M4 Notes
Cultural Differences Matter
Perhaps nothing causes more problems for Americans negotiating in other countries than their impatience. Everyone around the world knows that delaying tactics work well against time-conscious U.S. bargainers.
Culture and Business Systems
Culture profoundly impacts business
Management style.
Business culture, management values, business methods and behavior.
Establishes criteria for day-to-day business behavior.
Forms general patterns of values and motivations.
Important for marketers to analyze to be successful.
Cultural analysis and understanding gives competitive edge.
Business etiquette a crucial component.
Required Adaptation
10 Basic Criteria to Do Business in a Foreign Country
Open tolerance
Flexibility
Humility
Justice/fairness
Ability to adjust to varying tempos
Curiosity/interest
Knowledge of the country
Liking for others
Ability to command respect
Ability to integrate oneself into the environment
Degree of Adaptation
Know local customs and accommodate differences.
Evaluate which foreign customs should be adhered to.
Be aware of self-reference criterion (SRC).
Own cultural background impacts understanding of other culture.
Importance of customs varies by country.
Cultural Imperatives: Business customs and expectations that must be met and conformed to or avoided
Cultural Electives: Behavior or customs that cultural aliens may wish to conform to or participate in, but not required
Cultural Exclusives: Customs or behaviors that foreigners are barred from and must not participate in
Context, Communication, and Cultures: Edward Hall’s Scale
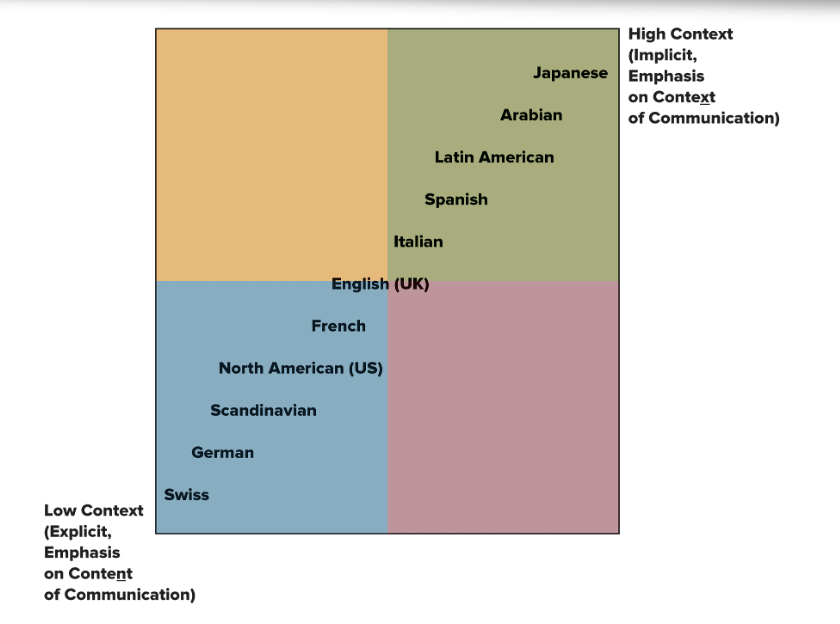
Synthesis: Relationship-Oriented vs. Information-Oriented Cultures
Correlation between Hall’s high/low context and Hofstede’s Individualism/Collective and Power Distance indices
Relationship orientation.
Information orientation.
General pattern international marketers can use.
Not every culture fits every dimension precisely.
Still important to learn about culture individually.
Dimensions of Culture: A Synthesis
