CH 01 : Binary Systems And Hexadecimal
The Binary System
==Binary System==: A system of ones(1) and zeroes(0) which is the building block in a computer.
- Computers have millions of tiny switches which can either be in an ON or OFF position.
- 1 represents ON and 0 represents OFF position of a switch.
- Different combinations of these 1s and 0s hold different meanings to a computer.
Binary is a number system based on the number ^^2,^^ i.e it counts in multiples of 2. Like 2,4,8,16 and so on.

Example use of Binary:
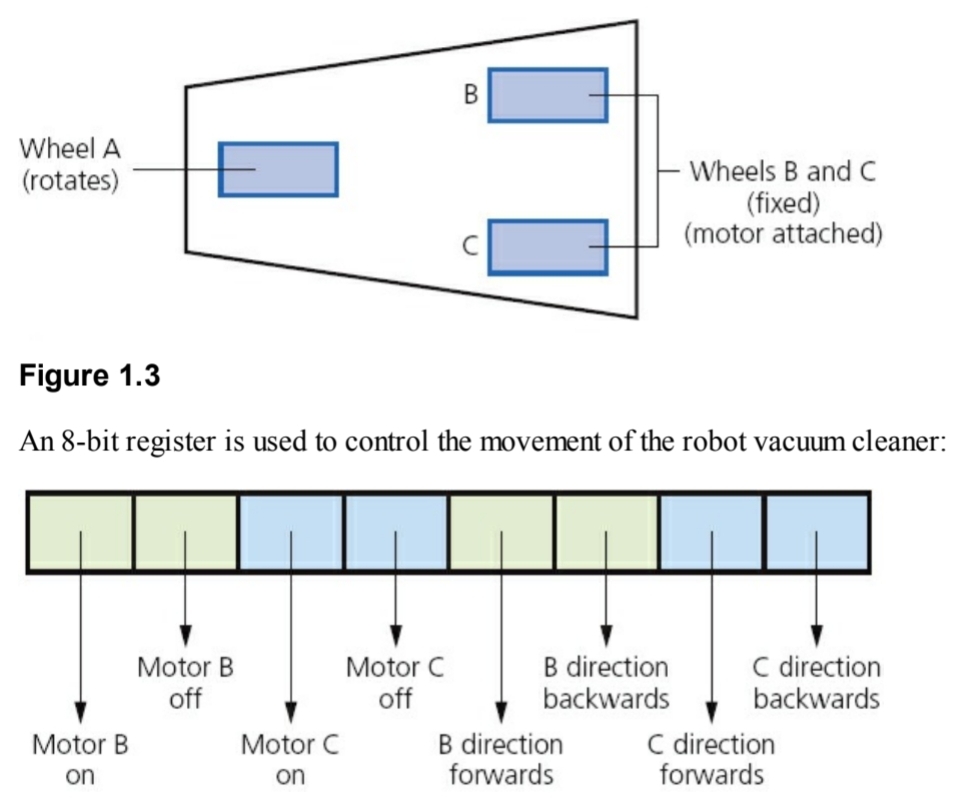
- If the register contains 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 this means ‘motor B is ON and motor C is ON and both motors are turning to produce FORWARDS motion’. Effectively, the vacuum cleaner is moving forwards.
Conversions Between Binary And Denary
- ==Denary==: A number system with a base of ^^10.^^
- While converting a Binary value to Denary, always begin from the ^^right hand side.^^
- Substitute the values with ^^powers^^ of 2 , starting from 2^0
- Add all the values in places of 1s only for the denary value. Using 00101101 as an example:
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2^7 = 128 | 2^6 = 64 | 2^5 = 32 | 2^4 = 16 | 2^3 = 8 | 2^2 = 4 | 2^1 = 2 | 2^0 = 1 |
32 + 8 + 4 + 1 = 45
In order to convert a Denary number to a Binary value, ^^repetitive division^^ is used. Using 107 as an example:

Measurement Of The Size Of Computer Memories
- ==Bit==: One Binary digit.
- ==Byte==: 8 Bits make up a Byte.
- Some computers also use larger Bytes but their Bits are always in multiples of 8.
- Different memory sizes:
| Name Of Memory Size | Number Of Bits | Number Of Bytes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 Kilobyte (KB) | 2^10 | 1024 |
| 1 Megabyte (MB) | 2^20 | 1024^2 |
| 1 Gigabyte (GB) | 2^30 | 1024^3 |
| 1 Terabyte (TB) | 2^40 | 1024^4 |
| 1 Petabyte (PB) | 2^50 | 1024^5 |
The Hexadecimal System
- ==Hexadecimal System==: A number system with base ^^16^^, thus every digit is represented by 16 values. Its also called ==‘Hex’.==
- The table for ^^equal^^ values of Binary, Denary and Hex:
| Binary | Denary | Hexadecimal |
|---|---|---|
| 0000 | 0 | 0 |
| 0001 | 1 | 1 |
| 0010 | 2 | 2 |
| 0011 | 3 | 3 |
| 0100 | 4 | 4 |
| 0101 | 5 | 5 |
| 0110 | 6 | 6 |
| 011q | 7 | 7 |
| 1000 | 8 | 8 |
| 1001 | 9 | 9 |
| 1010 | 10 | A |
| 1011 | 11 | B |
| 1100 | 12 | C |
| 1101 | 13 | D |
| 1110 | 14 | E |
| 1111 | 15 | F |
Conversions Between Binary And Hexadecimal
- Converting from Binary to Hexadecimal is a fairly easy process.
- ^^Starting from the right^^ and moving left, split the binary number into groups of ^^4 bits^^. If the last group has less than 4 bits, then simply fill in with 0s from the left.
- Take each group of 4 bits and convert it into the ^^equivalent^^ hexadecimal digit using the table.
- To convert from Hex to Binary, simply look at the corresponding values in the table.
Conversions Between Hexadecimal And Denary
- To convert from Hex to Denary, use the same method as when converting from Binary to Denary, except using the ^^powers^^ of 16 instead of 2 this time. Add the total to get the Denary value.
- In conversion from Denary to Hex, yet again a familiar method is used.
- Repeatedly divide the number by 16.
- Read the remainders from the ^^bottom^^.
- Replace two digit numbers with Hex values.
Uses Of Hexadecimal System
- ==Memory Dumps==: The contents from the computer memory which are being sent to a printer or monitor etc.
- Hex is used as it takes ^^lesser space^^ than Binary and is ^^easier^^ to use.
- It is also used to ^^trace errors^^ in softwares and programs.
- It can represent the ^^location^^ of contents in computer memory.
- ==Hyper Text Markup Language (HTML):== A markup language used in developing web pages.
- Hex values are used to store colours of text.
- ==Media Access Control (MAC)==: A unique address given to a device to identify it on the Internet.
- It refers to the ^^Network Interface Card (NIC)^^ of the device.
- Made of 48 Bits shown as 6 groups of Hex Digits.
- Form: ^^NN – NN – NN – DD – DD – DD or NN:NN:NN:DD:DD:DD^^
- The first half is identity number of manufacturer and second half is serial number of the device.
- Two types of MAC addresses, ==Universally Administered MAC Address (UAA)== and ==Locally Administered MAC Address (LAA).==
- ==UAA:== Common and set by the manufacturer at the factory. Very rarely changed.
- ==LAA==: Set by an organisation when a change of MAC address may be needed. The possible reasons for this might be:
- Certain software used on mainframe systems needing all the MAC addresses of devices to fall into a ^^strict format.^^
- To bypass a MAC address ^^filter^^ on a router or a firewall for security reasons.
- To get past certain types of network ^^restrictions^^.
- Web Addresses:
- ==ASCII Code==: A code written in Hex and given to each character on a keyboard.
- Used in representing web addresses in URLs.
- Assembly and Machine Code: True codes are written in Binary but as it is more ^^error prone, time consuming and complicated,^^ Hexadecimal is used by programmers.