A&P Notes (Exam 1)
Chapter 1
Introduction to the field
-Anatomy Studies structures
→ Gross Anatomy
→ Microscopic anatomy
→ Regional Anatomy: examining all the structures within a specific area of the body, such as the ankle and foot, to understand how they interact and function together
→ Systemic Anatomy (this course)
-Physiology studies the chemistry of the human body, what things do in the body (combined completes a full understanding of the human bodies)
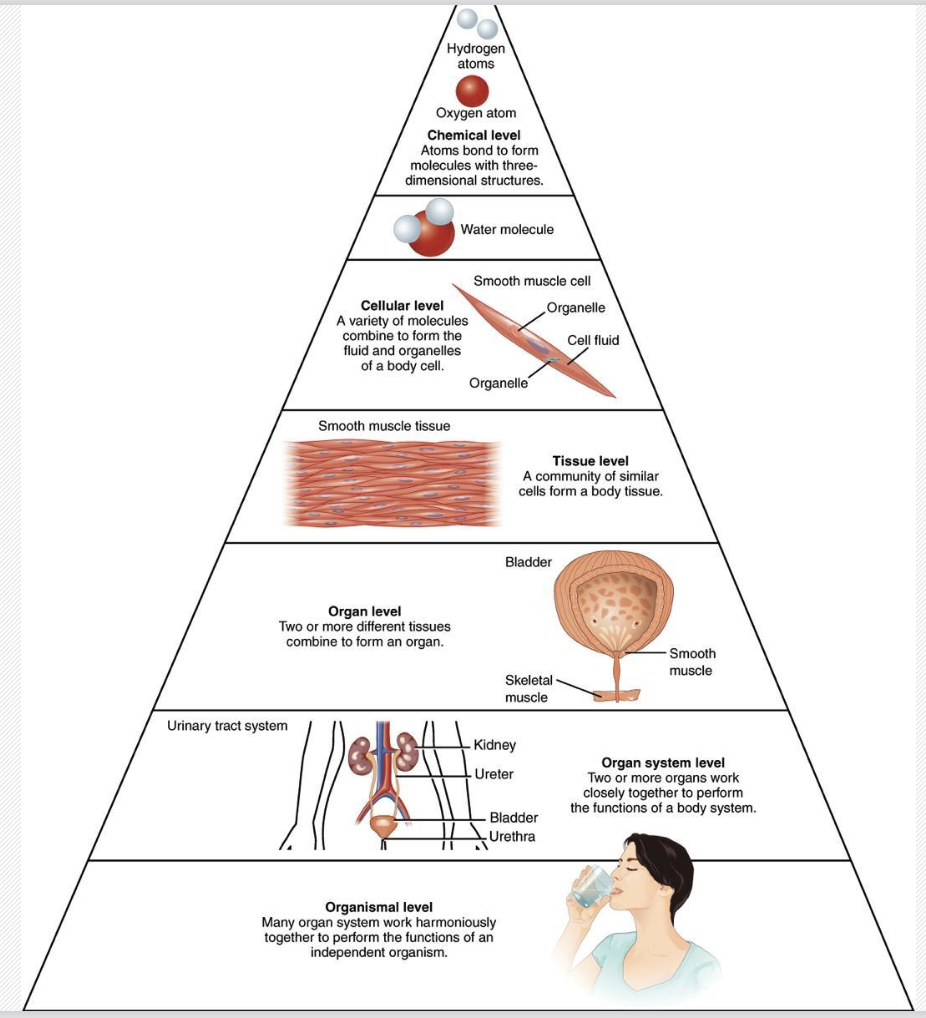
Levels of Organization
-Chemical Level: smallest level, atoms and molecules
-Cellular Level: unit of life, Cells
-Tissue Level: Groups of similar cells that work together
-Organ Level: Tissues working together
-Organ System Level: organs perform coordinated functions to meet demands of the body, digestive system
-Organismal level: human body as a whole (animal, any living thing)
→ all levels are connected and stacking, one makes the other from top to bottom
Organ Systems
-integumentary system
-Skeletal system
-Muscle system
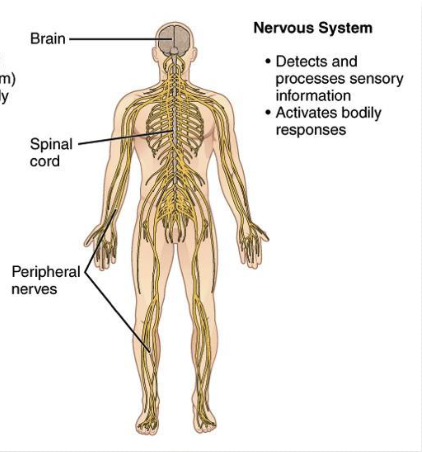
-Nervous system
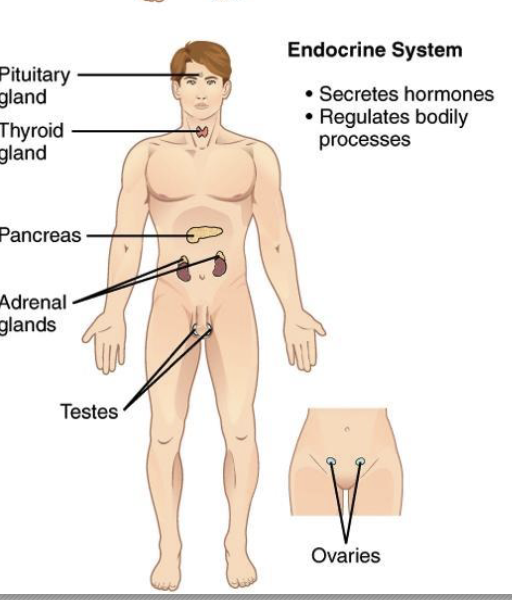
-endocrine system:
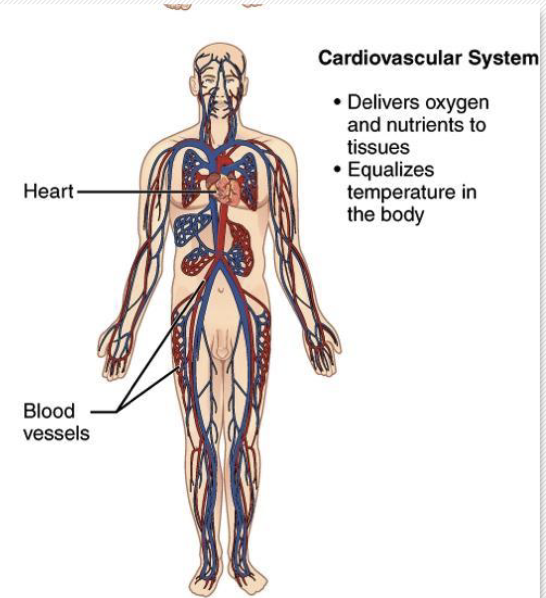
-Cardiovascular system:
Anatomical Position
-hands are supinated (facing upward, palms up)
-left and right side are based on patients position
-Prone: facing forwards (standard position)
-Supine: facing backwards (aka see your spine)
Regional or directional terms
-describing relative locations (rough area)
-Axial Region: Head neck and trunk
-Appendicular Region: Limbs and girdles
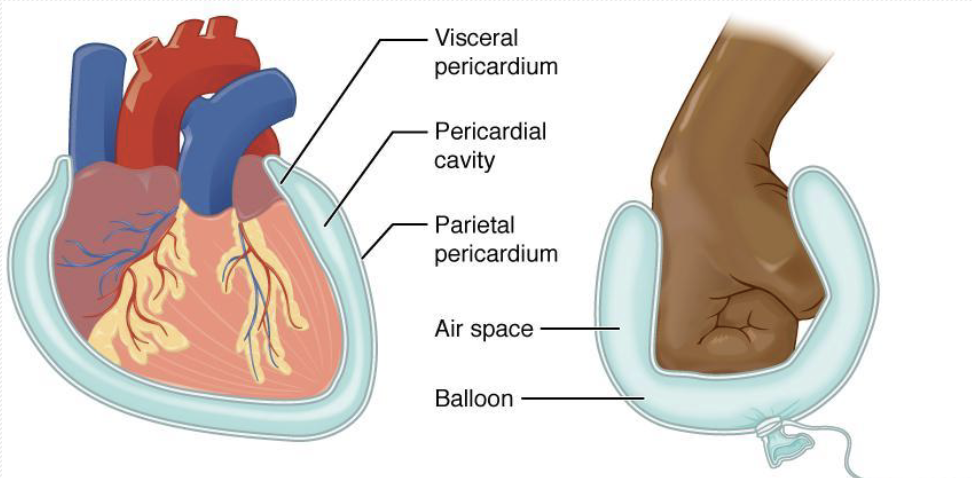
Serous Membranes
-Covers Walls and organs in thoracic cavity
→ parietal (lines wall of cavity) vs. Visceral layer (lines outside or organ itself)
→ space between filled with fluid to prevent friction between organs and wall
-pleura cavity: surrounds lungs
-Pericardium cavity: pericardial activity, heart
-Peritoneum cavity:
Organization
-trillions of cells all stacking on one another
→ atoms→ molecules→cells→tissues→organs→systems
-multiple compartments
-leads to metabolism
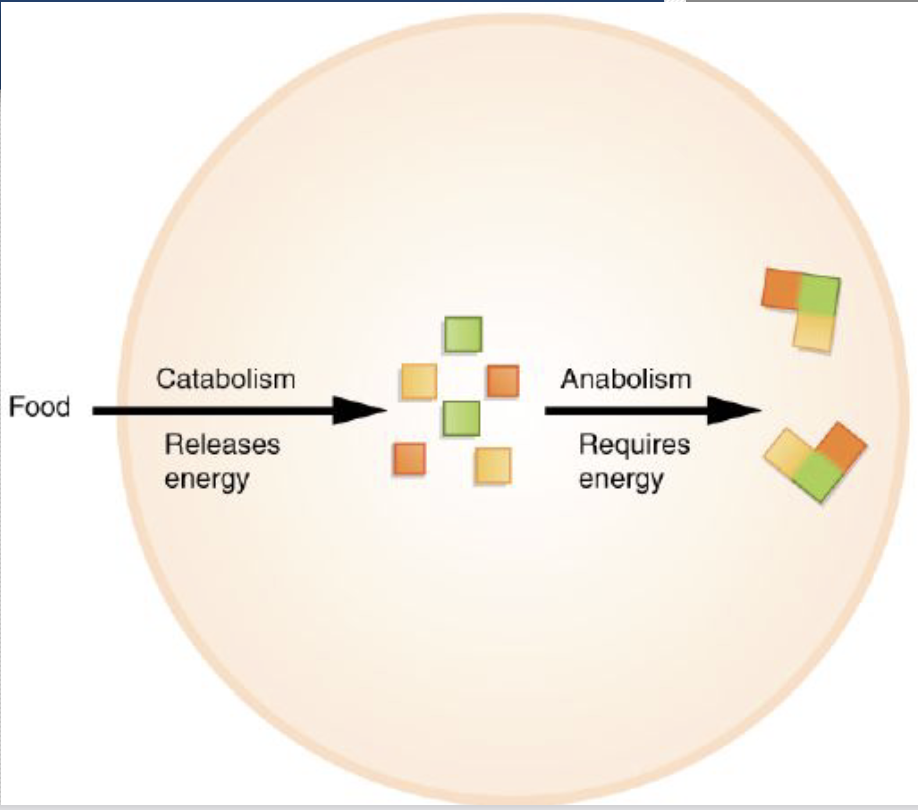
Metabolism
-first law of thermodynamics: energy cannot be created or destroyed
-anabolism(small/ similar molecules combined in a larger or more complex substance) vs. catabolism reactions (Complex broken down and energy is released as a result)
-ATP=energy
-adenosine triphosphate
Functions of Human life
-Responsiveness: ability of an organism to react/adjust to situations (react to stimuli)
-Movement: motion of the body and its parts
→ joints of the body
→ digestive system through digestive track
→ movement of cells through the body to keep proper function
→ development(differentiation): changes body goes through as it gets older, cells become specialized for specific functions
→ growth: increase in size and number of cells, through utero
→ reproduction: producing new cells or organisms, procreation
Requirements for Human Life
-Oxygen: Needed for ATP production
-Nutrients: substance in foods and beverages essential to human survival
→ Water (most Critical)
→ Macronutrients: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins which provide amino acids
→Micronutrients: vitamins and minerals
-temperature and pressure ranges: 37C or 98.6 Fahrenheit
→ when body is outside of ranges the feedback loops get out body back to homeostasis
-Pressure: dissolved gasses, ability to breath
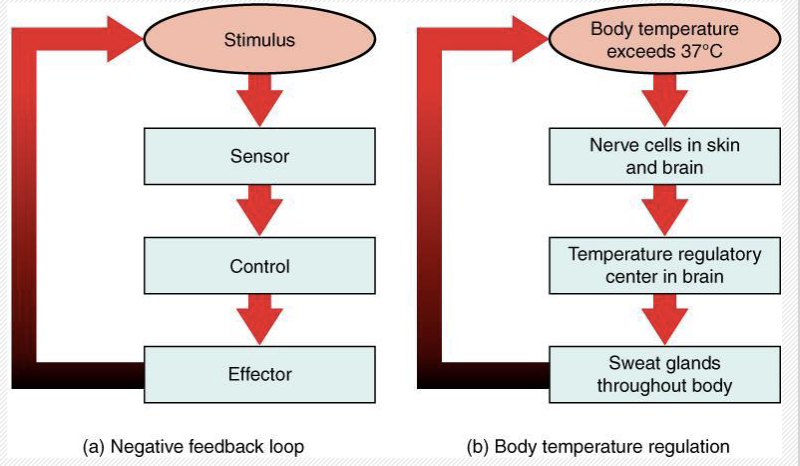
Homeostasis/ Negative Feedback/ Positive feedback
-maintenance of a stable internal environment
→ feedback systems
→ Set point: ideal setting of body temperature
→ Normal Range: amt of fluctuation allowed before feedback systems are put in place
→ Negative Feedback system: reverses deviation from set point
→ receptor: sensor, detects change in body and sends signal through afferent pathway to control center in the body
→ control center: interpret signal, exit out efferent pathway to the effector
→ effector: organ or system that acts out the homeostasis
→Positive feedback system: intensifies change, only used when there is a definite endpoint (produce a result that will return body to homeostasis)
→ childbirth aka pushing/contractions and blood clotting, secreting oxytocin
→ blood clotting after a cut or blood
Homeostasis between systems
-health of skeleton requires calcium ions (integumentary, digestive and urinary systems work together to maintain normal range or calcium ions in bloodstream)
-Blood Pressure (BP): normal range is 120/80, Circulatory, urinary, endocrine system work to maintain stable BP
-Respiratory: function: Circulatory, muscular and nervous systems work together to maintain a normal respiratory function
Important Questions
-what is homeostasis
-what is the point we are looking to get to in homeostasis, set point
-what is negative feedback, reverses body system to return to homeostasis
-what is positive feedback system: intensifying action
-when is a positive feedback system put into play?
-how many anatomical planes? 3, frontal, sagittal, transverse
Chapter 2
The Chemical Level of Organization

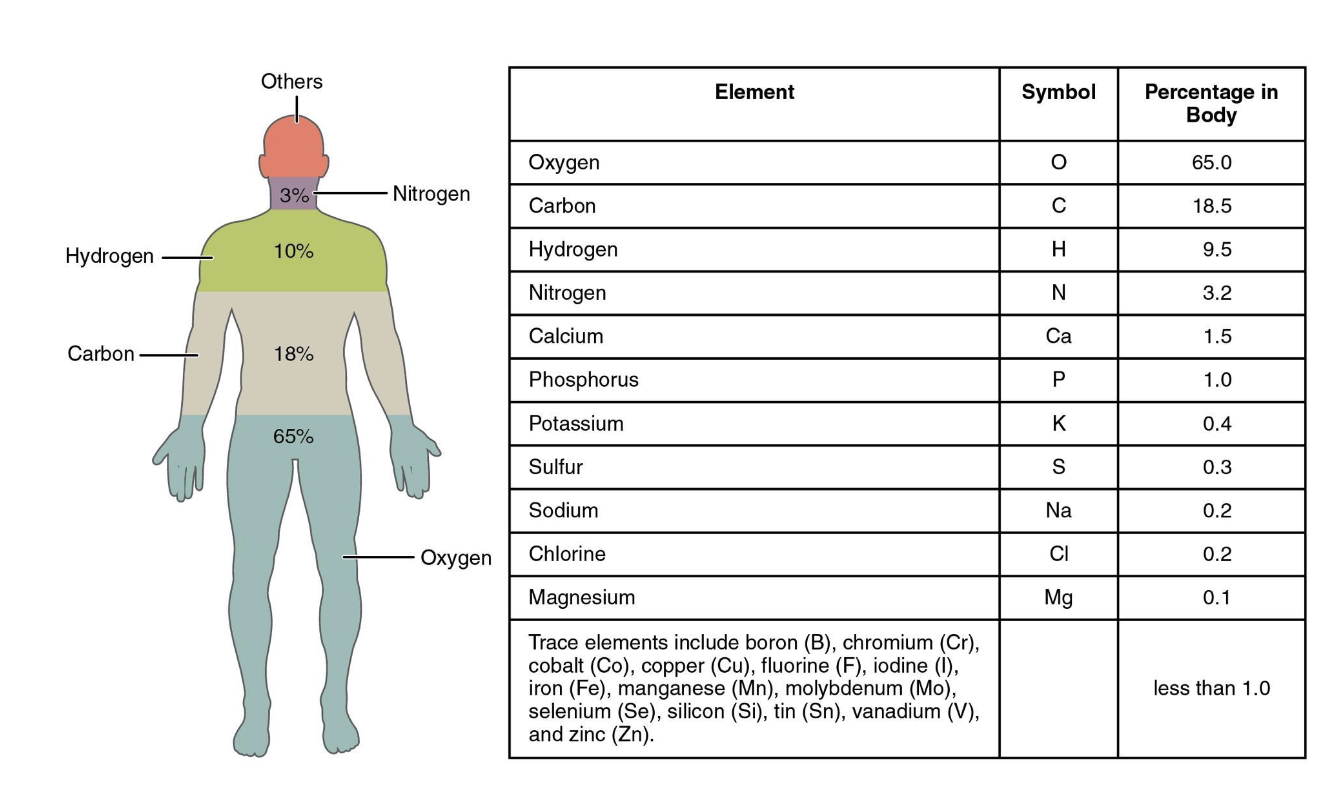
Elements and atoms
-anything that occupies space and has mass
-Matter: the substance of the universe
→ mass: amount of matter contained in an object
→ weight: mass affected by the pull of gravity
-Element: pure substance made of subatomic particles, cannot be created or broken down by ordinary chemicals
-Compound: Two or more elements joined by chemical bonds
-Atoms: smallest unit of an element (protons +, neutrons +/-, Electrons -)
→ atomic mass number (# of protons and neutrons) and Atomic Number (# of protons in nucleus)
*chemistry notes from last year describe this better
Atomic Structure
-Planetary Model: electrons orbit the nucleus like a planet (limited electrons per orbital)
-Electron Cloud Model: electrons float and bounce around nucleus, more accurate representation
-hydrogen(1), sodium(11), potassium(19), calcium(20), carbon(6), nitrogen(7), oxygen(8)
-electron shells: 1-5 shells,
→ first shell holds 2, the rest hold 8
→ s(2)-p(6)-d(10)-f(14),
→ Valence Shell-outermost ring of e- (full shell would make the atom more reactive, want to have a full 8, think of lewis structure with the octet rule)
-Isotope: different number of neutrons in the nucleus (radioactive Isotope-nucleus decays which gives off subatomic particles and electromagnetic energy)
Chemical Bonds

Covalent Bonds
-Ionic Bonds: ions of opposite charges attract each other, transfer of electrons
→ cations(+) and anions(-) attract each other
-Covalent Bonds: sharing of electrons to stabilize (polar[arrows face the same direction] and nonpolar[arrows pulling apart])
-Hydrogen Bonds: weak bonds between polar molecules
→ connecting S+ and S-
Chemical Reactions
-energy(ATP) is required to break and create new chemical bonds

→ Kinetic energy
→ Potential Energy
→ Chemical Energy:
→ Mechanical, Radiant, Electrical
-Characteristics:
→ reactant: one or more substances that enter the reaction
→ Product: one or more substances produced by a chemical reaction
-Synthesis: two components bond (Note+Book→ Notebook)(A + B → AB)
-Decomposition: one component breaks into two (BookWorm→ Book + Worm) (AB → A + B)
-Exchange: Components are rearranged (Notebook+ Worm→ Note+BookWorm)(AB+C→A+BC)
-Influencing factors:
→properties of reactants
→ temp
→ concentration
→ pressure
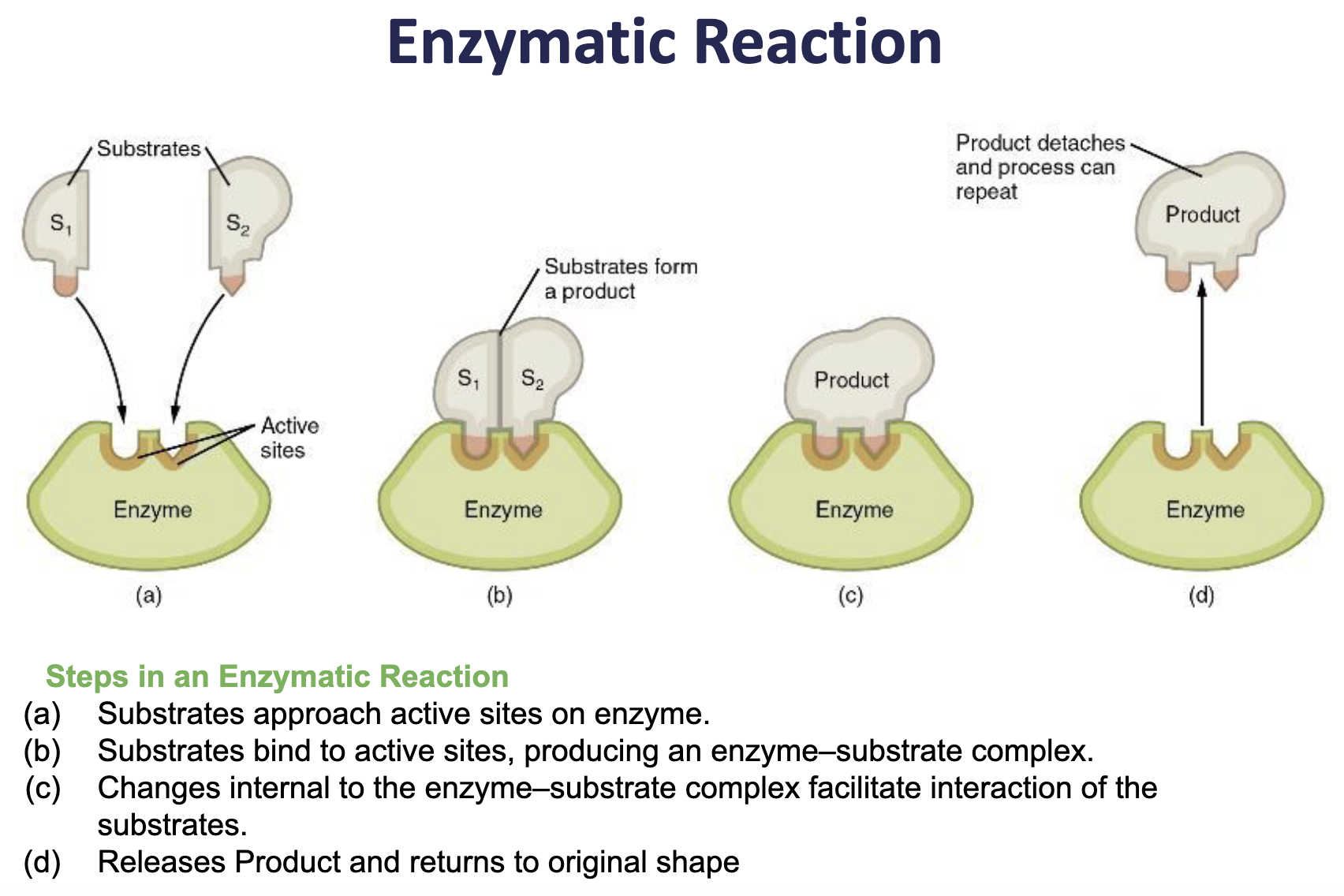
→ catalysts (enzyme)
-Activation energy
Acids/Bases/Salts

-pH Scale: how acidic or how basic an element is (0-14)
→ less than 7 is acidic
→ 7 is neutral
→ above 7 is basic
-represented in x^10 with each step up the scale (reverse for going down)
Buffers
-Buffer: weak Acid and conjugate base
→ physiological buffers: respiratory and urinary systems
→ Chemical Buffers: kidney, protein systems, lung
→ acidosis and alkalosis
Water

→ temperature regulation
→ hydrophilic: like water, will dissolve
→ Hydrophobic: doesnt like water, will not dissolve
-Dehydration Synthesis(removal of H2O) : removal of OH from one side and H from the other side of the reaction
-Hydrolysis(addition of H2O): adding OH to one side of the reactions and H to the other
-1 Mole (M) = 1 Liter

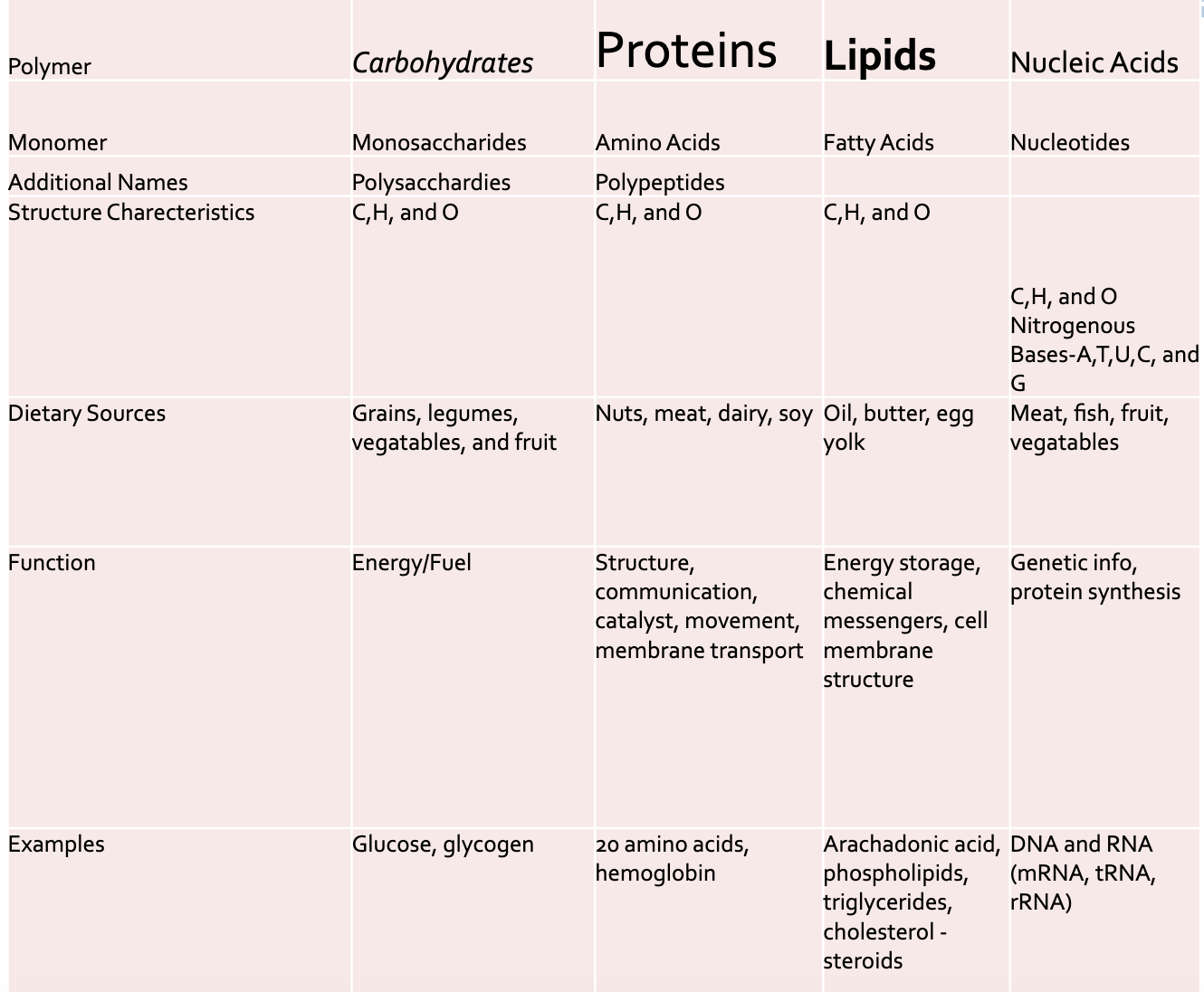
Macronutrients
-Monomer- a repeating subunit of polymer (simple sugar, amino acids, fatty acids, nucleotides)
-Polymer: many linked monomers (carbohydrates-hydrated carbon-, proteins, phospholipids, DNA/RNA)
→ both are required to sustain life and fuel our cellular processes
-Macromolecules: will always have some sort of carbon bonding (carbon is important in the body)

Carbohydrate basics
*used for quick energy, first energy source used*
-monosaccharides (simple sugars), serve as fuel source
→ all body cells can use glucose, when glucose is broken down it produces ATP
→ cell structure: binds with proteins and lipids
-five monosaccharides:
→ 3 hexose sugars (glucose, fructose, galactose)
→ 2 pentose sugars (ribose[make DNA], deoxyribose[Make RNA])
-Disaccharides
→ pairs of monosaccharides connected through Glycosidic bonds (Glyco – sugar)
→sucrose, lactose, and Maltose
→ consumed in diet (Split into monosaccharides via hydrolysis)
- Polysaccharides
→Starches (plant-based foods, Easily digestible)
→Glycogen (stored in tissues)
→ Cellulose (cell wall, fiber, great for digestive process but not easily broken down)
Lipids: Triglycerides
-lipid: non polar hydrocarbon, hydrophobic
-Triglycerides: found in body tissues and referred to as fat, formed through the combination of glyceride and the fatty acid chain
→ fuel source (active while sleeping, used during long slow activities)
→ secondary food source to carbohydrates
→ vitamin absorption, cushion
-Fatty acid chains:
→ saturated: no double bonds (butter, lard) carbon is all bonded to hydrogen
→ unsaturated: double bonds (olive oil) wants to bond with fatty acid
→ trans fats:
-Other important types
→ phospholipids: disperse fats and lipids, keeping water inside
→ steroids: production of hormones (sex hormones) derived from cholesterol
→ prostaglandin: signaling molecules from unsaturated fatty acid chains

-fats allow us to float in water
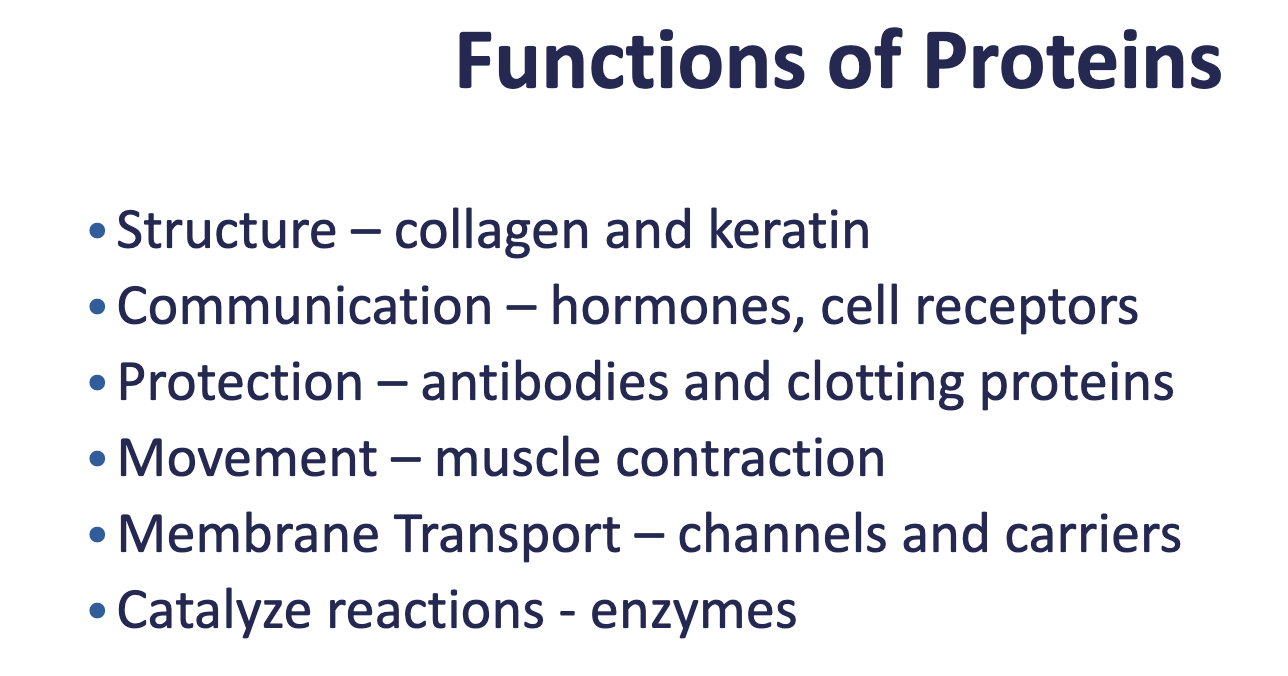
Proteins
-molecules composed of amino acids and linked through peptide bonds
→ contain Hydrogen, Carbon, Nitrogen, Oxygen (Sometimes Sodium)
→ dehydration synthesis
-Amino Acid Monomers
→ amino group + carboxyl group
→ 9 essential amino acids obtained through eating, other 11 can be created in the body (20 total)
→ contains acid and base
-Polypeptide: strand of fewer than 100 amino acids
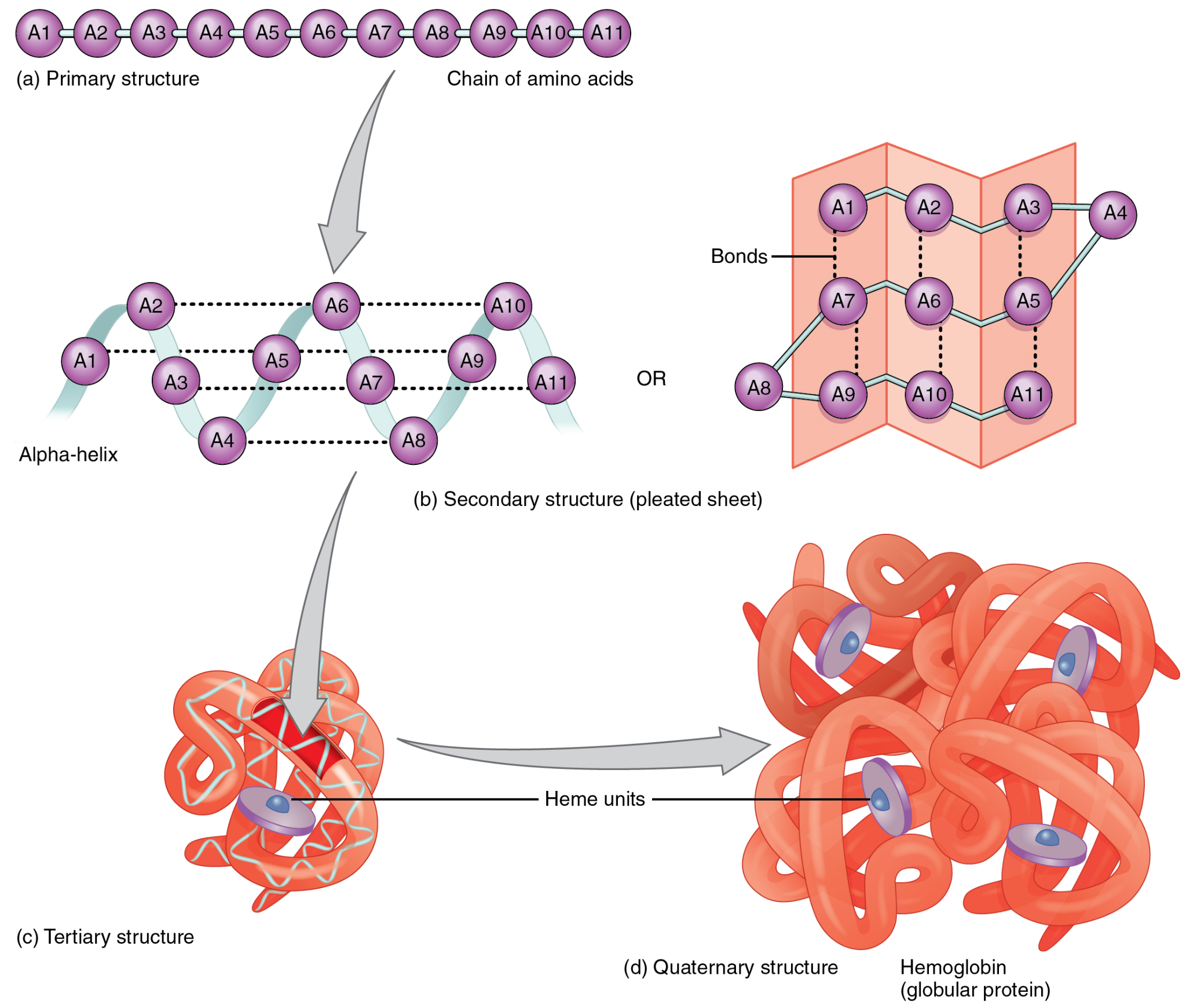
← primary is the simplest form
← four polypeptides arranged together
Denaturation
-change in a proteins molecular structure due to heat or chemicals, loose their 3D shape (sometimes reversible)
Nucleotides
-phosphate group: one or more
→ pentose sugars (genetic coding, continual fuel source we have with ATP, nucleotides become our DNA and RNA)
→ attach via hydrogen bonds between the bases of the component nucleotides.

Chapter 3: The Cellular level or Organization
Cell/Cellular Membrane
-Cell: smallest unit of life, organized for metabolism, senses and responds to environment(homeostasis), reproduction
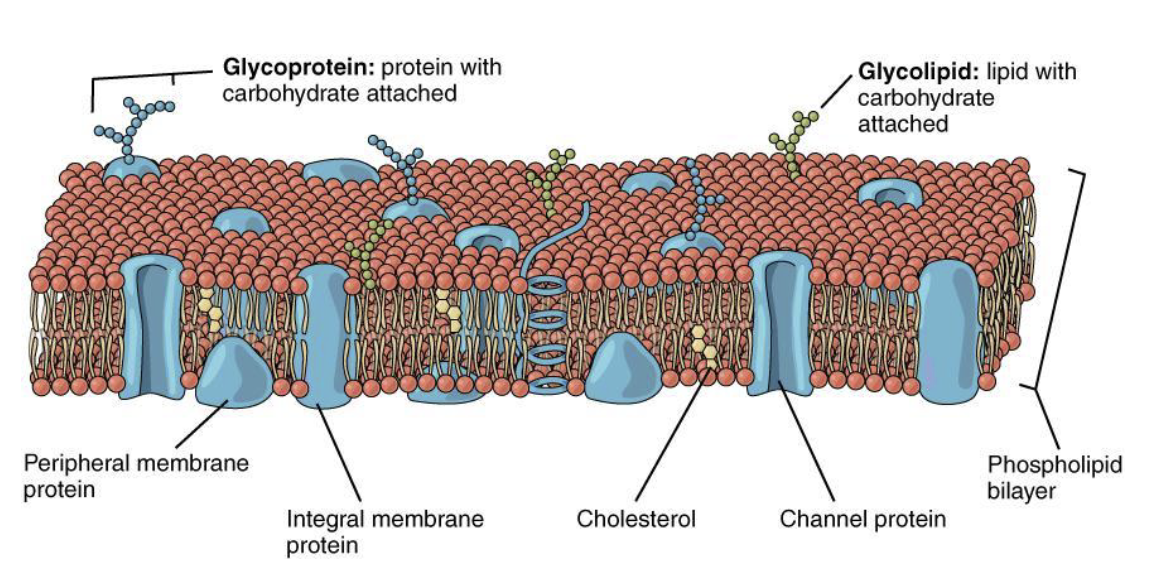
-Membrane structure:
→ Phospholipids (Amphipathic):
→lipid bilayer,
→ Heads: both polar and hydrophobic (attracted to intracellular and extracellular fluid)
→ Tails: non-polar and hydrophobic
→ Interstitial fluid
-Membrane Proteins: Cholesterol
→ types of proteins: integral (run through protein) & peripheral(runs on one side of the cell and serves a specific function), glycoproteins(identifies what the cell is and why it is in our body), channel (allow ions to pass through cell membrane)
→ carriers: carry substance into the cell itself, need ATP and energy to bring substance across membrane (think of potassium pump)
Cellular Differentiation
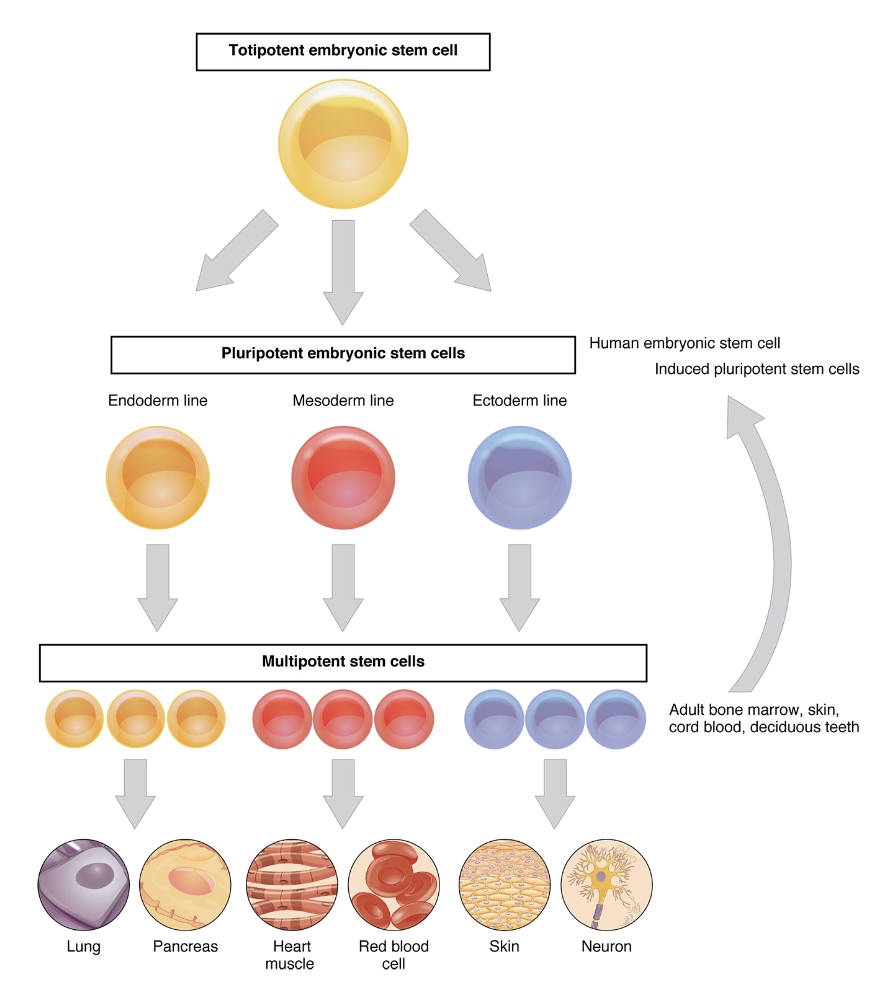
Stem cell – unspecialized, divide without limit, several categories
•Totipotent – can become anything
•Pluripotent – can become any human tissue cell
•Multipotent – can differentiate within a certain cell lineage (ectoderm, mesoderm, or endoderm)
•Oligopotent – can become 1 of a few different cell types
•Unipotent – can only make more of its own cell type
Cell Connections
-Desmosomes: Anchoring junctions found in intercalated discs (skin and heart) able to move but do not break, allows for the heart to beat
-Gap Junctions: openings that let ions pass from 1 cell to the next, found in intercalated discs (Heart cells)
-Tight junctions: Keeps space between cells close together (stomach and skin) sealed and does not allow anything to pass through cells (waterproof)
Membrane Transport:
-Selective permeability: allow only certain substances that meet certain criteria to pass through (lipids)
-Passive Transport:
→ no energy use
→ happens because of concentration gradient: difference of concentration of substances across the membrane (high concentration with move to lower concentration until it is equal across-homeostasis through diffusion)
→facilitated diffusion: cant cross lipid bilayer due to size, charge, or polarity (carrier protein transports inside) EX= glucose and glucose transporter into cytoplasm
→filtration:
→osmosis: simple diffusion of water (leads to isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic solutions)
-Active Transport:
→ energy use (ATP must be present)
→ exocytosis (out of cell) and endocytosis (into a cell)
→ phagocytosis: cell eating of large particles (slide 13)
→ pinocytosis: cell drinking-fluids into cell membrane
Fluid Balance:

-trigger response of osmosis to bring homeostasis
-ICF: intercellular fluid
Overview of the Cell
-Cytosol + Organelles = Cytoplasm
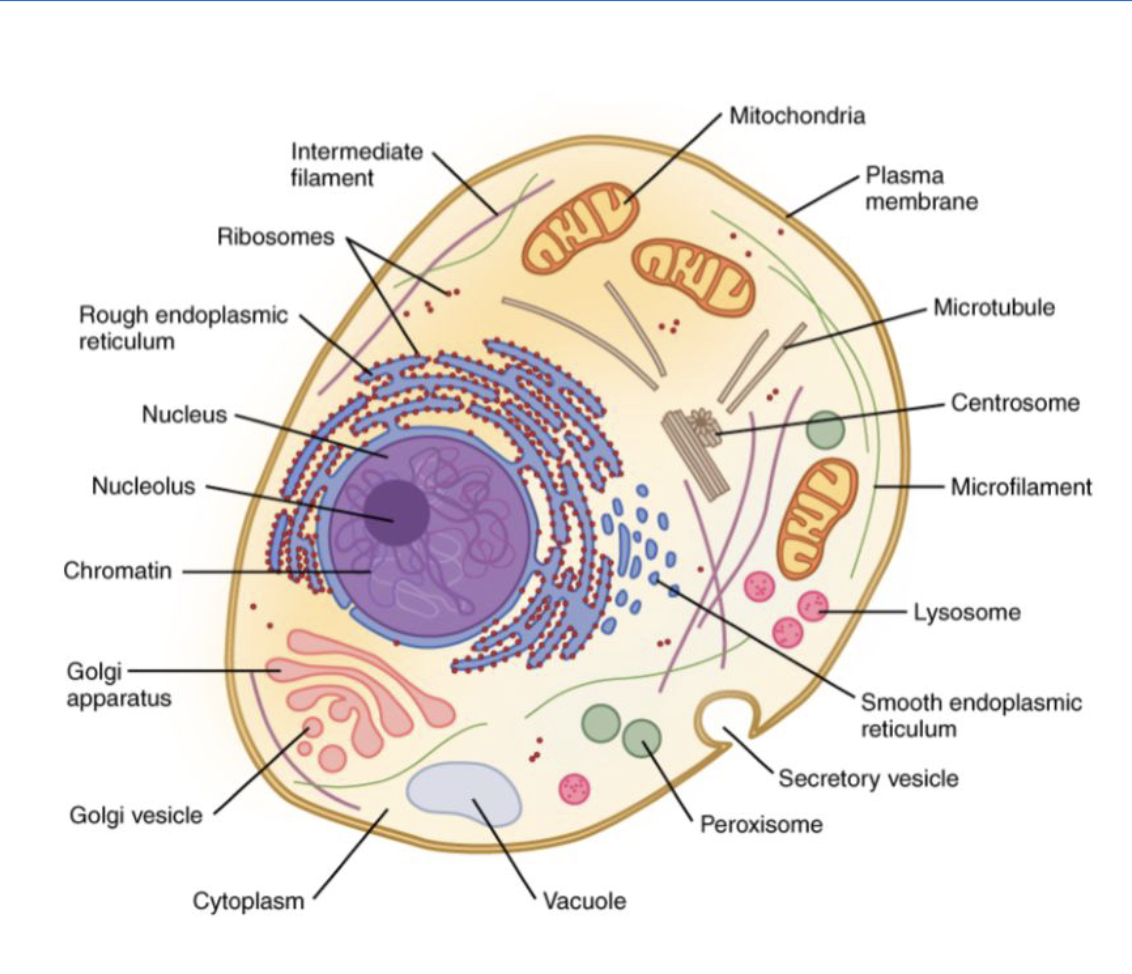
-nucleus contains cells DNA
-Endomembrane system: System of channels continuous with nuclear membrane, provides passage for transporting, synthesizing, and storing
→Rough ER: embedded with Ribosomes, synthesis and modification of proteins
→Smooth ER: no ribosomes, synthesis of lipids
→ Golgi Apparatus: sorts, modifies, and ships products from RER
→ Vesicles:
→ lysosomes: Autophagy and Autolysis (self eating, breaking itself down, program death of a cell)
-Mitochondria: powerhouse of the cell, produce ATP with the presence of oxygen
-Peroxisomes: Contains enzymes and is a reactive oxygen species (lipid metabolism and detox)
-Cytoskeleton: Microfilaments (muscle contraction), intermediate filaments (resisting tension on the cell) and microtubules(provides structural support)
→ allows movement (cilla, flagella, transport of materials, muscles)
-The Nucleus: Control center of the cell, largest organelle, some cells may have multiple nuclei
→ lipid bilayer that surrounds it
→ nucleolus: deep center, produces rna for ribosomes
→ nuclear pores: regulated pathways
→ DNA packaging: Chromatin, Histone, Nucleosome, and chromosome
Cell Growth and Division

Sister chromatids
-After DNA synthesis, 2 chromosomes are connected by centromere
- 2 identical chromosomes are called sister chromatids
-chromatids split apart and each be a chromosome
Phases of Mitosis

-Timing of Mitosis:
→ checkpoints to make sure things are going correctly
→cells could become abnormalities or cancerous
→Immune system is designed to find and destroy abnormal cells
DNA Structure
-two strands that compliment each other
-Twisted ladder formation
-Four DNA Bases:
→ Adenine (A)
→Thymine (T)
→ Cytosine (C)
→ Guanine (G)
-Replication: cells split into daughter cells each with the same DNA (nerve, skeletal, and cardiac muscle cells do not divide) creating the exact same genetic code within the two daughter cells
-DNA: composed of 4 nitrogenous bases (adenine-thymine[A-T] and cytosine-guanine[C-G]) each with a sugar-phosphate backbone
-New DNA is scanned for mistakes, mistakes are then corrected is applicable
-Transcription-DNA into mRNA (messenger RNA-code goes into ribosomes to be translated into polypeptide for protein)
→ no thymine is is RNA (AUCG) Uracil replaces thymine in RNA transcription
-translation: DNA into polypeptide or protein
Protein Synthesis
-Genes determine which proteins are made
-these nitrogenous bases (DNA→ RNA) are grouped into triplet and each triplet is a code for a certain amino acid (happens in ribosomes)
- mRNA brings a chain of nucleotides to the ribosomes in Rough ER
-tRNA will have an amino acid and it will attach to the specific triplet codon creating the next link in the polypeptide chain
→ has the anticodon that will match the mRNA codon for an Amino Acid
→ rRNA: makes the ribosome and helps to read the mRNA during translation
-Polypeptide chain finishes, takes shape and is a protein
→ most chains are 200-300 Amino Acids long
Triplets
-RNA switches uracil for thymine to match up with adenine
-RNA only codes a part of the DNA strand called transcription
-RNA polymerase adds the nucleotides to make the mRNA strand
-Non coding regions must be spliced before protein synthesis
→ different riplets linked to different amino acids to create polypeptide chain
Review Questions
What are the types of membrane transport?
-Passive transport: concentration gradient does not require energy
-active transport: always uses energy
What are the Phases of Mitosis?
Prophase
(cytokinesis occurs during cleavage furrow formation)
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
What are the four DNA Bases?
Adenine, Guanine, Thymine (replaced with Uracil in mRNA), Cytosine
→ A-T, G-C
Chapter 4 :The tissue level of organization
Types of Tissues
-Epithelial tissue (epithelium, covers external surface, lining of tract and hollow organs, serves as a barrier from the outside world)
-Connective Tissue (lines cells and organs of the body, binds things together)
-Muscle Tissue (movement)
-Nervous Tissue (electrochemical signals)
Embryonic Origin of Tissues
-Totipotent cells: can divide and differentiate
-Three germ layers
→ ectoderm
→ mesoderm
→ endoderm
Tissue Membranes
-Thin layer of cells that cover connective tissue membranes and epithelial membranes
→ epithelial membranes include (connect to connective tissue membranes): mucus membranes, serous membranes, cutaneous membranes
Basics of Epithelial Tissue/Membranes
-covers all surfaces exposed to the outside of our bodies (hollow organs, blood vessels, and body cavities covered by endothelium)
-comes from all three germ layers
-little extracellular space between cells at the cell junctions (Avascular- no blood vessels cross)
-Basal Side has glycoproteins and collagen to connect to connective tissue, opposite side is the apical side
-Basal lamina and reticular lamina form a basement membrane
-Regeneration: rapidly replace dead or damaged cells (first line of protection against chemical, physical, and biological harm)
→ may secrete mucus or enzymes for defense
-Polarity: has a basal (near basement membrane) and apical surface
→ may have cilia on the apical membrane
→ innervated (has nerve fibers)
Classification
-based on shape of cell and number
of cell layers that are formed
-Squamous: flat and thin, simple found in kidney tubules, alveoli of lungs, and capillaries, most common to be stratified
→ looks like scales and have nuclei that are flat and horizontal
→ makes up endothelium
-Cuboidal: boxy, like a square, they are active is secretion and absorption
→ create ducts of glands for secretion, observed in the lining
-Columnar: taller than wide,may have cilia, good for secretion
→ nuclei located towards the bottom
-have Cilia (fibers are the top for absorption and secretion in digestion and reproduction areas)
-Pseudostratified: irregular shaped, appear to be stratified, but they are simple, may have cilia, good for secretion
→ not all nuclei are at the same level, may or may not have cilia, respiratory tract
Transitional Epithelium (not a classification, own unique area within epithelium)
-unique in that it changes shape
- only in urinary system
→ empty bladder: convoluted shape with cuboidal apical cells
→ full bladder: squamous shaped apical cells
Glandular Epithelium
-made up of modified cells to make and secrete various substances
→ Endocrine (releasing substances inside body- hormones) and exocrine (releasing substances outside body through a duct system- sweat, saliva)
→ Glandular structure (Unicellular and Multicellular)
Glandular Secretions:

most common type is sweat glands
Breaks off portion of cell (armpits and private areas) with bacteria breakdown causing smell
Ruptured cell to release substance secretion
Glands include: Serous Glands (watery, bloody) Mucous Glands (thicker, urinary or reproductive), and Ceruminous Gland (ear wax in ear canal)