Nervous System Overview
Nervous System consists of:
- Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Brain
- Spinal cord
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Cranial nerves
- Spinal nerves
}}Central Nervous System (CNS)}}
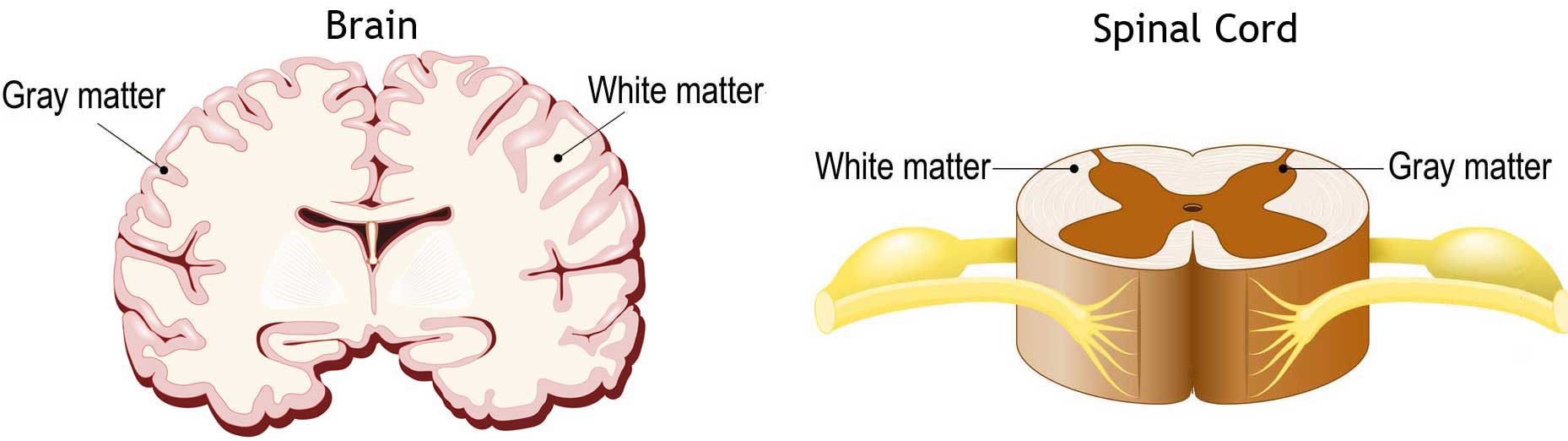
Brain: white matter surrounded by grey matter.
^^3 main parts of the Brain :^^
- cerebrum
- brainstem
- cerebellum
White matter: mainly nerve fibres with their myelin sheaths
Grey matter: mainly nerve cell bodies and branching dendrites
Spinal cord: gray matter surrounded by white matter.
}}Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)}}
- Somatic Nervous System
- skeletal muscle
- Autonomic Nervous System
- glands, smooth muscles, cardiac muscles
- Parasympathetic Nervous System: (discrete activation)
- Sympathetic Nervous System: (diffuse activation)
<<^^12 pairs of cranial nerves:^^<<
- olfactory (CN I)
- optic (CN II)
- oculomotor (CN III)
- trochlear (CN IV)
- trigeminal (CN V)
- abducent (or abducens; CN VI)
- facial (CN VII)
- vestibulocochlear (CN VIII)
- glossopharyngeal (CN IX)
- vagus (CN X)
- accessory (CN XI)
- hypoglossal (CN XII)
<<^^31 pairs of spinal nerves:^^<<
- 8 cervical nerve pairs (C1-C8)
- 12 thoracic nerve pairs (T1-T12)
- 5 lumbar nerve pairs (L1-L5)
- 5 sacral (S1-S5)
- 1 coccygeal nerve pair
<<^^Types of Neurons:^^<<
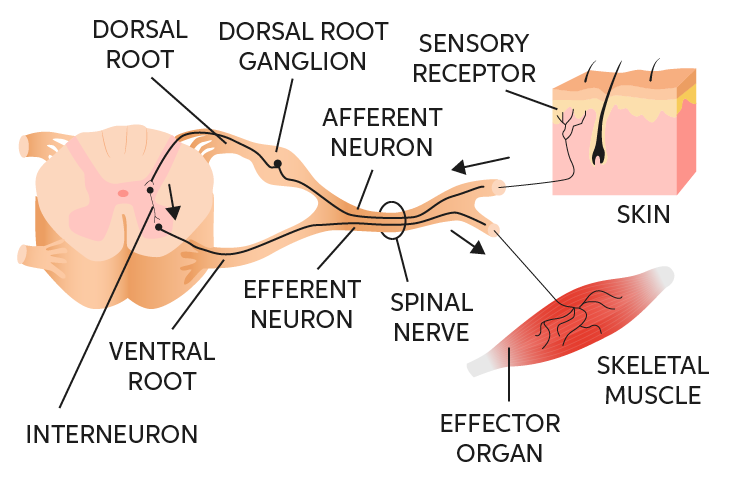
Afferent (sensory neurons): nerve fibers responsible for bringing sensory information from different parts of the body to the CNS.
- cell bodies are located just outside of the spinal cord in the dorsal root ganglion
Interneurons: central nodes of neural circuits, enabling communication between sensory or motor neurons and the CNS.
Efferent nerves: nerves that carry nerve impulses away from the CNS.
cell bodies located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord
<<Somatic vs Autonomic Nervous System<<
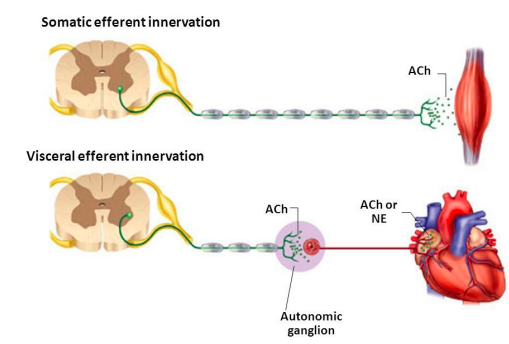
| }}Somatic Nervous System}} | }}Autonomic Nervous System}} |
|---|---|
| voluntary | involuntary |
| innervate skeletal muscles | innervate smooth muscles |
| one neuron between CNS and the target organ | two neurons between CNS and the target organ |
| efferent arise from ventral horn cells | efferent arise from lateral horn cells |
| chemical transmitter: acetylcholine | either: acetylcholine or norepinephrine |