Geological Oceonagraphy
71% of the earth is covered by water
N. Hemisphere ~ 60%
S. Hemisphere ~ 81%
Oceans are the main source of saltwater
5 oceans that scientists identified but refer to as the main bodies that create waves, currents, and other ocean phenomena
Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, Arctic
Out of the 5, the Southern is the newest, relatively identified
Pacific is the largest/deepest
Atlantic is the second largest, and the smallest is the Arctic. The Southern Ocean is the second smallest
Earth is created based on density
Density: how much something weighs in a particular area
The more weight is spread out, the easier it is to manage
Ex) An 80-pound cell phone versus an 80-pound ceiling. You can hold up the latter in one hand
Oceanic Crust (Oceanic plates/Continental plates)
Younger, thinner, but extremely heavy
Continental crust
Older, thicker, but lighter
Both of them are lighter than the mantle
Diverging plates vs Converging plates
Diverging plates:
Move away from each other
Forms mid-ocean ridge
Big crack in the Atlantic Ocean, from the N. Pole to S. Pole, the only part of Earth where new land is being formed constantly is in the Atlantic Ocean
Convergent plates:
2 oceanic crusts form a subduction zone
Deep sea trench
Lots of lifeforms in these environments are undiscovered
Subduction zones: The region where an oceanic plate sinks down into the asthenosphere at a convergent boundary, between continental and oceanic plates
Hydrothermal vents:
Organisms are constantly being found and identified in the hydrothermal vents, they’re a land of their own
Lots of bacteria and fish
The Pacific Ocean has converging plates, the Atlantic Ocean has diverging
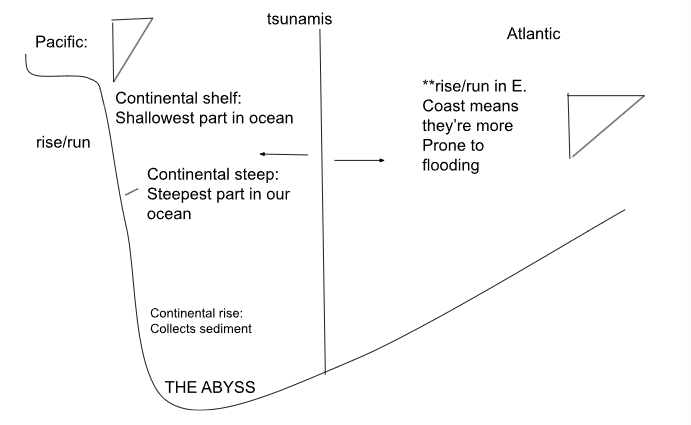
Further elaboration: You can walk around 100 yards in the Atlantic Ocean on the East Coast and still be only ankle high. However, if you take a few steps in the Pacific, you’ll be met with a steep drop because there is only a tiny portion of the water is shallow
Earthquake activity is increased towards the Pacific, a tsunami is formed by earthquakes, and there’s more earthquake activity there
A huge amount of energy in a small space increases its pressure. The pressure creates a massive tsunami, and the drastic change of slope forces the water to be pressurized
Earthquakes have to happen in the open ocean
 Knowt
Knowt