Big Idea 4: Computer Systems and Networks (copy)
The Internet
Internet: is a network of networks.
The word Internet came from “interconnection of computer networks.”
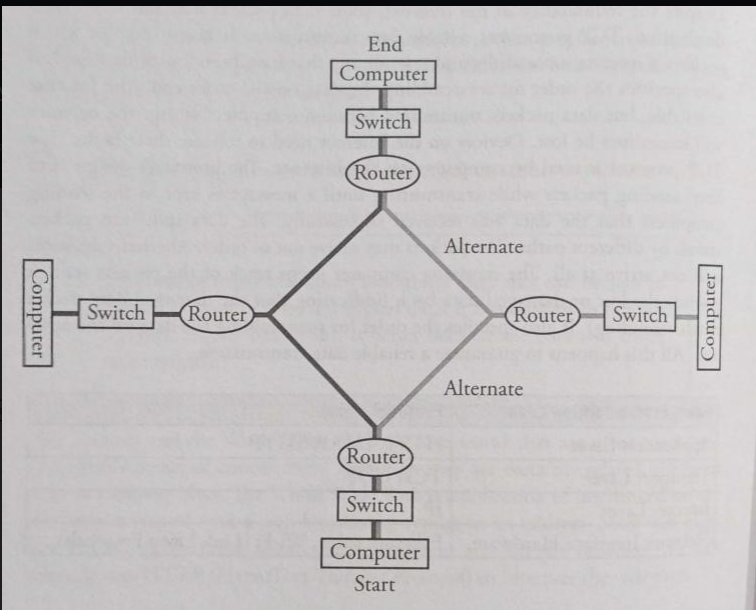
The Internet is hardware-driven with wires, cables, and devices such as routers and servers.
Routers are computing devices along a path that send information to the next stop on the path.
Routing: is the process of finding a path from sender to receiver
Bandwidth: is a measure of the maximum amount of data that can be transferred through a channel or network connection.
It's measured in bits per second, and it determines how quickly you can download and upload files from the internet.
Internet protocol (IP): is responsible for addressing and routing your online requests.
Transmission control protocol (TCP): is a protocol that defines how computers send packets of data to each other.
User datagram protocol (UDP): is a protocol that allows computer applications to send messages without checking for missing packets to save on time needed to retransmit missing packets.
Scalability
Scalability: is the ability of a system, network, or process to handle a growing amount of work efficiently.
It can also be defined as the capacity to increase services and products quickly with minimal interruption and cost.
This is especially important in software engineering, where scalability is crucial when developing applications that are expected to handle large amounts of traffic or data.
Minimizing HTTP requests can reduce load time
Fault Tolerance
Hardware Failure
Hardware failure: is when a hardware device, such as a computer or printer, stops working properly due to an issue with the physical components.
The cause of the failure can be anything from electrical wiring issues to incorrect installation and configuration of hardware components.
In any case, diagnosing and repairing hardware failures can be difficult without proper tools and experience in dealing with this type of issue.
Operational Failures
Operational failures: are any issues or breakdowns in the operation of a business, machine, system, process, etc.
They can range from unexpected downtime to incorrect results due to faulty programming.
Operational failures can have significant impacts on profitability and reputation if not addressed swiftly and appropriately.
Weather
The internet has cables and wires spanning the world that connect computers.
Natural disasters: could cause the hardware to be destroyed, bringing the network activity to a halt.
Solar Flare: is an intense radiation that is released from the sun.
This happens because of the release from the sun.
Cyberattacks
Cyberattacks: are malicious attempts to damage or disrupt computer systems, networks, and data.
They can be carried out by individuals, groups, or organizations with malicious intent.
Cyberattacks typically involve the use of malware such as viruses and ransomware that allow attackers to gain access to a system for a variety of nefarious purposes including stealing data and financial information or launching denial-of-service attacks.
Some cyberattack methods used today include phishing campaigns; social engineering attacks; website defacement; distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks; SQL injection exploits; man-in-the middle (MITM) attack vectors etc.
DDoS attacks
Works by overwhelming a network with a flood of internet traffic
Can be mitigated by increasing the bandwidth
SQL Injection
A code injection
Placed malicious code in SQL statements —> input these statements into entry fields
Targets vulnerabilities in web applications’ databases
Can read and manipulate data
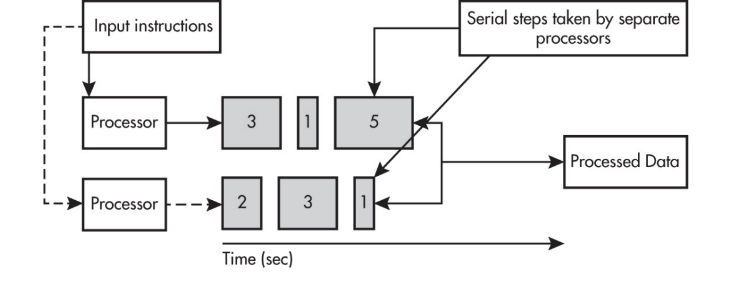
Parallel and Distributed Computing
Parallel Computing
Parallel computing solution takes as long as the longest of the tasks done in parallel.
A parallel computing solution takes as long as its sequential tasks plus the longest of its parallel tasks.
Parallel computing can consist of a parallel portion and a sequential portion.
Why Is Parallel Computing Used?
Parallel computing is needed for real-world simulations and modeling.
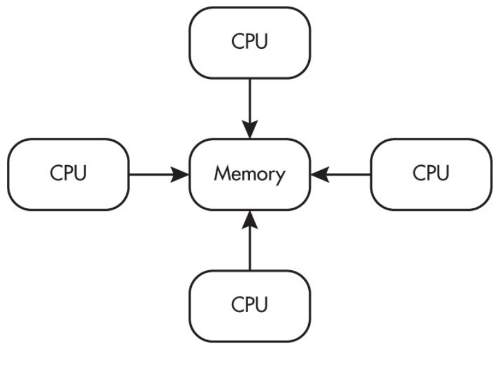
Multiple processors can operate independently but share the same memory resources.
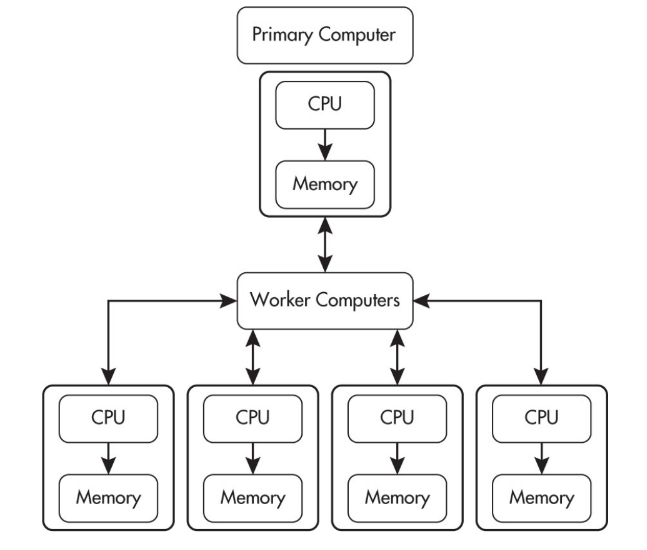
Distributed Computing
Distributed computing allows problems to be solved that could not be solved on a single computer because of either the processing time or storage needs involved.
Parallel computing uses a single computer with multiple processors.
Distributed computing uses multiple computing devices to process those tasks.
Content distributing networks
Stores content in multiple geographical locations
When a user requests content, it can be received from the nearest server location
Reduces the time it takes for the content to travel over the internet
Cloud services
Allows you to easily scale your resources up and down based on your current needs
Cloud computing resources —> scalability
Useful for testing applications
HTTP vs HTTPs
HTTP: Many people can attack websites
HTTPs (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure): Protests the privacy of users and prevents tampering
A.K.A. HTTP over TLS —> encrypts HTTP requests and responses with TLS protocol
Ensures that only the browser and secured domain can see the data in the HTTP requests and responses
Prevents tampering with website content —> TLS can detect packet alterations
 Knowt
Knowt