
Rocks & Minerals
What is a mineral?
A mineral is a naturally occurring, inorganic substance which includes a crystalline substance and a chemical composition.
What is a rock?
A rock is a naturally occurring, inorganic substance comprised of many different minerals and other organic debris. Rocks can be classified into 3 different groups based on how they are formed.
Properties of Rocks and Minerals
Colour - What ray of light shines onto the substance?
Weight - How heavy is the object?
Transparency - Is the object see through?
Density - How compact are the substance’s particles?
Hardness - Can this object get scratched or cut through by another object? (Test with the Mohs Hardness Scale)
Lustre - What type of shine is on the mineral?
Streak - When scratched an object, wat colour powder does the mineral leave off?
Mohs Hardness Scale -
What is the Mohs Hardness Scale?
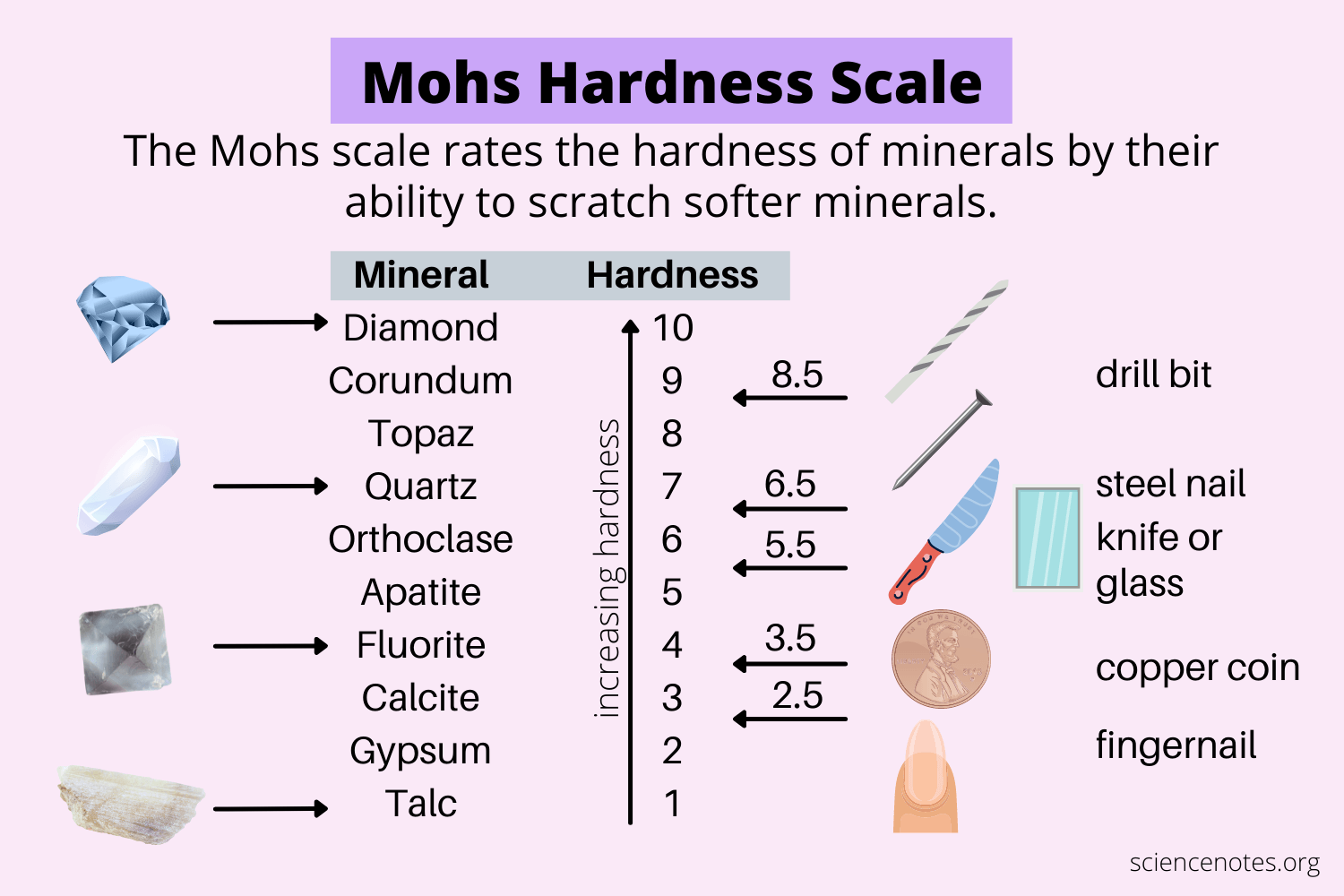
The Mohs Hardness Scale indicates how prone a mineral or rock is to scratching. The higher the number on the scale the harder it is.
Example:
On the picture, we can see that quartz has a higher rank than fluorite. We know this as quartz has a 7 on the hardness scale and fluorite has a 4. This means that quartz has the ability to scratch fluorite.
What are the three types of rocks?
The three types of rocks are sedimentary, igneous and metamorphic. Rocks are classified by how they are formed. Each of these categories have different subclasses.
What is an igneous rock?
Igneous rocks are formed by cooled magma, (melted rock below the Earth surface) Igneous rocks and be classified into two subclasses, extrusive (volcanic) igneous rock and intrusive (plutonic) igneous rock. Some examples of igneous rock are granite, pumice, basalt and obsidian.
What are the features of all igneous rock?
An igneous rock is usually quite hard an solid, as all igneous rocks have interlocking crystals. Due to the extreme heat of magma, igneous rocks will never have fossils.
What is an intrusive igneous rock?
An intrusive igneous rock is also known as plutonic rock. These rocks are formed by cooled magma underneath the ground. This process happens quite slowly, allowing lots of crystals to grow. As a result, these rocks are coarse grained (has a rough texture)
What is an extrusive igneous rock?
An extrusive igneous rock (or volcanic rock) is formed when a volcano erupts and the lava quickly cools. Because of the quick cooling, there isn’t enough time for crystals to grow, and the rock become fine grained (has a smooth texture.
What are some examples of igneous rock?
Granite - Granite is an intrusive igneous rock which is well known because of its salt and pepper colour. Granite also has obvious crystals
Diorite - Diorite is a form of granite and looks very similar to it.
Pumice - Pumice is an extrusive igneous rock that is most known for its porous texture. Pumice is also very lightweight
Basalt - Basalt is an extensive igneous rock with a curved and glassy texture
What is a sedimentary rock?
A sedimentary rock is a rock that is formed by sediments which are stuck together by pressure and natural cements made by chemicals in the soil.There are 3 subclasses of sedimentary rocks, clastic, chemical and organic.
What are the features of sedimentary rocks?
Sedimentary rocks are often formed nearby a water source and are porous ( lots of little holes). Most sedimentary rocks are often quite soft compared to igneous rocks.
What is a clastic sedimentary rock?
A clastic sedimentary rock is a sedimentary rock which has layers and is formed by pieces of weathered rock (a type of sediment) and are usually quite soft as the grains don’t interlock. These rocks may contain fossils.
What is a chemical sedimentary rock?
A chemical sedimentary rock is formed when minerals that were dissolved in water come out of a solution. These rocks contains crystals and have a chemical composition. These rocks are soft.
What is an organic sedimentary rock?
An organic sedimentary rock is comprised of mostly dead plant and animal materials can in some cases can be layered. These rocks are soft and can can fossils.
What are some example of sedimentary rocks?
Sandstone - Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock formed by compressed sand particles. These rocks have obvious layers, and when you rub your finger over them, it will give off a sandy texture.
Conglomerate - Conglomerate is a clastic sedimentary rock which is formed by small pieces of gravel stuck together with red mud. Although it is quite different to other clastic rocks, it is quite easy to identify.
Shale - Shale is a clastic sedimentary rock which is formed by compressed silt or mud. Colours may vary, but shale is usually grey. Layers are quite visible.
Rock Salt - Rock salt is a chemical sedimentary rock where it is formed by sediments that are discovered after water evaporates. Rock salt also has a chemical composition (NaCl) and it has a metallic lustre
Chert - Chert is a chemical sedimentary rock comprised mainly of quartz. It has a chemical composition of silicon oxide (SiO2) and has a fine grained texture.
Dolomite - Dolomite is a chemical sedimentary rock comprised of calcite. It looks and is quite similar to limestone.
Coal - Coal is an example of organic sedimentary rock and is mostly comprised of dead plant material compressed over the years. Coal is a deep black colour.
Coquina - Coquina is an organic sedimentary rock comprised of the shells of dead molluscs or clams.
Chalk - Chalk is a variety of limestone which is known for its fine texture.
What is a metamorphic rock?
A metamorphic rock is created by an igneous or sedimentary rock undergoing intense heat and pressure underneath earths crust. There are two types of metamorphic rock, foliated and non foliated. They are usually much harder than sedimentary rocks
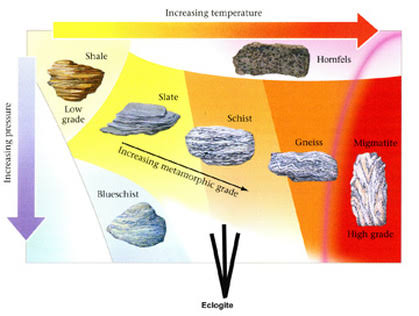
What is a foliated metamorphic rock?
A foliated metamorphic rock is a metamorphic rock that has layers or bands of crystals
What is a non foliated metamorphic rock?
A non foliated rock is a rock where the crystals are randomly arranged.
What are some examples of metamorphic rock?
Gneiss - Gneiss is a foliated rock where schist and other igneous rocks are put through intense heat and pressure. Gneiss looks similar to granite but it has layers.
Slate - Slate is a fine grained and foliated rock, which is created under the alteration of shale or mudstone. It can be split into thin sheets
Schist - Schist is a foliated metamorphic rock. Schist is formed by mudstone or shale, and has decently large grains
Marble - Marble is a hard smooth rock made by limestone or chalk through strong heat and low pressure
Quartzite - Quartzite is created through high heat and pressure on quartz rich sandstone, which effectively fuses them together
Hornfels - Hornfels is a non foliated metamorphic rock which is usually quite dark in colour
Rocks & Minerals
What is a mineral?
A mineral is a naturally occurring, inorganic substance which includes a crystalline substance and a chemical composition.
What is a rock?
A rock is a naturally occurring, inorganic substance comprised of many different minerals and other organic debris. Rocks can be classified into 3 different groups based on how they are formed.
Properties of Rocks and Minerals
Colour - What ray of light shines onto the substance?
Weight - How heavy is the object?
Transparency - Is the object see through?
Density - How compact are the substance’s particles?
Hardness - Can this object get scratched or cut through by another object? (Test with the Mohs Hardness Scale)
Lustre - What type of shine is on the mineral?
Streak - When scratched an object, wat colour powder does the mineral leave off?
Mohs Hardness Scale -
What is the Mohs Hardness Scale?

The Mohs Hardness Scale indicates how prone a mineral or rock is to scratching. The higher the number on the scale the harder it is.
Example:
On the picture, we can see that quartz has a higher rank than fluorite. We know this as quartz has a 7 on the hardness scale and fluorite has a 4. This means that quartz has the ability to scratch fluorite.
What are the three types of rocks?
The three types of rocks are sedimentary, igneous and metamorphic. Rocks are classified by how they are formed. Each of these categories have different subclasses.
What is an igneous rock?
Igneous rocks are formed by cooled magma, (melted rock below the Earth surface) Igneous rocks and be classified into two subclasses, extrusive (volcanic) igneous rock and intrusive (plutonic) igneous rock. Some examples of igneous rock are granite, pumice, basalt and obsidian.
What are the features of all igneous rock?
An igneous rock is usually quite hard an solid, as all igneous rocks have interlocking crystals. Due to the extreme heat of magma, igneous rocks will never have fossils.
What is an intrusive igneous rock?
An intrusive igneous rock is also known as plutonic rock. These rocks are formed by cooled magma underneath the ground. This process happens quite slowly, allowing lots of crystals to grow. As a result, these rocks are coarse grained (has a rough texture)
What is an extrusive igneous rock?
An extrusive igneous rock (or volcanic rock) is formed when a volcano erupts and the lava quickly cools. Because of the quick cooling, there isn’t enough time for crystals to grow, and the rock become fine grained (has a smooth texture.
What are some examples of igneous rock?
Granite - Granite is an intrusive igneous rock which is well known because of its salt and pepper colour. Granite also has obvious crystals
Diorite - Diorite is a form of granite and looks very similar to it.
Pumice - Pumice is an extrusive igneous rock that is most known for its porous texture. Pumice is also very lightweight
Basalt - Basalt is an extensive igneous rock with a curved and glassy texture
What is a sedimentary rock?
A sedimentary rock is a rock that is formed by sediments which are stuck together by pressure and natural cements made by chemicals in the soil.There are 3 subclasses of sedimentary rocks, clastic, chemical and organic.
What are the features of sedimentary rocks?
Sedimentary rocks are often formed nearby a water source and are porous ( lots of little holes). Most sedimentary rocks are often quite soft compared to igneous rocks.
What is a clastic sedimentary rock?
A clastic sedimentary rock is a sedimentary rock which has layers and is formed by pieces of weathered rock (a type of sediment) and are usually quite soft as the grains don’t interlock. These rocks may contain fossils.
What is a chemical sedimentary rock?
A chemical sedimentary rock is formed when minerals that were dissolved in water come out of a solution. These rocks contains crystals and have a chemical composition. These rocks are soft.
What is an organic sedimentary rock?
An organic sedimentary rock is comprised of mostly dead plant and animal materials can in some cases can be layered. These rocks are soft and can can fossils.
What are some example of sedimentary rocks?
Sandstone - Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock formed by compressed sand particles. These rocks have obvious layers, and when you rub your finger over them, it will give off a sandy texture.
Conglomerate - Conglomerate is a clastic sedimentary rock which is formed by small pieces of gravel stuck together with red mud. Although it is quite different to other clastic rocks, it is quite easy to identify.
Shale - Shale is a clastic sedimentary rock which is formed by compressed silt or mud. Colours may vary, but shale is usually grey. Layers are quite visible.
Rock Salt - Rock salt is a chemical sedimentary rock where it is formed by sediments that are discovered after water evaporates. Rock salt also has a chemical composition (NaCl) and it has a metallic lustre
Chert - Chert is a chemical sedimentary rock comprised mainly of quartz. It has a chemical composition of silicon oxide (SiO2) and has a fine grained texture.
Dolomite - Dolomite is a chemical sedimentary rock comprised of calcite. It looks and is quite similar to limestone.
Coal - Coal is an example of organic sedimentary rock and is mostly comprised of dead plant material compressed over the years. Coal is a deep black colour.
Coquina - Coquina is an organic sedimentary rock comprised of the shells of dead molluscs or clams.
Chalk - Chalk is a variety of limestone which is known for its fine texture.
What is a metamorphic rock?
A metamorphic rock is created by an igneous or sedimentary rock undergoing intense heat and pressure underneath earths crust. There are two types of metamorphic rock, foliated and non foliated. They are usually much harder than sedimentary rocks

What is a foliated metamorphic rock?
A foliated metamorphic rock is a metamorphic rock that has layers or bands of crystals
What is a non foliated metamorphic rock?
A non foliated rock is a rock where the crystals are randomly arranged.
What are some examples of metamorphic rock?
Gneiss - Gneiss is a foliated rock where schist and other igneous rocks are put through intense heat and pressure. Gneiss looks similar to granite but it has layers.
Slate - Slate is a fine grained and foliated rock, which is created under the alteration of shale or mudstone. It can be split into thin sheets
Schist - Schist is a foliated metamorphic rock. Schist is formed by mudstone or shale, and has decently large grains
Marble - Marble is a hard smooth rock made by limestone or chalk through strong heat and low pressure
Quartzite - Quartzite is created through high heat and pressure on quartz rich sandstone, which effectively fuses them together
Hornfels - Hornfels is a non foliated metamorphic rock which is usually quite dark in colour
 Knowt
Knowt
