5.2 DNA Replication (Elongation)
UNIT 3: MOLECULAR GENETICS
Lesson 3: DNA Replication (Elongation)
DNA Replication Overview
Phases of DNA Replication:
Initiation
Unwinding of the DNA double helix.
Bases become exposed for new base pairing.
Elongation
Creation of two new DNA strands using parent DNA as a template.
New DNA forms double helices containing one parent and one daughter strand.
Termination
Completion of replication process, allowing two new DNA molecules to separate and re-form double helix.
Dismantling of replication machinery.
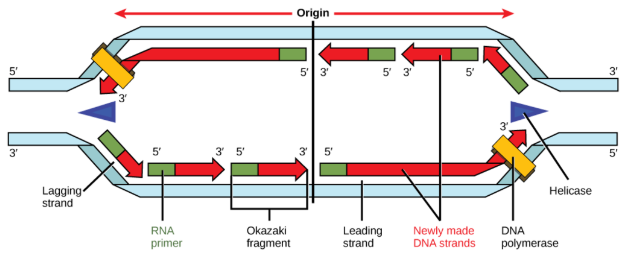
Origin of Replication
Formation of Replication Bubble
DNA strands unwind to create a replication bubble.
DNA replication begins at two replication forks and continues outward.
DNA synthesis occurs in both directions from the forks.
Elongation Phase
RNA Primers
Necessary for the formation of new DNA strands.
RNA Primer:
Small segment of RNA laid down on the parent strand by enzyme RNA Primase.
Defines where DNA polymerase III binds for nucleotide addition.
Function of DNA Polymerase III
Catalyzes the addition of deoxyribonucleotides to the new strand.
Adds nucleotides to the 3’ hydroxyl end of an existing chain, synthesizing in a 5’ to 3’ direction.
Leading Strand
Synthesized continuously in the 5’ to 3’ direction.
New nucleotides added by DNA polymerase III, complementary to the parent strand, from the origin towards the replication fork.
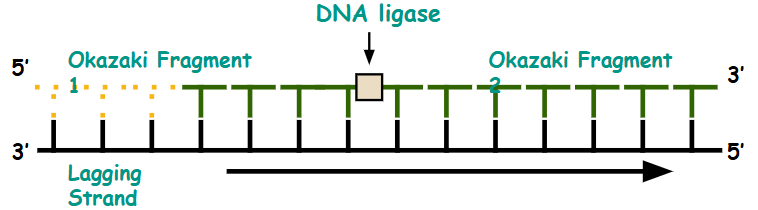
Lagging Strand
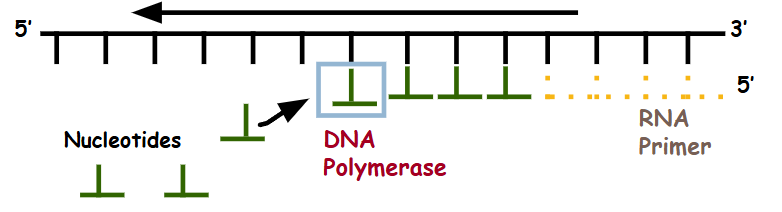
Synthesized discontinuously using short segments known as Okazaki Fragments due to opposing orientation of DNA strands (anti-parallel structure).
Each Okazaki fragment starts with a separate RNA primer laid down by RNA primase.
DNA Polymerase III adds nucleotides 5’ to 3’, moving away from the replication fork.

Completion of Lagging Strand
Exonuclease removes RNA primers, and DNA Polymerase I fills the gaps between Okazaki fragments with complementary DNA nucleotides.
DNA Ligase: seals the Okazaki fragments by forming phosphodiester bonds.