Inventory control
WHAT IS INVENTORY?
things such as raw materials , semi finished goods and components make up the inventory of a business. these are used to make products which are then sold to customers. some businesses also hold inventories of their finished goods before they are sold to customers.
THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF INVENTORIES :
raw materials and components : purchased from suppliers before production. delays in production can be avoided if materials are already present rather than waiting for new stock to be delivered
work in progress : partly finished goods that have to go through a few more steps in the production line to be completed
finished goods : goods that are fully ready to be sold. they are mainly kept to cope with sudden changes in demand like an unexpected rise in demand. firms will be able to meet urgent orders by supplying from their inventory holdings
FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE INVENTORY LEVELS :
demand : businesses need to hold sufficient stocks to be able to satisfy the usual levels of demand , they also need to have enough inventory to cover the growth of sales and unexpected demand. stocks that are held to satisfy sudden increase in demand are called ‘buffer stocks’
buffer stocks ; the minimum stocks that should be held to ensure that production could still take place should a delay in delivery occur or production rates increase
stockpile goods : some businesses will build up inventory for certain times during the year so they have sufficient supplies later or in case of emergencies. For example; toy manufacturers will build up inventories of toys as they know demand will rise around christmas
costs of inventory holding : if inventory is expensive to hold , then only a small amount will be held and if its not costly to keep inventory , its likely that the business will hold higher levels of inventory if needed
amount of working capital available : a business that is short on working capital may not be able to purchase additional inventory even when needed. in addition to this, while the money for the inventory is paid, a business cannot generate revenue from it until they are selling the inventory
the type of inventory : if the good is perishable , its unlikely that the business will hold large amounts of inventory as the goods will end up being wasted if held too long. its possible that stocks can go out of date when replaced with new models , too.
lead time : the longer the lead time , the higher the need for a minimum level of inventory
lead time : the normal time taken between ordering new stocks and their delivery
STOCK CONTROL DIAGRAM :
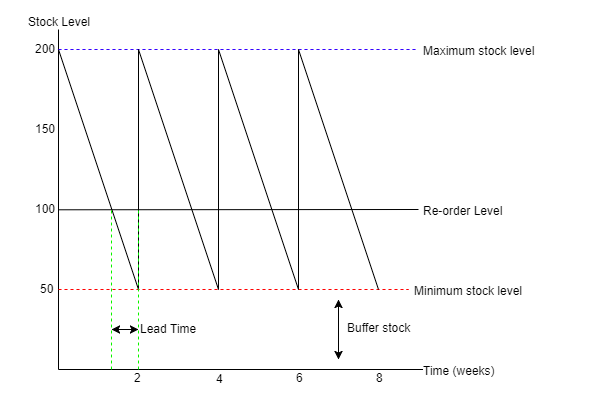
re-order quantity : the amount of stock ordered when a new order is placed
re-order level : the level of stock currently held when a new order is placed
BUFFER STOCKS :
this is an emergency stock held just in case there is a shortage. for example , if there is a sudden increase in demand , in this case , the business will take out of the 50 stock they had has buffer stock. another reason may be due to delivery taking longer than it initially was, so the new inventory will arrive late , and if the business doesnt have buffer stock they wont be able to sell goods until the order has arrived. thus , by holding buffer stock they can sell goods from there until the new order arrives. as a result , they will not miss out on sales opportunity nor will customers be dissatisfied.
RESULTS OF POOR INVENTORY CONTROL :
FOR HOLDING TOO MUCH INVENTORY ;
storage : inventory of raw materials , components and finished goods hold and occupy space in buildings. there will also be security costs , for example , and rent too which will increase the costs to the business
opportunity costs : capital tied up to inventory earns no rewards , the money used to purchase inventory could have been put to other uses such as buying new machinery or promoting their products
spoilage costs : the quality of some inventory may deteriorate over time , such as perishable goods and some goods may go out of date or become obsolete
administrative costs : costs include the cost of placing and processing orders and recording the inventories
unsold inventories : if demand suddenly falls , the business will have unsold goods that will eventually go to waste
FOR HOLDING TOO LITTLE INVENTORY ;
there may be sudden increase in demand so the business will not have sufficient goods to sell , as a result , customers may be lost if they are let down too often
if inventory deliveries are delayed , the firm may have to stop production because they dont have backup goods to sell or produce with ( raw materials ) , this will lead to inactive labour and machinery, while the labours still have to be paid regardless of whether they are working or not
holding too little inventory may mean frequent orders have to be placed whilst trying to produce goods , this will raise total ordering costs because they will lose out on the discounts of bulk buying
JUST IN TIME :
just in time is a stock control method that aims to avoid holding stocks by requiring supplies to arrive just as they are needed in production and completed products are produced to order. this is an important part of lean production and kaizen.
ADVANTAGES ;
improves cash flow as money is not tied up in stock
reduces wastage as goods arent made if they’re not ordered for
more factory space available for productive use
costs of stock holding are reduced
DISADVANTAGES ;
too much reliance on the reliability and flexibility of suppliers
increased ordering and administration cost
advantage of bulk buying may be lost
at risk of break in supply
difficult to cope with sharp increases in demand
WAYS TO MINIMISE WASTE :
if goods are perishable they must be placed in chilled storage
businesses should be conscientious when forecasting demand patterns for perishable goods
a suitable stock rotation method should be adopted , with fifo its better to use for perishable goods
computerised systems can be programmed to automatically order inventory when the re-order level is reached
goods should be transported rapidly if they are perishable
LEAN PRODUCTION :
lean production is producing goods and services with the minimum of wasted resources while maintaining high quality. it aims to use fewer resources in production.
kaizen , cell production , flexible manufacturing , teamworking and multiskilling are used to minimise waste. they are likely to have a competitive advantage as a reduction in waste and resources will lead to lower production costs.
it helps with :
raising productivity
reducing costs and cutting lead time
lowers the number of faulty products
as a result , the business will be able to charge lower prices with better quality
 Knowt
Knowt