Macromolecules
Organic Molecules
- What is an organic molecule
- Process that builds polymers- Dehydration synthesis
- Process that breaks down monomers- Hydrolysis
Carbohydrates
- C,H, O (in a 1:2:1 ratio)
- Structure/Function: provides both energy and structure to many organisms
- Monosaccharides (Glucose, Fructose, Galactose)
- Disaccharides (Sucrose, Lactose, Maltose)
- Polysaccharides (Starch, Cellulose, Glycogen)
Lipids
- Made of: glycerol backbone, 2 fatty acid tails (hydrophobic), and a phosphate group (hydrophilic).
- C,H,O(No ratio)
- Phospholipid
- Triglycerides
- Steroids
Proteins
Structure of amino acids : 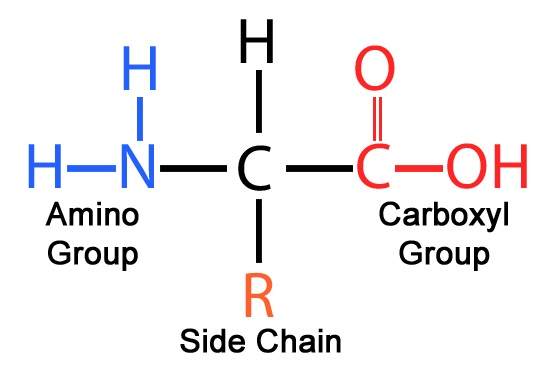
An R-Group is a side chain attached to the α-carbon of all amino acids. It decides the chemical versatility of the amino acid. For example, some R-Groups carry a charge, creating a polar molecule. Some R-groups are hydrophobic or hydrophillic.
Peptide Bond: 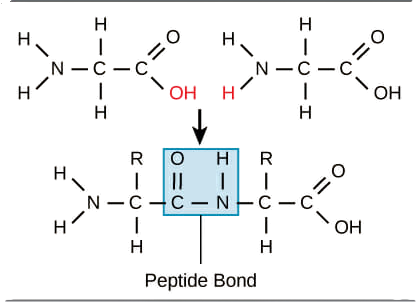
Protein Folding
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Quaternary Structure: 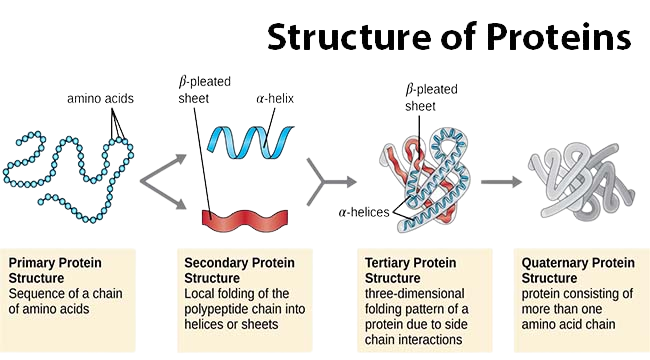
Denaturation happens when there is a change in pH and temperature. Denaturation is the unfolding or breaking up of a protein, modifying its standard three-dimensional structure.
Enzymatics
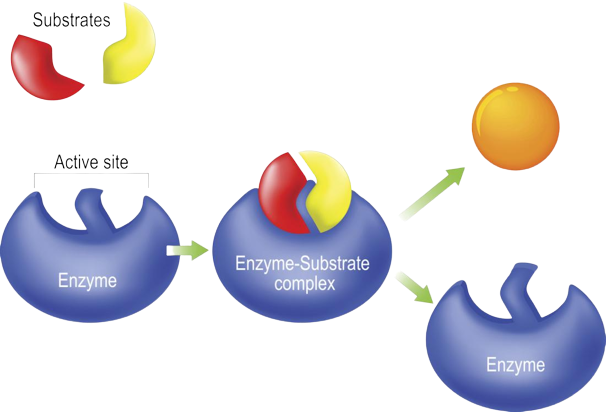
Substrate**:** a molecule that an enzyme reacts with.
Active Site**:** the part of an enzyme to which substrates bind.
Enzyme**:** proteins that help speed up metabolism.
Enyme-Substrate Complex**:** a temporary molecule formed when an enzyme comes into perfect contact with its substrate.
Nucleic Acids
Structure/Function
Building blocks
DNA vs. RNA
Base pairing