1.6 - CompTIA A+ Core 2
1.6a - The Windows Control Panel: Professor Messer
Internet Options
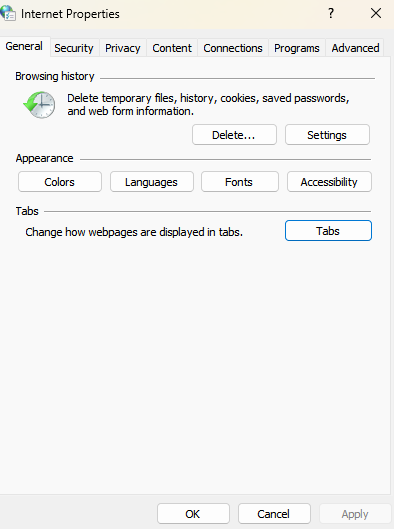
Internet Options: Windows Control Panel utility that manages how a Windows machine accesses the Internet through Internet Explorer and similar browsers. It controls settings for appearance, security, privacy (pop-ups/cookies), digital certificates, VPNs/LANs, and browser extensions.
Devices and Printers
Devices and Printers: Windows Control Panel utility that manages devices on a network, including desktops, laptops, printers, and peripherals (e.g., microphones). Easier to view and administer compared to Device Manager (
devmgmt.msc).
Program and Features
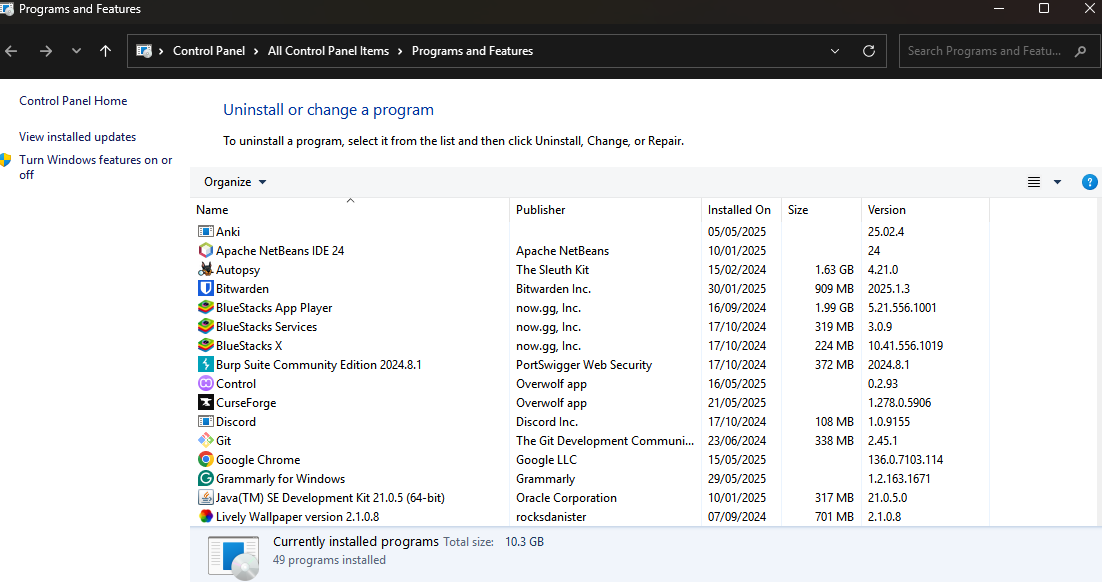
Programs and Features: Windows Control Panel utility that displays all installed applications on a Windows machine, including their size, version, and allows users to uninstall them as necessary. Also allows enabling and disabling of Windows features/services.
Network and Sharing Center
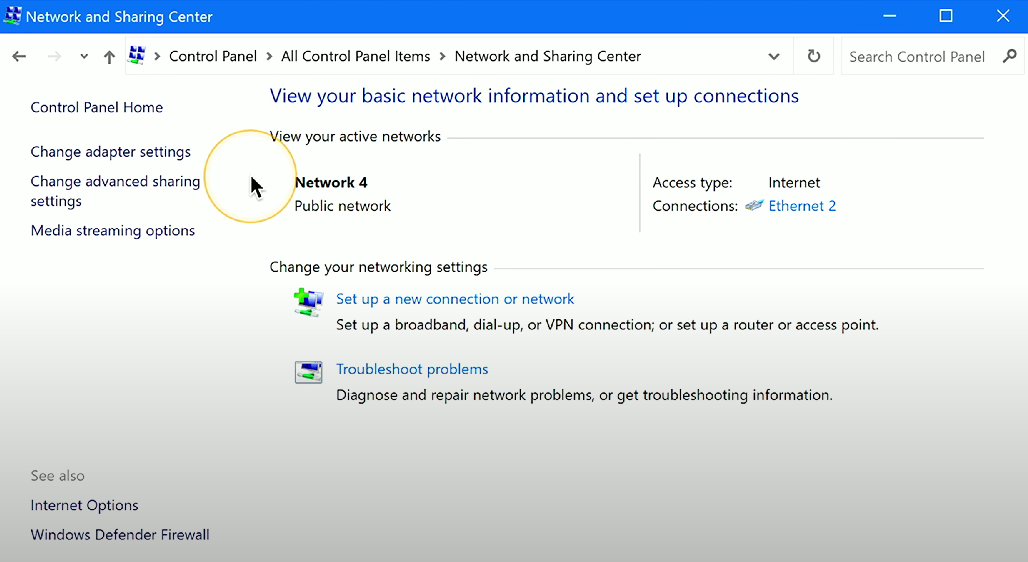
Network and Sharing Center: Windows Control Panel utility that displays the status of wired and wireless network connections, and allows for adapter and network address settings.
System
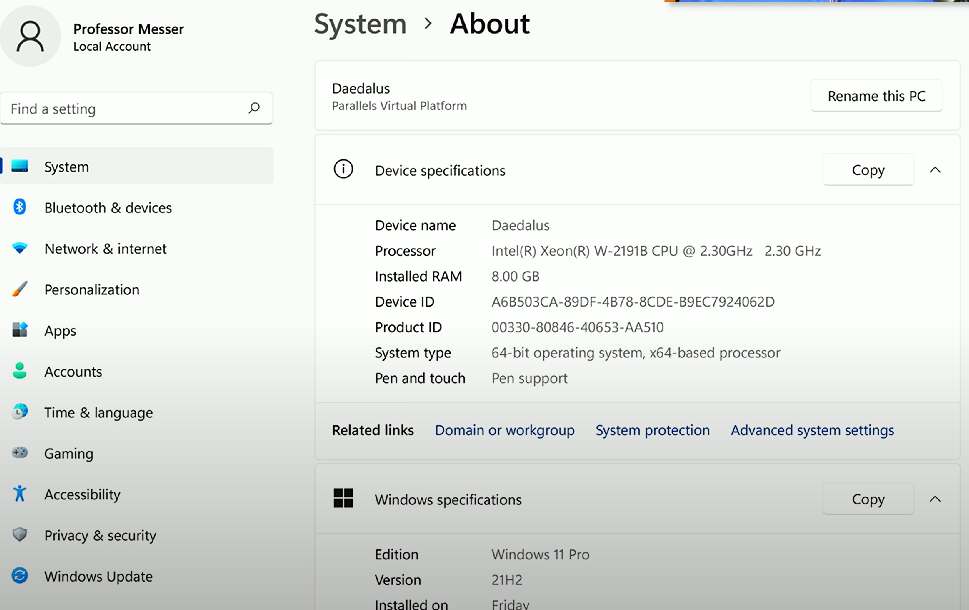
Contains information about the current Windows machine, including Windows version, the edition, RAM #, CPU, and storage.
Windows Defender Firewall
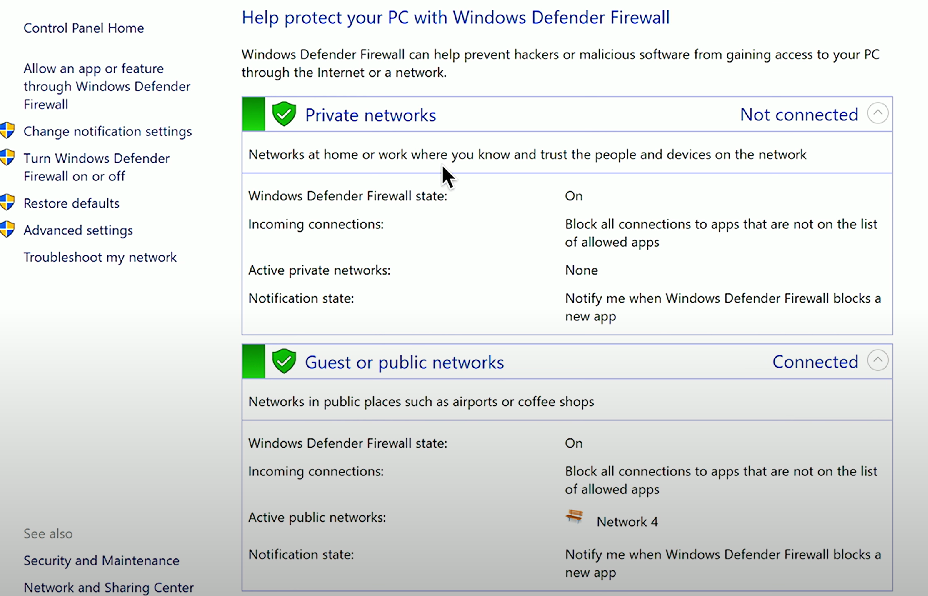
Windows Defender Firewall: A security feature of Windows that helps protect the PC from unauthorized access and threats by filtering incoming and outgoing traffic.
Found via Control Panel → Windows Defender Firewall
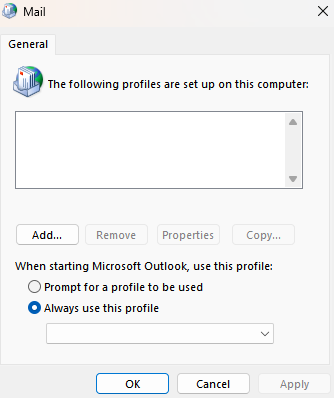
Mail: Windows Control applet that controls email accounts and data files. Doesn’t appear unless the user has installed a desktop mail client (e.g., Microsoft Outlook).
Sound
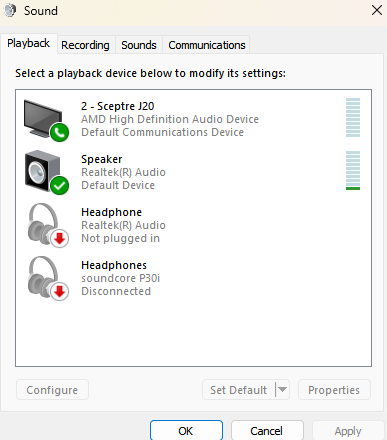
Sound: Windows control applet that controls audio input/output devices. Multiple options for input/output are available.
User Accounts
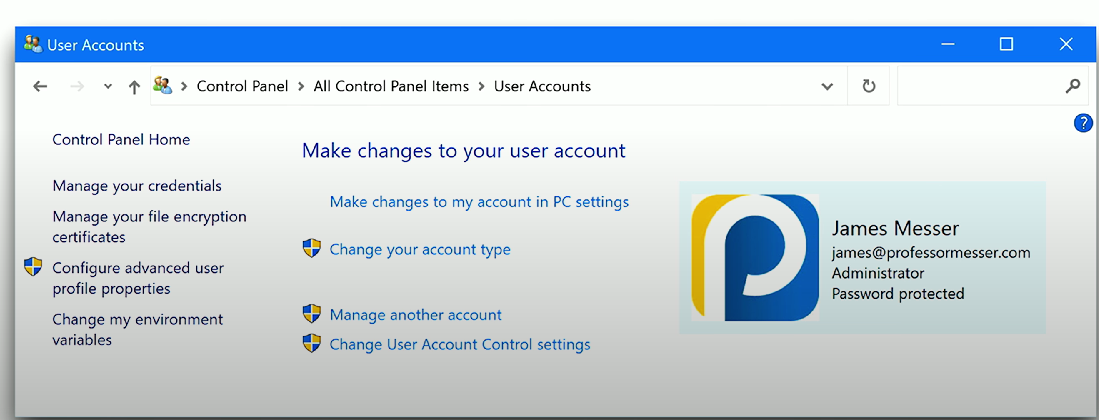
User Account: Stores information about local user accounts (i.e., accounts on your Windows workstation/laptop) - domain accounts are stored elsewhere. Contains info about account name, type, password, picture, and digital certificate information.
Device Manager
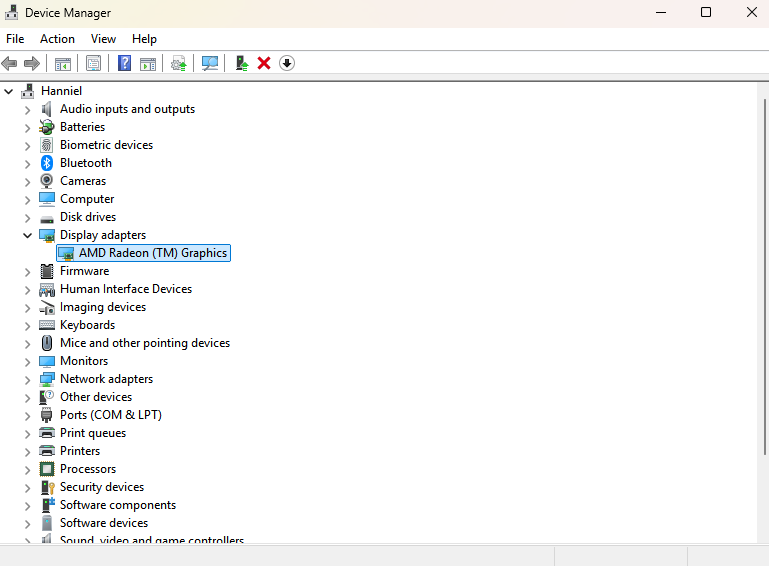
Device Manager: Windows Control Panel utility that allows centralized management of peripheral devices (e.g., keyboards, mice, speakers), and their associated device drivers. Also provides the ability to add, update, disable, or uninstall system drivers. First stop for non-functional hardware/peripherals.
General tab: Displays the device type the adapter is connected to, and device status (if the device is working properly).
Driver tab: Displays detailed information about the driver, including the driver version, date, provider, and associated files, allowing users to troubleshoot or roll back drivers if necessary.
Details tab: Displays values for the device based on the different properties the user selects (dropdown tab).
Events tab: Shows every event associated with the device.
Properties tab: Displays relevant hardware requirements/configurations for the device.
Indexing Options
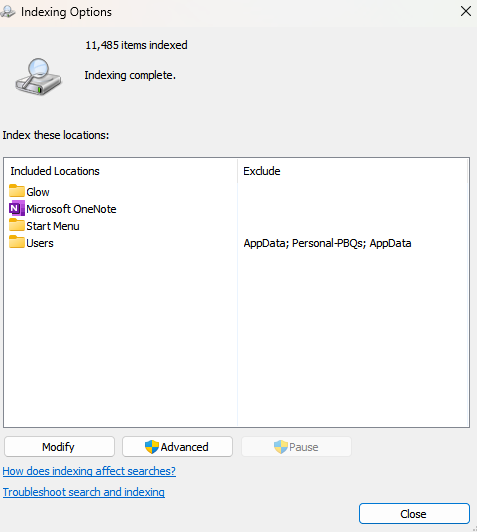
Indexing Options: Allows users to manually update Windows’ search index to speed up the file search process, including adding or removing files/folders from the indexing process.
Administrative/Windows Tools
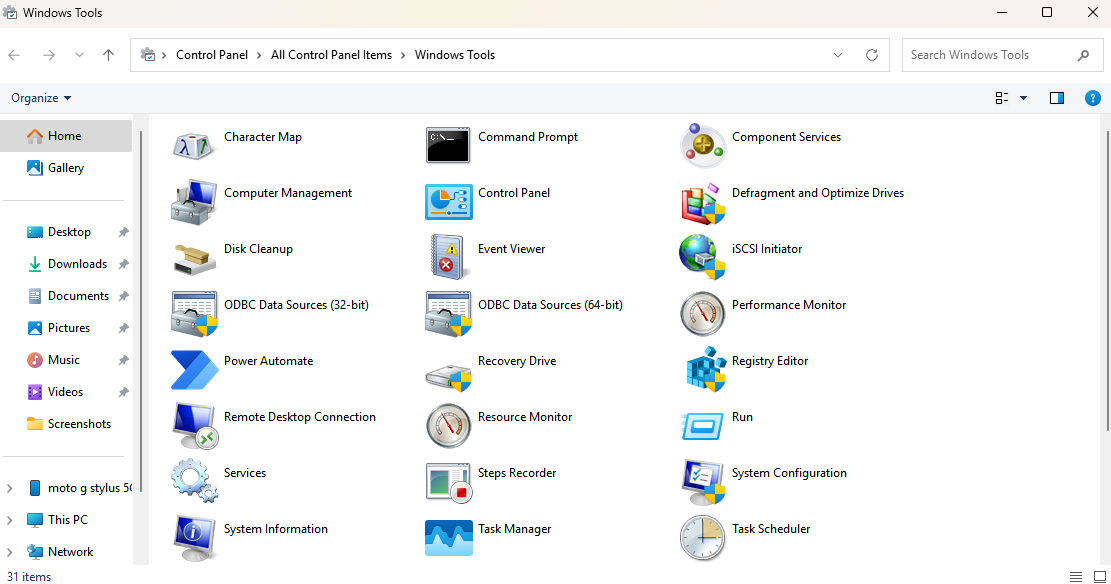
Administrative/Windows Tools: Uncommon Windows Control Panel utilities - commonly used for system administration.
File Explorer Options
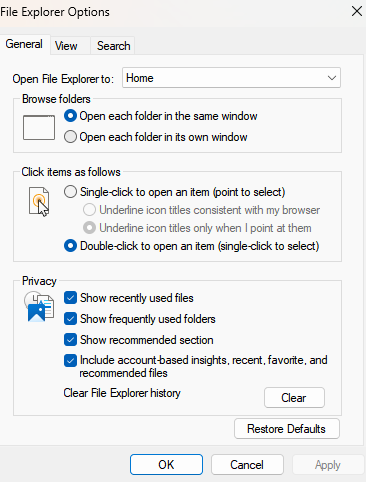
Windows File Explorer: An application that allows users to explore/select files available on a Windows system.
File Explorer Options: Windows Control Panel utility that controls Windows File Explorer. These settings in the Windows Control Panel allow users to customize the default folder opened by File Explorer, adjust click actions, manage privacy settings (General tab), control file and folder views (View tab), and configure advanced search behaviors and file extension visibility (Search tab).
View hidden files
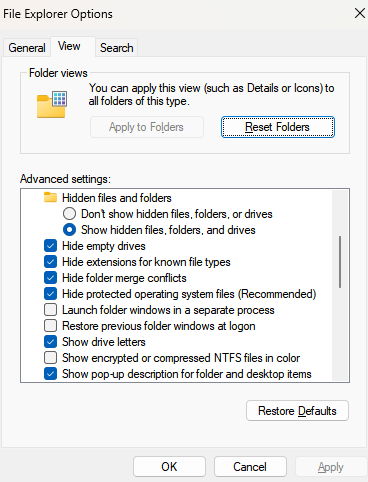
A radio button option that can be selected/deselected under the “View” tab in File Explorer options.
Hide extensions
A checkbox setting in File Explorer Options, when enabled, conceals file extensions of known file types in File Explorer to streamline the displayed information and reduce clutter.
General options
Settings in the Windows Control Panel allow users to customize the default folder opened by File Explorer, adjust click actions, and manage privacy settings. Found via the General tab.
View options
Controls the visibility of files, drives, and file extensions for Windows File Explorer.
Power Options
Allows users to manage the power consumption settings of their device, including sleep, hibernate, and shutdown options.
Hibernate
Hibernate: Power Options setting that saves open docs and apps to storage disks. Common on laptops and used for fast startup.
Power plans
Power plans are available in Power Options (Windows Control Panel) to determine the system’s power usage.
Sleep/Standby
Sleep/standby: Power Options setting that saves open apps & docs in memory. Requires and allows for quick startups. Standby mode will switch to Hibernate if the power settings are too low.
Choose what closing the lid does
Choose what closing the lid does: Power Options (WCP) setting that controls what closing the lid does. Useful for docking stations.
Turn on fast startup
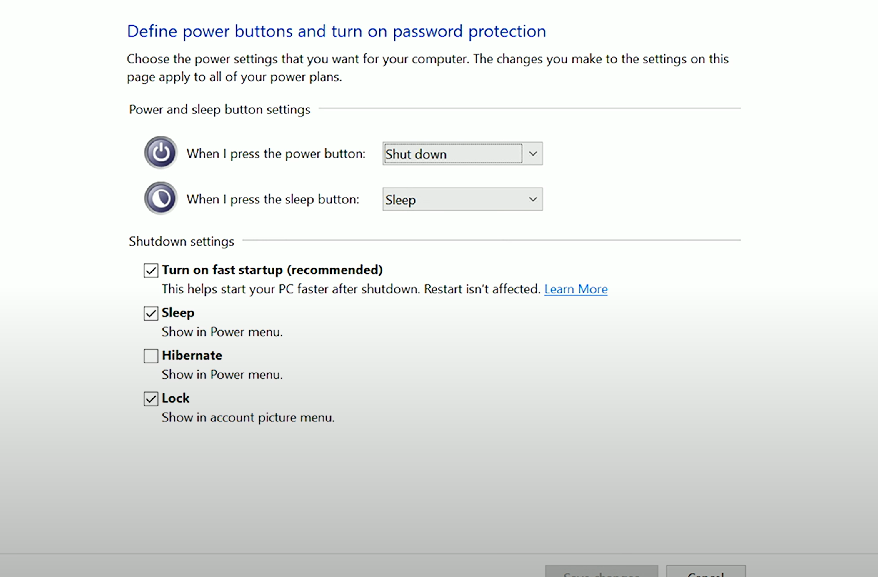
Fast startup: A feature that enables the computer to start/boot faster when pressing the power button. It is possible because Windows technically does not shut down while using Fast Startup, and can be enabled/disabled for troubleshooting purposes.
USB selective suspend
USB selective suspend: Allows disabling of individual USB devices to save power.
Ease of Access
Ease of Access: Windows Control Panel feature that includes usability enhancements (e.g., reading text sections aloud, keyboard magnifiers, high-contrast settings).
1.6b - Windows Settings: Professor Messer
Windows Settings: Windows utility for customizing system settings. Provides an upgraded and consistent layout compared to the Windows Control Panel.
Time & language
Time & language: Provides configurations for time, language, keyboard, and speech.
Date & time: Settings related to time - useful as Active Directory requires consistent time synchronization for encryption.
Language & region: Specifies the language you’d like to use for your Windows OS. Also allows region settings to show local content/applications.
Update and Security
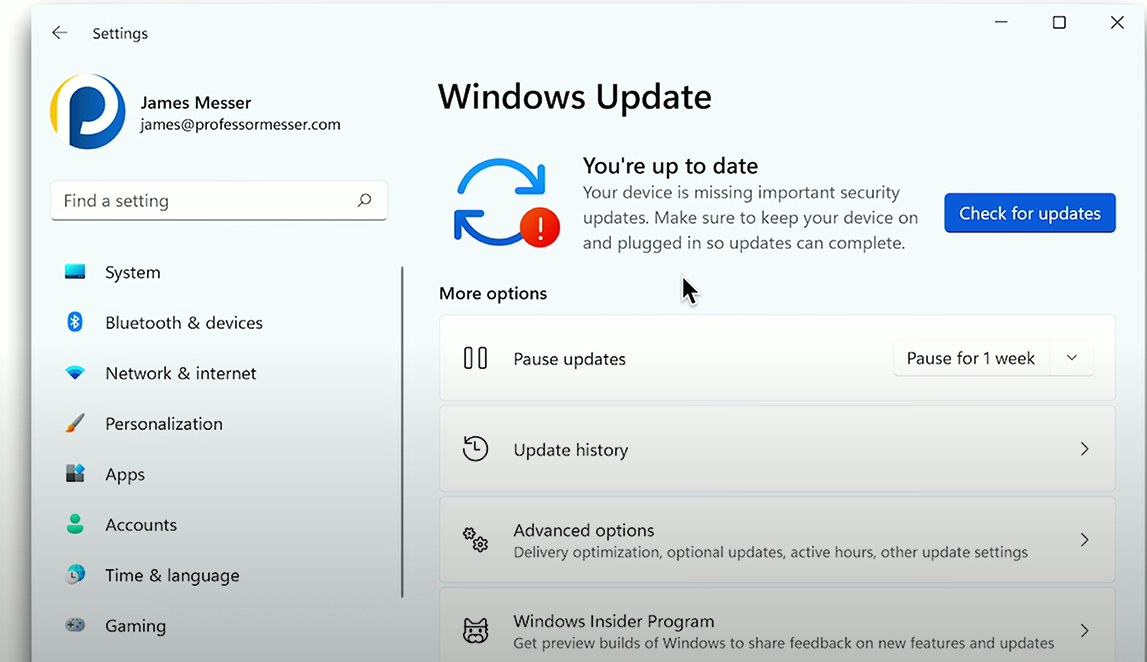
Update and Security: Manages security patches and bug fixes within Windows to ensure the operating system remains up-to-date. Allows users to set automatic installations and active hours to avoid updates. Also, logs update the history.
Personalization
Personalization: Changes Window’s appearance - shows colors, wallpaper, lock screen, etc. In a corporate environment, some of these features are disabled.
Apps
Apps: Manages installed applications within Windows settings. Apps are uninstalled or modified from here, and Windows features are added with these settings (e.g., OpenSSH server, SNMP support).
Privacy & security
Privacy & security: Manages multiple security utilities, such as antivirus software (Windows Security), and device encryption.
Users can also configure advertising preferences (sending data for targeted advertisements).
Bluetooth & devices
Bluetooth & devices: Allows management of peripheral devices, including Bluetooth connections, printers, mice, keyboards, and stylus pens.
Network & internet
Network & internet: Offers settings for managing Wi-Fi connections, Ethernet settings, VPN configurations, and IP settings.
Gaming
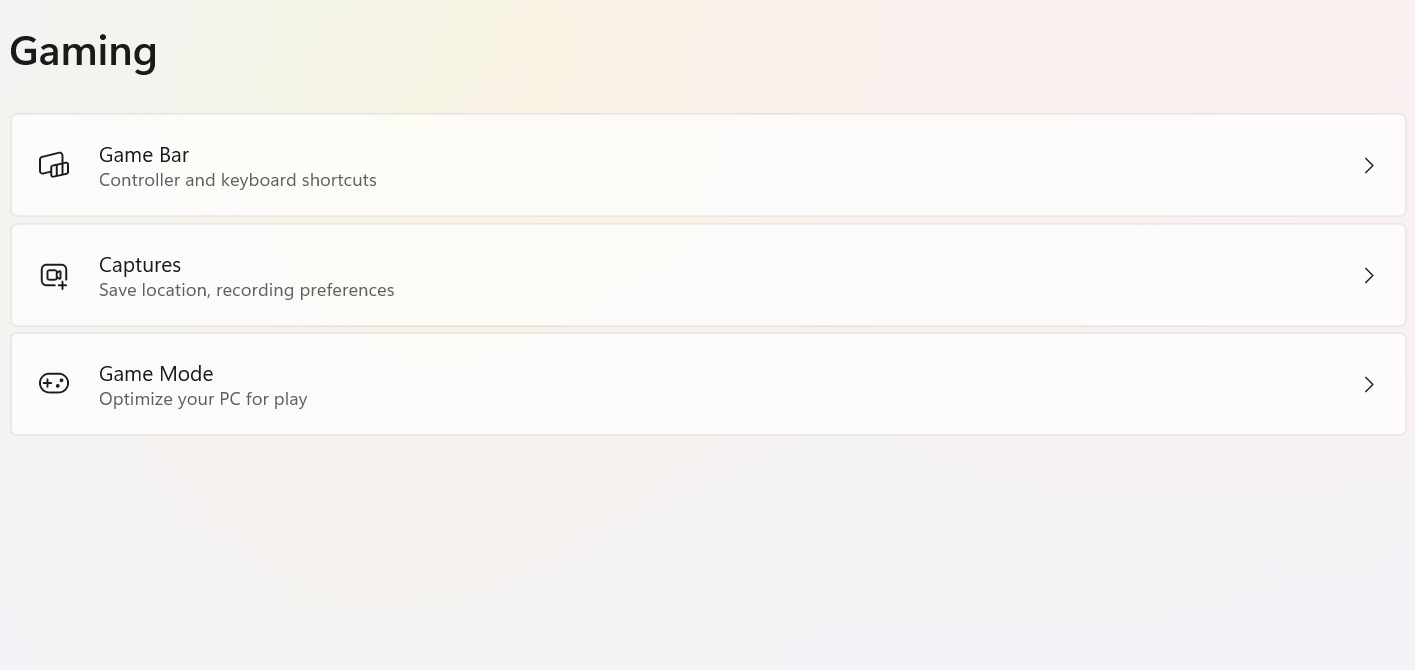
Gaming: Provides settings related to gaming - such as Xbox Game Bar, and game capture/recording preferences.
Accounts
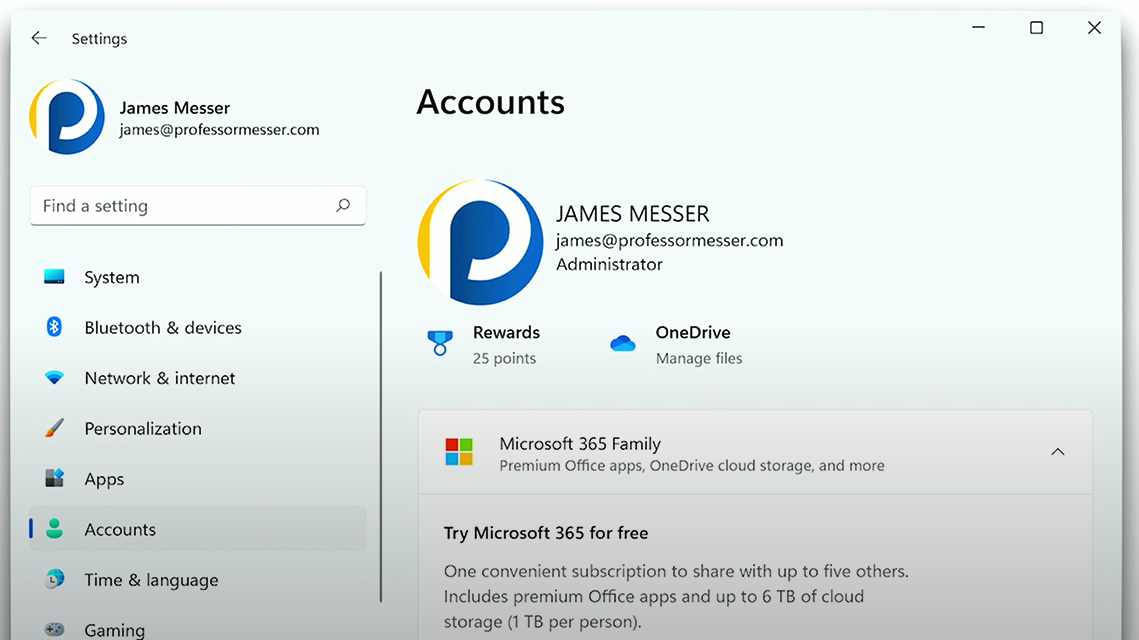
Accounts: Allows management of a user’s Microsoft account and local Windows account in Windows Settings, email config, and setting authentication methods (password, PIN, biometrics, MFA)