Infor Chem Test Deux
Energy is considered a property of matter—the ability to perform work or produce heat.
Elementary substances contain atoms of a single element, e.g., Mg, while chemical compounds contain atoms of two or more elements bound together by chemical forces, e.g., MgS.
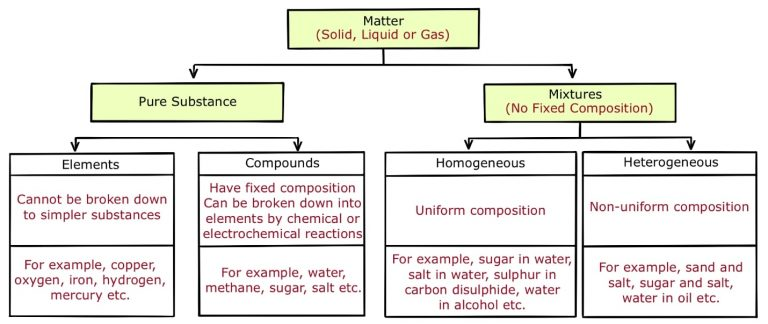
Mixtures contain more than one element or compound in no fixed ratio, which are not chemically bonded and so can be separated by physical methods.
Homogeneous: particles are evenly distributed; eg air is a mixture of nitrogen (20%) and oxygen (80%).
Heterogenous: not evenly distributed; eg mixture of solids; eg natural milk has the cream rise to the top.
Each component of a mixture maintains its physical + chemical property, unlike water.
The Four Techniques
The solids can be separated if we understand their intermolecular forces.
Filtration
A mixture of sand + sugar is placed into water; the solution can then be poured through a filter paper placed inside a funnel. Large sand particles will not pass through & remain on the filter paper; sand will dry. Sugar can be obtained by evaporating the water from the filter (solution which passed through the filter paper).
Destillation
Used to separate miscible liquids (two liquids that seem to be completely mixed) with different boiling points. Ethanol has a lower boiling point and will evapourate first once the vapours rise up a cooling column (which cools the rising vapours, causing water to condense + flow back while ethanol, which is more volatile (turns to vapour quicker), continues to upward.)
Paper Chromatography
Used by separating substances, often used for analysing ink, dyes, or colours. A small spot of the mixture (dye,ink) is placed on a strip of filter paper. The paper is then placed in a container with a solvent (water or alcohol), but only the bottom edge of the paper touches the solvent, not the spot. The solvent moves up the paper, carrying components of the mixture with it. Different substances (like inks) move at different speeds depending on their solubility + interaction with the paper. This shows that more soluble substances are further ahead while less soluble substances stay closer to the starting point. Stationary phase is the filter paper itself, while mobile phase is the solvent moving up the paper by capillary actions.
Crystallisation + dissolution
Crystallisation is when dissolved particles reform into a solid; substances are dissolved in a solvent, and when conditions change (e.g., cooling), the dissolved substances form solid crystals.
Dissolution is when solute particles disperse into a solvent, breaking their bonds or interactions and forming a uniform solution. Basically, it’s the process in which a solute dissolves in a substance, forming a solution, e.g., NaCl + H2O.
Solid
Fixed volume, fixed shape, cannot be be compressed, attraction between particles is strong, do not move around.
Liquids
Fixed volume, no fixed shape, cannot be compressed, attraction between particles weaker than solid, slower than gas.
Gas
No fixed volume, no fixed shape, can be compressed, attraction is negligible, particles vibrate, rotate, and move faster than liquid.
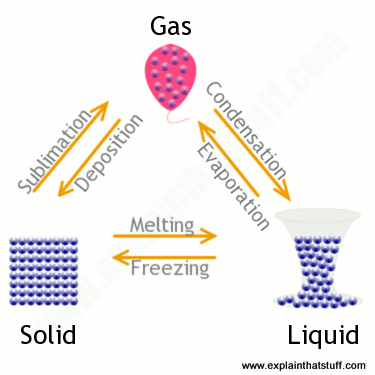
When a substance changes from a more condensed state to a less condensed state, energy is absorbed by the particles from the surroundings, e.g., solid to gas or liquid to gas; this is an endothermic process.
When a substance changes from less condensed to more, the particles will lose energy to the surroundings,, and for a molecular substance the intermolecular forces become stronger, eg gas to liquid, solid or liquid to solid, this is an exothermic process.
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of particles. When water is heated, the temperature stays constant because the energy is being used to break the intermolecular forces holding the ice structure, not to raise the temperature. When vaporising or boiling, the temperature stays constant because the energy is used to overcome the liquid water molecules together.
0 celsius = 273.15 K. Absolute zero implies that at this temperature the particles cannot transfer any kinetic energy on collisions. 0 K is - 273.15 celsius.