Ch.1 The Basic Economic Problem
The Nature of the Economic Problem
What are Resources?
Inputs or factors of production needed to produce goods and services.
What is Scarcity?
Shortage of something (in this context, resources).
The unlimited wants of consumers and limited resources causes scarcity.
This is the basic economic problem. To effectively allocate the limited resources to satisfy the unlimited wants of consumers.
Applicable to consumers, producers, workers and the government in how efficiently they allocate the resources.
What are Economic goods?
- Goods that are scarce/limited in supply
- Thus, need to be produced with an economic cost or consumed with a price.
- Economic goods come with an opportunity cost. E.g. clothes, shoes, food, drinks, etc.
What are Free goods?
- Goods that have an abundant supply. (not scarce) E.g. natural resources such as air, sunlight.
However, in economics we deal with the allocation of economic goods that are scarce in nature.
The Factors of Production
Inputs or resources used to produce output/goods and services are known as the factors of production. They are: Land, Labor, Capital, and Enterprise.
Land: Includes all natural resources in an economy such as the surface of the earth, lakes, rivers, forests, etc. Rent is the reward or income received for land.
Labor: Includes all human resources in an economy. The skills, services and mental/physical efforts of workers. The reward for this effort is salary or wages.
Capital: Includes all man-made resources available in an economy. Goods that help to produce others goods are classified as capital goods. Such as, machinery, vehicles, equipment’s, etc. The reward received for capital goods is interest.
Enterprise: The ability to take a risk, startup and run a business. The person who does this and owns the business is known as entrepreneur. Entrepreneurs bring together all the factors of production efficiently and take the necessary risks as well as decision for the smooth running of the business. The reward for this is profit generated from the operations conducted in the firm.
 \n
\n With the help of all the inputs/factors of production the firm is able to produce a certain level of output/goods & services to satisfy the consumers.
All factors of production (FOP) are scarce in nature. This is why the basic economic problem exists and a choice needs to be made i.e. opportunity cost.
Opportunity Cost
- The giving up or sacrificing the next best alternative.
For example, government needs to decide whether to spend on the roads of the country or to build a hospital. Choosing roads makes hospital and the several patients that could have been treated an opportunity cost.
Why opportunity cost exists?
- Because of scarcity. Due to the limited resources available not all wants can be satisfied thus a choice needs to be made. Since resources have alternative uses, choice becomes paramount.
Production Possibility Curve (PPC)
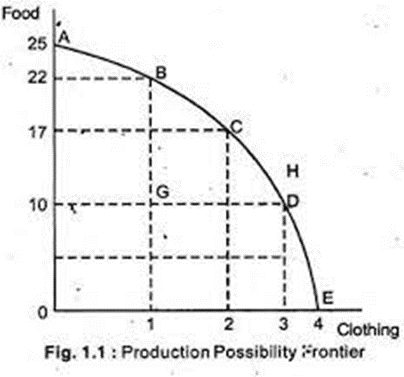
A curve that shows all the possible combinations of products that can be produced given the limited number of resources.
Highlights the tradeoffs and opportunity costs associated with the allocation of the scarce resources.
 \n .
\n .PPC is concave or downward sloping since increasing the production of one good will require reducing the production of the other.
All the points on the curve (A-E) show efficient allocation of resources.
Any production done below the PPC (point G) would mean underutilization of resources or inefficient allocation of resources as the economy is producing less than its capacity causing an inward shift.
Inward shifts may occur due to:
- Natural disasters
- Little to no investment in technology
- Running out of resources
This shall result in the economy shrinking.
- Any production above the PPC (point H) is unattainable and can only be achieved through an outward shift in the PPC.
Outward shifts can occur only if the economy:
- Discovers a new raw material, e.g. new oil fields
- Invests in latest technology and production methods to increase productivity.
- Training of employees that increases productivity.
- An outward shift in PPC, that is higher production possibility, will result in economic growth.
Calculating Opportunity Cost
- With the help of PPC, governments, individuals or firms can compute the opportunity cost to take effective decisions.
- Based on the above PPC, if a firm decides to increase the production of food from 10 to 17 the opportunity cost of this decision would 1 (as production of clothing falls from 3 to 2).