PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE & BOSTON MATRIX
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE shows the different stages that a product passes through over time and the sales that can be expected in each stage / The product life cycle describes the different stages a product goes through from its conception to its eventual decline in sales. there are five stages of the product life cycle.
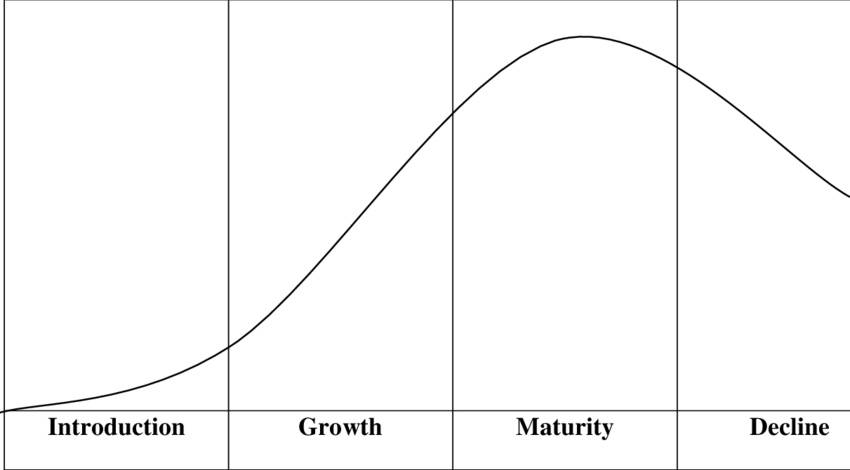
this helps businesses plan for the future.
DEVELOPMENT: during the development stage , the product is being researched and designed. suitable ideas are investigated , developed and tested. if an idea is considered worth following there may be a prototype made , then there will be a decision regarding whether to launch the product or not.
- The focus is on designing and developing the product
- The business usually incurs high costs for research and development, market research, and product testing
due to this ,
- Cash flow is usually negative during this stage, as the company is investing heavily in the product without generating any revenue
- The marketing strategy during this stage is focused on creating awareness , though its likely that there wont be any promotion
INTRODUCTION: the start of this stage is when the product is launched , as the product is new , the initial sales are likely to be slow and costs will be incurred as the product is launched. it may be necessary to build a new production line and the business will have to meet different distribution and promotion costs. its likely that the product will not be profitable initially.
- Characterised by slow sales growth as the product is still new and unknown to most consumers
due to this ,
- Cash flow is usually negative as the business usually incurs high costs for promotion, advertising and distribution
- Marketing efforts are focused on creating awareness and generating interest in the product
GROWTH: once the product is established and consumers are aware of it , sales is likely to increase rapidly as new customers will begin to buy the product and older customers will repeat purchase. unit costs may fall as production increases to meet demand and the product may become profitable at this point , but due to this competition may arise which could possibly slow down sales.
- The product enters this stage when sales begin to increase rapidly
- The business focus shifts to building market share and increasing production to meet the growing demand
due to this ,
- Cash flow usually turns positive during this stage as sales revenue increases and costs are spread out over a larger volume of production
- The marketing strategy is to differentiate the product from its competitors and build brand loyalty
MATURITY: at this point , the growth of sales is going to end , or grow at a much slower rate if there is any growth at all. the product will have become established and will usually have a stable market share at this point so sales will have well reached their highest point. as more firms will enter the market , it will become saturated and some businesses will leave the market. some businesses may start to use extension strategies.
- Characterised by slowing sales growth as the product reaches its peak in terms of market penetration
due to this ,
- Cash flow is usually positive during this stage as sales revenue continues to come in and costs are reduced through economies of scale and efficient production processes
- The marketing strategy aims to maintain market share and increase profitability by cutting costs and finding new markets
DECLINE: for most products , sales will usually decline due to changing customer tastes , new technology or introduction of new products. hence, the product will lose its appeal to customers. at this stage the product may be discontinued.
- Starts when sales begin to decline as the product becomes obsolete or is replaced by newer products
- The business focus shifts to managing the product's decline and reducing costs
due to this ,
- Cash flow usually turns negative as sales revenue declines and costs associated with the product's decline increase
- The marketing strategy may involve discontinuing the product, reducing its price to clear inventory, or finding new uses for the product
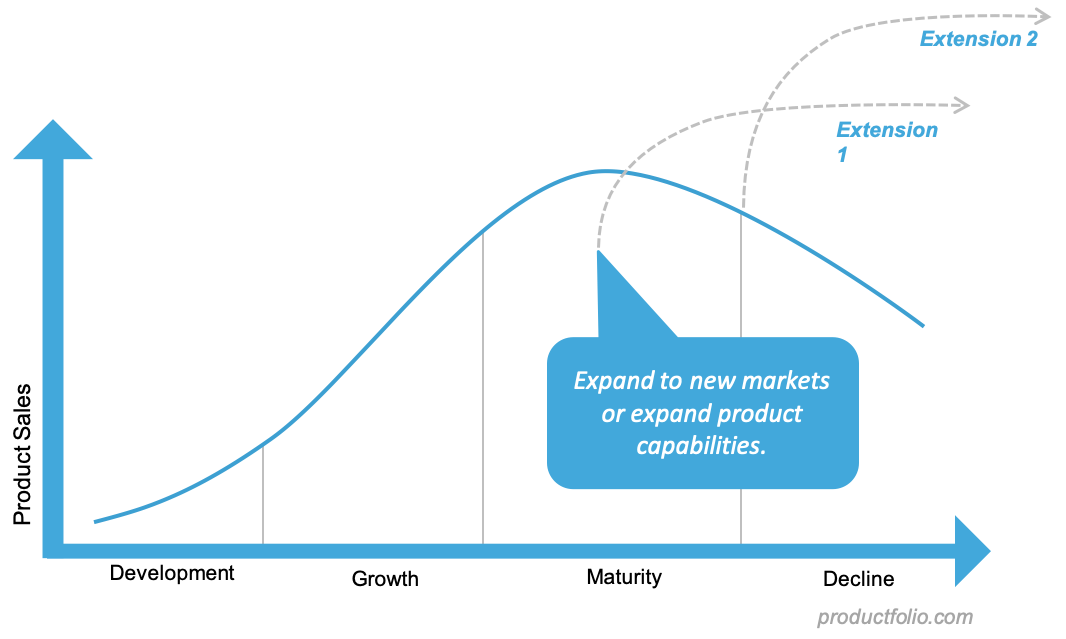
EXTENSION STRATEGIES:
product adjustments
promotion
lower price
enter new market
The purpose of extension strategies is to prolong the life cycle of a product by maintaining or increasing sales after it reaches the maturity or decline stage. Businesses use these strategies to prevent revenue loss, maximize profits, and delay the introduction of replacement products
BOSTON MATRIX:
the boston consulting group matrix ( BCG ) or BOSTON MATRIX is a marketing tool used to examine an organisations product portfolio. there are two dimensions to the matrix:
market share: how strong is the product in the market? is it the leader? or is it one of the businesses that follow the leader? market share = sales of a business / total sales in a market x 100
market growth: how fast is the market for the product growing? is it declining or is it expanding? sales of a product is likely to be higher in a growing market compared to a mature or declining market.
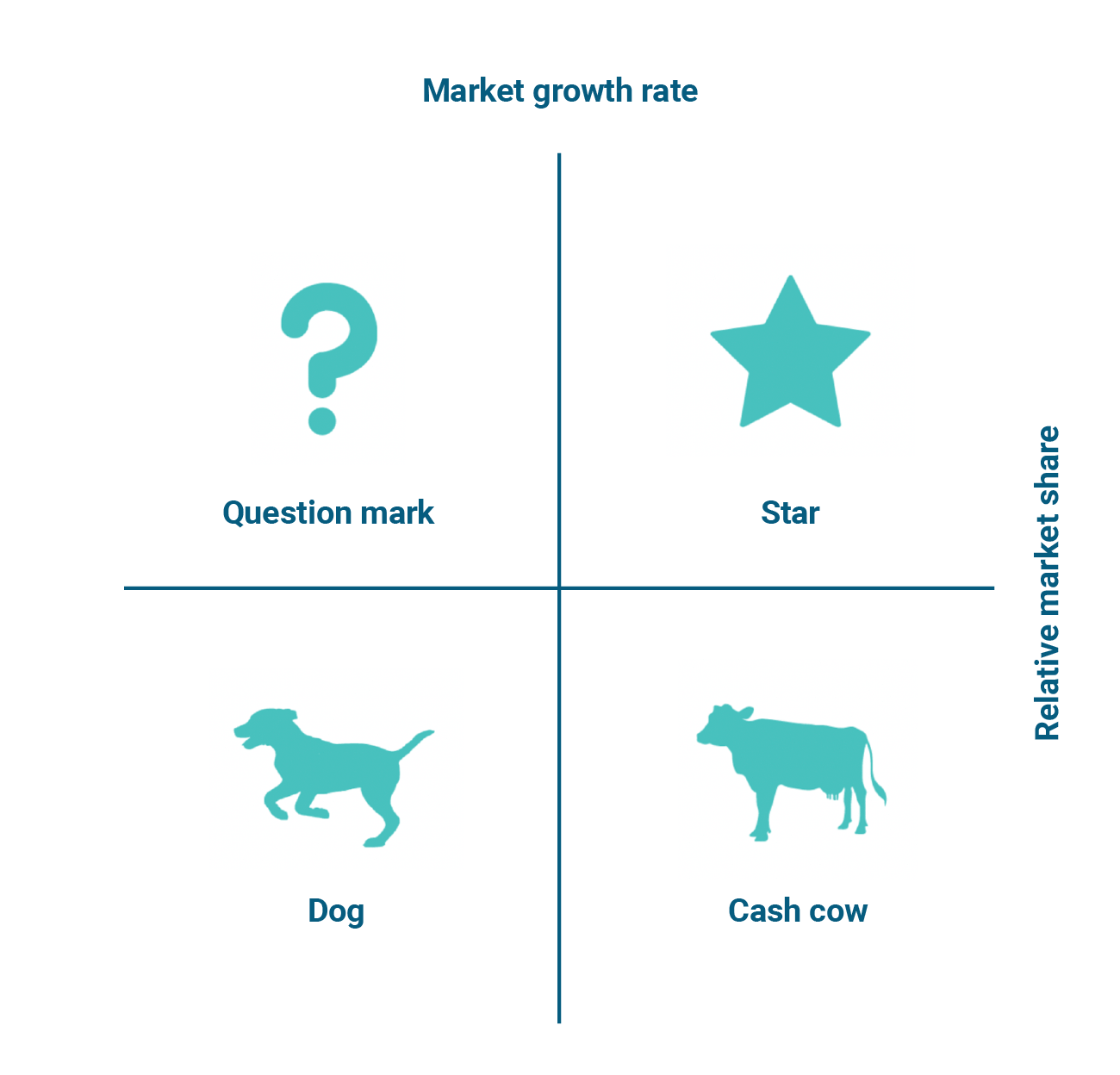
QUESTION MARKS: products that have a low market share in a high growth market, the aim is to convert them into stars. These products have the potential to become stars if the company invests in their development. their features :
high market growth
low market share
introduction stage in PLC
drain cash flow
- If the investment does not result in growing the business may discontinue the product
- Marketing efforts focus on increasing their market share and brand recognition
STARS: products with a high market growth in a relatively high market share. they are valuable to businesses as the product is in a strong position due to high market share , and the business will have the opportunity to exploit high market growth. a star is generally very profitable but the business will still need to invest in the product to cope with the growing market. features:
high market share
high market growth
growth stage in PLC
can be turned into cash cow
- They generate significant positive cash flow and have the potential for continued growth
- Marketing efforts focus on building brand recognition, increasing market share, and maintaining profitability
- Stars are valuable assets and the business should focus on maximising their potential
CASH COWS: product with a relatively high market share in a market with weak growth. it will positioned in the market and is likely to be profitable but there ie less scope for increasing sales in the future. cash cows have a strong and positive net cash flow. features:
high market share
maturity stage in PLC
main generator of cash
- They generate significant positive cash flow but have low growth potential
- The business invests minimal resources in cash cows as they are seen as stable sources of income
- Marketing efforts focus on maintaining their market share and profitability
- Cash cows are valuable assets and can be used to fund the development of new products
DOGS: these are products with low market share in a low market growth , they have poor prospects for future sales and profits , they may generate some positive net cash flow as they may earn little profit. But overall , they drain cash from the organisation and in some cases they may be discontinued. features:
low market growth
low market share
decline stage in PLC
divest to prevent further losses
- They generate little revenue for the company and have no growth potential
- Businesses often move away (divest) from these to focus on more profitable products
- Marketing efforts for dog products are minimal or zero