Chapter 7
Deviance
violation of social norms
Crime
violation of a social norm encoded by law
Difference between Deviance and Crime
Severity it social response
perceived harmfulness
degree of public agreement
Both depend on the context though: some see certain acts like selling organs as legal, whereas other parts of the world see it as unethical and terrible
Sanctions
Informal Punishments → mild + raise eyebrows
Stigmatism
Formal Punishments
Severity depends on the severity of the crime
Types of Deviance and Crime
Social Diversions
Social Deviances
Conflict Crimes
Consensus Crimes
Measuring Crime
Uniform Crime Reporting (UCR), collected by police
TREND: overall decline in Police-Reported Crime Rate
Either measured through Tradition Crime Rate or Crime Severity Index
4/5ths of reports have no violence
1st Shortcoming: victimless crimes are less seen
2nd Shortcoming: police decide what to share and what to ignore
Victimless Crimes
violations of the law where a victim does not come forward, potentially due to the humiliation/stigmatization
Self-Report Surveys
Asking respondents to indicate their involvement in criminal activities, either as perpetrators or as victims
Illustrate the overall engagement in crime: 1/4th of the population has been a victim [most of which do not go to court]
Victimization Surveys
People are asked whether they have or have not been a victim of crime
example: General Social Survey (GSS)
TREND: Victimization Rates DECLINED since 2004, mostly non-violent and theft of personal property
More among single/women than married/a man
4 Types of Crime is increasing since 2014:
Fraud
Cybercrime
SA
Shoplifting
TREND: Hate crime increasing
Explanations for Decrease in Crime Rate since 1992
Better trained police force and law
Young men do the most crime, but their age cohort has decreased
Baby Bust ;-;
Lower unemployment rates
Legalization of Abortion
Less unwanted babies to felt neglect and turned to crime
Criminal Profile
More Men being accused of SA than women in court
Race/Ethnicity
TREND: increase in Indigenous incarcerations, but why?
More street crimes than white-collar crimes, which are more noticeable
They live in poverty and have to do crime to live
Discrimination of police and law enforcement
Western Culture made ruined Indigenous social life, so less cohesion/morals
Above also applies to black people
THEREFORE: certain races are NOT “more law-abiding” than others, social forces rather determine incarceration rate
Symbolic Interactionalists
Labelling Theory
People become deviant only when they are labelled deviant and embody a deviant identity when they otherwise would not
When being surrounded by people who’s deviances are normalized, you tend to take on such acts too and do not see yourself as deviant
Deviance is learned and can also be unlearned
Howard S. Becker’s “Learning Deviance”
TREND: parents seeing their kids as deviant make them more deviant, resulting in more trouble with the police and more sever punishments from law enforcement
Functionalists
Durkheim: Crime is functional because:
Reminds people of common values
Fosters collaboration in punishing somebody
Can drive Social Change (ex: Martin Luther King)
Robert Morton: Strain Theory
Not having your cultural ideals met by society results in strain, which is dysfunctional
Society never provides enough opportunities for all to succeed
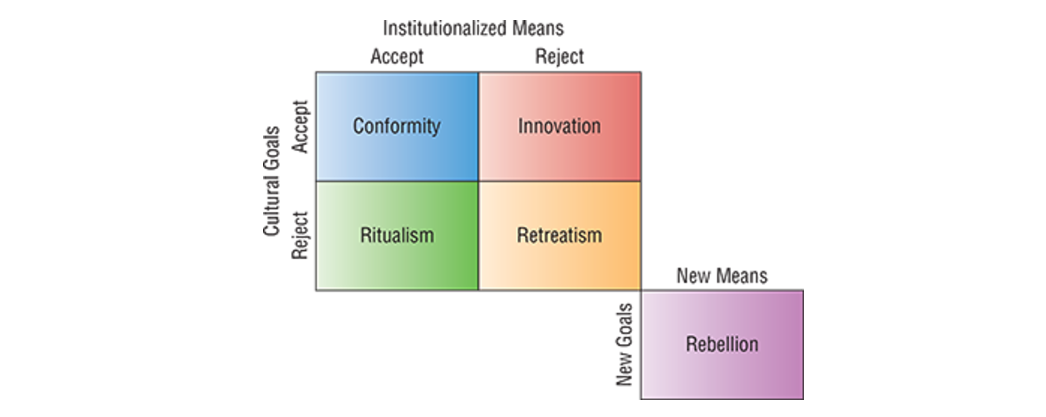
Criminal Subcultures: people adapting to strain caused by social dysfunction
Majority black and Indigenous → due to oppression and poverty
These groups tend to normalize criminal activities, as if morally acceptable
Critique: They stress the relationship between Crime and Social Class too much
All do crime, but the TYPE of crime differs:
Rich, economic greed → white-collar crimes
Poor, economic need → street crimes
Conflict Theory