Q3 MATH
It is the distance of the point from the origin measured along the x-axis.
x-coordinate
It is the intersection of the point of the x-axis and y-axis.
origin
The ordered pair that represents a point is called.
coordinates
It is the point at which the graph of an equation crosses the x-axis.
x-intercept
It is the distance of the point from the origin measured along the y-axis.
y-coordinate
The line on the Cartesian plane that runs horizontally is called.
x-axis
It is defined as two number lines that are perpendicular to each other.
cartesian plane
It is the point at which the graph of an equation crosses the y-axis.
y-intercept
The line on the Cartesian plane that runs vertically is called.
y-axis
It is a set of ordered pairs of real numbers in which no two distinct ordered pairs have the same first component.
function
( x , y )
x - abscissa
y - ordinate
Slope of a Line I
Formula: m = y₂ - y₁
x₂ - x₁
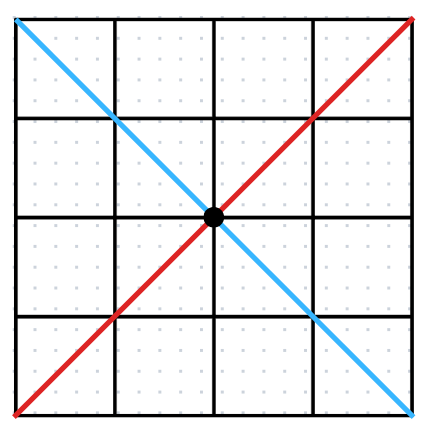
Why do we have the condition x2 ≠ x1?
If they are equal, then the denominator will be 0, and the final answer will be undefined.
How does the sign of the slope affect the graph?
If the graph of a line rises from left to right, the slope is positive.
If the graph of the line falls from left to right the slope is negative.
The Slope of a Line II
Formula: m = y₂ - y₁
x₂ - x₁
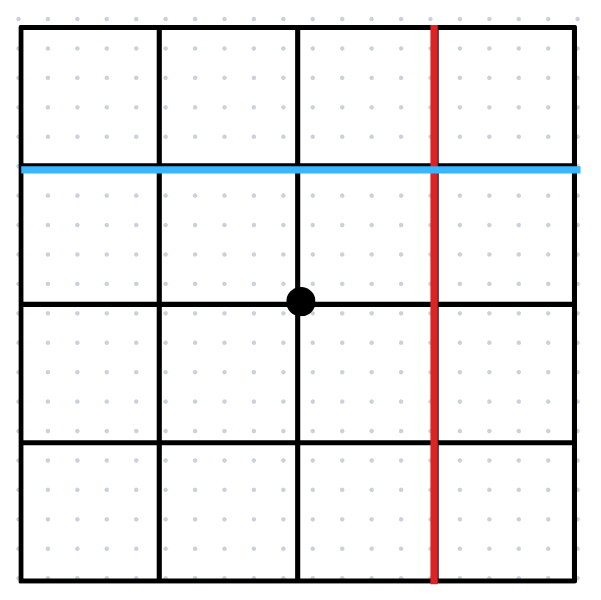
If the given points have identical y-coordinates, the slope of a horizontal line is 0.
If the given points have identical x-coordinates, the slope of a vertical line is undefined.
Slope - Intercept Form
Formula: y=mx+b
m = slope
b = y-intercept
Graph with the rise and run of the slope and start from the y-intercept
Rise means how many units you move up or down from point to point.
Run means how far left or right you move from point to point.
The Equation of a Line: The Slope-Intercept Method
Formula: y=mx+b
#1: Substitute the given slope for m and the given y-intercept for b
#2: Substitute the given slope for m and substitute the given point with x and y. Find the y-intercept and substitute the slope for m and the y-intercept for b
Slope-Intercept Form: y = mx + b (variable = coefficient variable + constant)
Standard Form: -x + y = b ([-]coefficient variable + variable = constant)
General Form: -x + y - b = 0 ([-]coefficient variable + variable [-]constant = 0)
The Equation of a Line: Two-Point Method
Formulas: m = y₂ - y₁ , y₂ - y₁ = m ( x₂ - x₁)
x₂ - x₁
#1: Find the slope
#2: Use any of the two points and substitute the x and y
Graphical Solution of a System of Linear Equations
I. Independent System
If the figure shows that the graph of the two equations intersect, the system is called the independent system.
If the two lines intersect → there is one solution which is the point of intersection.
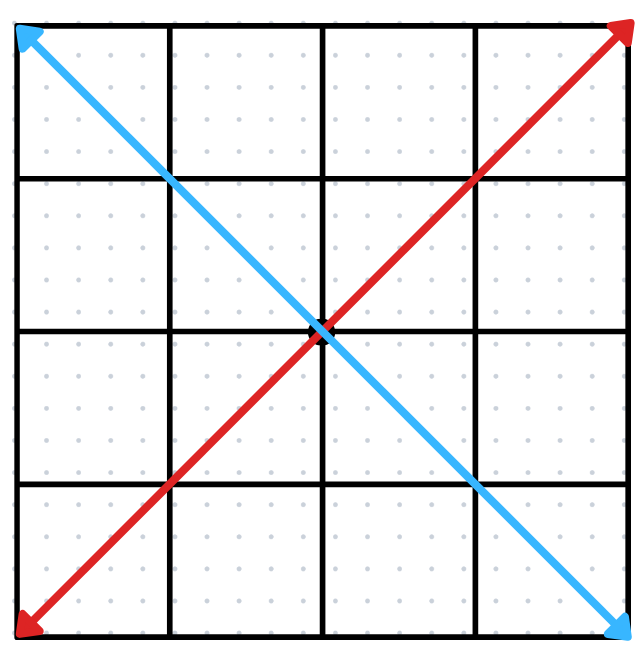
II. Inconsistent System
If the graphs of the two equations are parallel and the two lines will not intersect or cross each other, this system is called an inconsistent system.
If the two lines are parallel → there is no solution since the lines will not intersect.
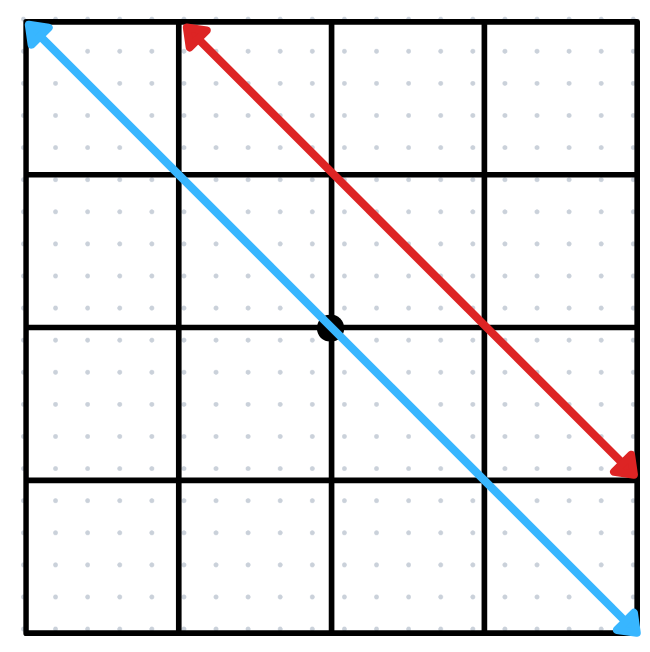
III. Dependent System
If the graphs of these equations are on the same line and every point on the common line is a solution, the system is what we call a dependent system.
If the two lines coincide → every point on the common line is a solution. Basically, there are an infinite number of solutions.
SOLUTION SETS:
Independent System: {(x , y)}
Inconsistent System: {( ∅ )}
Dependent System: {( -∞ , ∞ )}