Note
0.0(0)
Chat with Kai
Explore Top Notes Note
Note Studied by 12 people
Studied by 12 people Note
Note Studied by 9 people
Studied by 9 people Note
Note Studied by 1 person
Studied by 1 person Note
Note Studied by 244 people
Studied by 244 people Note
Note Studied by 3 people
Studied by 3 people Note
Note Studied by 41 people
Studied by 41 people
Urbanization (Prehistoric Era to 600 CE)
5.0(1)
Cluster Headache
5.0(1)
Cells Control Enzyme Catalysis
5.0(1)
Chapter 7: Populations
5.0(3)
Lecture 1: Intro to Business
5.0(1)
PATHOLOGY
5.0(1)
Chapter 24:Alcohols and Carboxylic acids
Alchohols
Alcohols contain the hydroxyl (-OH) functional group
Alcohols are a homologous series of compounds that have the general formula CnH2n+1OH
They differ by one -CH2 in the molecular formulae
Ethanol : C2H6OH
Methanol CH3OH
Propanol C3H7OH
Butanol C4H9OH
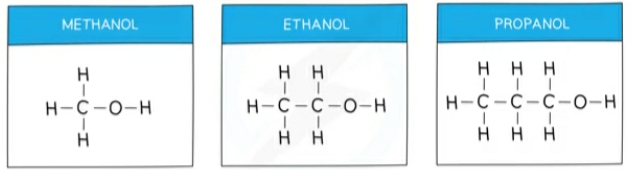
There are two methods used to manufacture ethanol:
1.The hydration of ethene with steam
- [ ] Ethene is bubbled through a phosphoric acid catalyst under pressure and at a temperature of 300°C.
- [ ] Ethene + steam ➡️ethanol
2.The fermentation of glucose
- [ ] Conversion of glucose /sugar to ethanol and carbon dioxide by the action of enzymes in yeast at 20°C
- [ ] Glucose ➡️ethanol + Carbon dioxide
Uses of ethanol
- Cosmetics
- solvents
- achoholic drinks
Carboxylic acids
compounds that all contain the same functional group: –COOH
They have the general formula: CnH2n+1COOH
They are colourless liquids
They react with alkaline solutions, turn blue litmus red and form salts called ethanoates
They have the general formula: CnH2n+1COOH
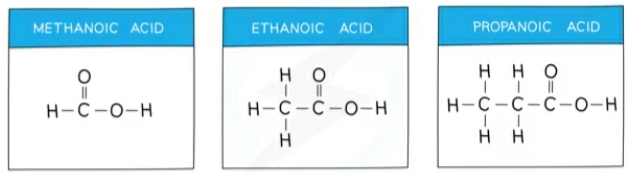
Two methods used to make carboxylic acids are:
1.Oxidation by fermentation
2.Using oxidising agents
Esters
- Alcohols and carboxylic acids react to make esters in esterification reactions
- Esters are compounds with the functional group R-COO-R
- Esters are sweet-smelling oily liquids used in food flavourings and perfumes
- Ethanoic acid will react with ethanol in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid (catalyst) to form ethyl ethanoate
Naming esters
- The first part of the name indicates the length of the carbon chain in the alcohol
- it ends with the letters ‘- yl’
- The second part of the name indicates the length of the carbon chain in the carboxylic acid
- and it ends with the letters ‘- oate’
Polymers
- Polymers are large molecules built by linking 50 or more smaller molecules called monomers
- Synthetic polymers are ones made in a factory, for example nylon.
Note
0.0(0)
Chat with Kai
Explore Top Notes Note
Note Studied by 12 people
Studied by 12 people Note
Note Studied by 9 people
Studied by 9 people Note
Note Studied by 1 person
Studied by 1 person Note
Note Studied by 244 people
Studied by 244 people Note
Note Studied by 3 people
Studied by 3 people Note
Note Studied by 41 people
Studied by 41 people
Urbanization (Prehistoric Era to 600 CE)
5.0(1)
Cluster Headache
5.0(1)
Cells Control Enzyme Catalysis
5.0(1)
Chapter 7: Populations
5.0(3)
Lecture 1: Intro to Business
5.0(1)
PATHOLOGY
5.0(1)