Lecture #6: Hinduism Flashcards
Lecture #6: Hinduism-
Foundations of Hinduism:
Origins of Hinduism:- not a founded religion
- No single founder
- Founding of Hinduism vs the foundations of Hinduism
Historical Orientation of Hinduism
- Indus Valley Civilization
- Aryans- ‘noble ones’- C. 1500 BCE
- Vedic period (1200-200 BCE)
Source of Hindu Myths:
Veda
- ‘Knowledge’ (Sanskrit)
- Collection of early Hindu religious scriptures
- Also known as samhitas (‘collection’)
Two general types of Vedic scriptures:
Shruti: ‘heard’; considered divinely inspired, fully authoritative
Smurti: ‘remembered’; products of the minds of the great Hindu sages interpretation of shruit and make them meaningful to followers.
Sages: wisdom people
What the vedas are
2 genres of literature
Upanishads:
- ‘Sitting down near’- upa= ‘near’; ni= ‘down’; sad= ‘to sit’
- Collection of teachings about self and ultimate reality
- Last part of Hindu scriptures
Bhagavad Gita:
- ‘The song of God’ (Sanskrit)- most cherished document in Hinduism
- Summarizes the fundamental beliefs of Hinduism- e.g., Ultimate Reality, Braham, atman, moksha, duties of life, how to live according to the laws of dharma, etc.
Understanding of Ultimate Reality:
Brahman:
- ‘Spirit’, ‘to be great’ (sanskrit)
- Divine reality at the heart of all things; present in all things
- Energy that sustains the universe-formless, eternal
- Creator, preserver, and transformer of everything
- Appears in created beings (e.g humans) as atman
Atman: in hinduism ___ is divine reality, in buddhism it is ____. Know atman and anatman.
- Divine reality at the heart of all things as experienced within oneself
- Brahman and atman are identical and in fact the same thing!
What does it mean to know Brahman?
- Lived experience that all things are holy because they come from the same sacred source. Therefore, all things are ultimately one.
- “The truth is One, but different sages call it by different names.” (Rig Veda 1.164.46)
Maya:
- ‘Illusion’ (Sanskrit)
- Belief that the world, as we know it, is an illusion, not true reality
- Through deep meditation, begin to know and understand true reality that all things are One because Brahman and atman are identical
Hindu Deities:
Trimurti:
- ‘Triple form’; also known as the Hindu Trinity
- Trinity- concept that god/deity has 3 aspects which are different forms of the same god/deity
- Brahma (creator, source of life) + Vishnu (preserver) + Shiva (transformer/destroyer)
- Together, represent the cosmic functions of creation, maintenance, and destruction of life (life, death, rebirth)
Other Hindu deities include:
- Indra- warrior deity, associated with thunderstorms
- Agni- God of fire, associated with the sun
- Soma- god of the drink consumed by priests during fire sacrifices
- Brihispati- patron deity of Hindu priests
Fundamental Hindu Beliefs:
Brahman- ultimate reality at the heart of all things
Atman- existence of an enduring atman that transmigrates from one physical form (body) to another at death
Human nature one of bondage to ignorance and illusion (maya) - but we can escape this
Samsara- means ‘to flow together’, eternal cycle of cosmic functions (wheel) of birth, suffering, death, and rebirth (NOTE difference between samsara and reincarnation) —birth, life, death, rebirth (constant cycle)
Reincarnation- belief that all things have a life force; when life forces loses one form (at death), the life force (atman) is reborn into another form; also known as the transmigration of the atman/soul- when we die, our life force transmigrates into another physical form– why you hear people talk about past life experiences. ***Know for exam
Hierarchy of life forms- humans are not the highest form (superhumans, gods/deities, etc)
Karma- means ‘action’; our actions and their consequences on this life and future lives; sum of a person’s actions and non-actions, thoughts, desires, and intentions in all lifetimes (everything!!) —all the different choices, thoughts, actions. Its cumulative from all of our lifetimes, determines our next rebirth. Good karma-fulfilling the purpose of that entity (purpose of bee is to make honey and pollinate things, a bee would get good karma by doing this. If a bee didn't make honey or do what bees do, then it would get bad karma)
Inherent moral consequence; determines direction of rebirth
If Karma unresolved, atman reborn into new body’ if Karma resolved, attain moksha
Authority of the Vedas and the Brahmins (Hindu priests)-brahma, brahmin, brahmacharin**** know these for exam
Moksha- liberation from rebirth; purpose of human life– we want to achieve this and resolve our karma (get off the wheel of samsara)--- come to understand that everything is Brahman, how we can achieve good karma is doing the things expected of us
Varna- caste system; hereditary division of Indian society; rigid social system
-central to varna are ideas of samsara, reincarnation, karma; if obey rules of case, reincarnation into higher caste is possible (social system) –if you follow the rules of how to live, you accumulate good karma
Dharma- rules of order of how to live**** know the difference between DHARMA in Hinduism and Buddhimsm
Fundamental Hindu Beliefs- Varna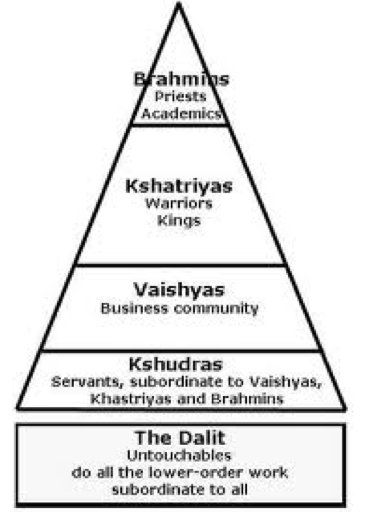
Varna:
Brahmins-priests and academics
Kshatriyas- warrior nobles, ruling class (governance)
Vaishyas- merchants, artisans (community) — if ur a good business owner and pay ur employees well u get good karma, if ur not a good business owner and treat ur workers bad you'll get bad karma
Kshudras-peasants, unskilled labourers, servants
Dalit/Harijan- untouchables, outside of caste system (people outside community)
Fundamental Hindu Beliefs-Goals/Purposes of Life:
- Primary goal is to escape bondage of ignorance and illusion (maya)
- Achieve this by knowing and understanding your place in life and fulfilling the goals appropriate for your station and stage of life
- Goal 1: Dharma
- Dharma = ‘law’, ‘teaching’
- Appropriate living, fulfilling the moral, social, and religious duties of your station
- Goal 2: Artha
- Prosperity, attaining financial and worldly success through legal means
- Goal 3: Kama- pleasure principle
- ‘Delight in the senses’, pleasure – satisfying desires and senses and drives in moderation (pleasure- sleep, sexuality, food, and drink, listening to something you enjoy, all done in moderation)
- Goal 4: Moksha
- Release from rebirth to attain freedom from reincarnation, highest purpose in life
Fundamental Hindu Beliefs- Stages of Life
- Primary goal is to escape bondage of ignorance and illusion (maya)
- Achieve this by knowing and understanding your place in life and fulfilling the goals appropriate for your station and stage of life
- Stage 1: Brahmacharin***
Student stage of life– achieving good karma– reading vedic scriptures, studying, being attentive to studies for school and spirituality - Stage 2: Grihasta
Householder stage of life- includes finding a life partner, marriage, kids, work, employment, contribute to society– achieve good karma (be a good spouse and parent, giving back to community) - Stage 3: Vanaprastha
Retiree stage of life- people are no longer working, spending more time studying scripture - Stage 4: Sannyasin
Renunciate, spiritual focus- someone who lets go of the social world, let go of material things, “hermits”, lives devoted to spiritual world, uncommon for most people (monk, non, clergy), not a social norm, focus is on spiritual pursuits
– follow dharma,
 Knowt
Knowt
