Sympathetic Nervous System
Sympathetic nervous system: subdivision of the autonomic nervous system
- ‘fight or flight’ system
- diffuse activation
<<Distribution of Sympathetic Nervous System<<
- Cervical division
- Cardio-pulmonary division
- Splanchnic division
- Somatic division
{{Cervical Division{{
%%arises from:%% lateral horn cells of T1, T2
%%ends:%% 1st superior cervical ganglion
- Eye
- Salivary glands
- Skin
- Cerebral blood vessels
{{Cardio-Pulmonary Division{{
%%arises from:%% lateral horn cells of T1, T2, T3, T4
%%ends:%% 3rd superior cervical ganglion and upper 4 thoracic ganglia
- Heart
- Lungs
{{Splanchnic Division{{
%%arises from%%: lateral horn cells of T5-L3
%%ends:%% collateral ganglia
- Greater splanchnic nerve (T5 - T9 and rely celiac ganglia):
- wall of GIT
- sphincters
- liver
- spleen
- adipose tissue
- adrenal medulla
- Lesser splanchnic nerve (L1 - L3, rely inferior mesenteric ganglia)(small splanchnic nerve arises from T10 - T12, rely in superior mesenteric ganglia):
- rectum
- urinary bladder
- sex organs
{{Somatic Division{{
%%arises from:%% lateral horn cells of T4 - L8 (upper limbs), T10- L12 (lower limbs)
%%relay in:%% the sympathetic chain
- Skin
- blood vessels
- sweat
- hair
- Skeletal muscles
- blood vessels
- chemical reactions
<<Sympathetic Effect on Organs<<
| }}Organ}} | }}Effect}} |
|---|---|
| Eye | mydriasis, contraction of tarsal muscle and elevation of the lids, relaxation of ciliary muscles for far vision |
| Salivary glands | increase secretion that is rich in proteins (enzymes) (viscus) |
| Skin | contraction of arrector pili muscles, pale skin, increase sweating |
| Blood vessels | vasoconstriction in all vessels, except skeletal muscles and heart |
| Heart | Increase all cardiac properties:contractility, rate, conductivity, excitability, increase blood pressure |
| Sex organs | Male: ejaculation, inhibition of erection.Female: vary according to hormones and menstrual cycle |
|---|---|
| Renal | Decrease micturition and urine formation |
| GIT | Decrease mobility, contraction of pyloric sphincter, decrease defecation, increase glycogenolysis in liver, release epinephrine and norepinephrine from adrenal medulla, contraction of spleen and release of red blood cells |
| Lungs | Broncho-dilation, inhibition of mucus secretion |
<<Organs supplied by Sympathetic Fibers Only<<
- Ventricles
- Skin structures
- Skeletal blood vessels
- Dilator pupillary muscles
- Adrenal medulla
<<Receptors<<
==α1 (stimulatory):== stimulation of sphincters.
==α2 (inhibitory):== relaxation of GIT wall.
==β1 (stimulatory):== increase heart rate.
==β2 (inhibitory):== relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle (bronchial dilation)
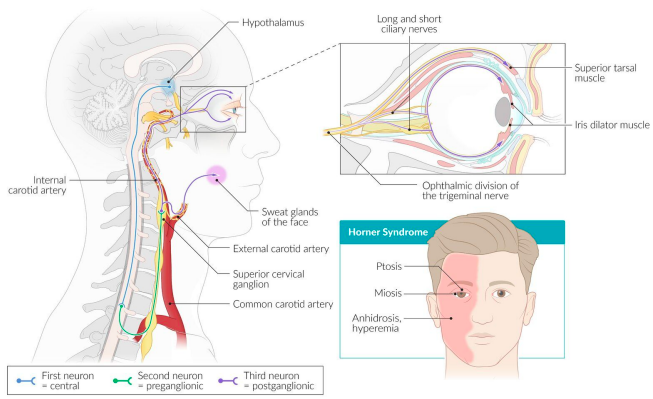
<<Horner’s Syndrome<<
Horner’s syndrome: results from an interruption of the sympathetic nerve supply to the eye (cervical sympathectomy) and is characterized by the classical triad of miosis (i.e. constricted pupil), partial ptosis and loss of hemifacial sweating (i.e. anhidrosis)
%%Can be caused by:%%
lesion of primary neuron
brainstem stroke or tumor or syrinx of the pre-ganglionic neuron
trauma to the brachial plexus
tumors or infection of the lung apex