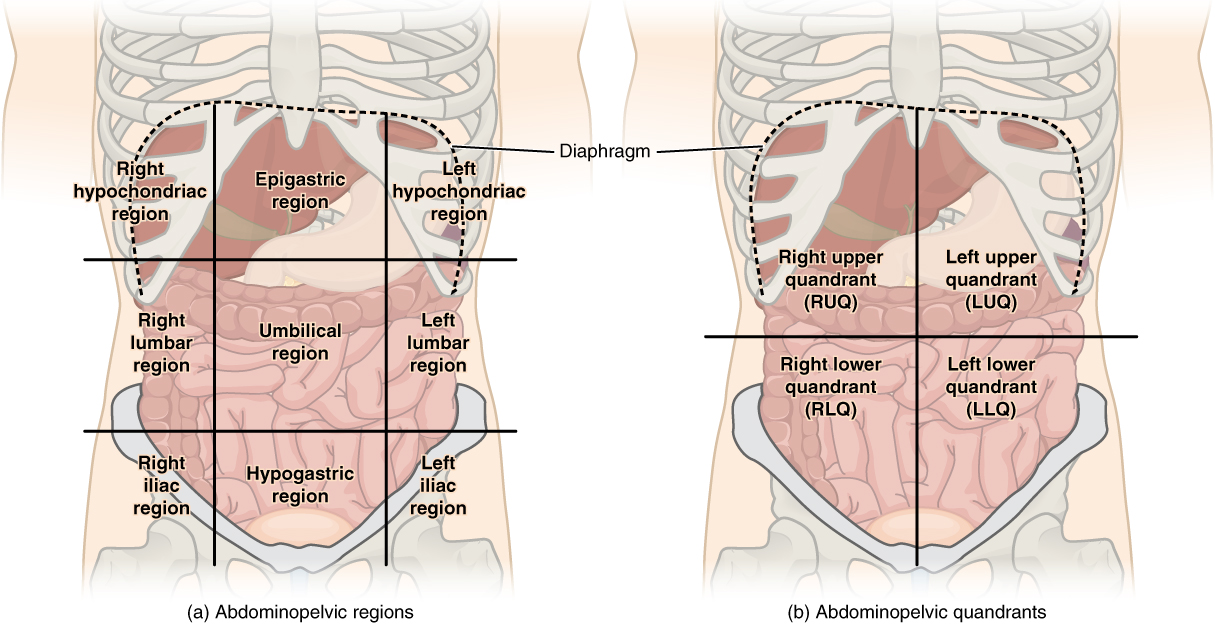
Abdominopelvic Divisions
Nine Abdominal Regions
Right Hypochondriac Region
Gallbladder
Liver
Right Lumbar Region
Ascending Colon
Right Iliac Region
Cecum
Appendix
Epigastric Region
Stomach
Liver
Pancreas
Umbilical Region
Small Intestine
Hypogastric Region
Urinary Bladder
Rectum
Left Hypochondriac Region
Stomach
Spleen
Left Lumbar Region
Descending colon
Left Iliac Region
Sigmoid Colon
Four abdominal quadrants
Right Upper Quadrant
Right Lower Quadrant
Left Upper Quadrant
Left Lower Quadrant
Serous Membranes
Cover organs of trunk cavities / line the Cavity
Inner Wall - Visceral Serous membrane: filled with lubricating serious fluid
Outer Wall - Parietal Serous membrane filled with lubricating serious fluid
Pericardium - Heart
Pleura - Lungs/Thoracic Cavity
Peritoneum - Abdominopelvic Cavity
Imaging
Radiology/ X-ray - Shadowy negative of internal body structures
Ultrasounds - Computer -analyzed sound waves bounded off a structure
2D or 3D
Transdermal or Transvaginal
Computed Tomography /CT Scan - Composite of radiograph; shows slices of Body
Digital Spatial Reconstructions/DSR - 3D version of CT Scan Both with or without contrast
Digital Subtraction Angiography/DSA - Comparison of radiographs with and without dye
blood vessel studies
Magnetic Resonance Imaging/MRI - Magnetism and Radio waves boking for varying alignment of protons in soft tissues
Position Emission Tomography/PET- Uses Radioactivity labeled glucose to calculate metabolic activity of cells
Abdominal Planes
Sagittal - Left and Right
Frontal/Coronal - Front and Back
Transverse/Horizontal - Top and Bottom
Oblique - Cut at Right Angle
Planes Through Organs
Longitudinal - Cut along length of an organ
Transverse - Cut at right angle along length of organ
Oblique - Cut at right angle
 Knowt
Knowt