test 2 study guide
Study Guide for Immune, Inflammation, Infection, Adrenergics and Cholinergics
- Immune/Inflammation
- Understand passive and active immunity and which uses gamma globulins
Active- natural contact with infection
Passive- transfer for mother to child OR injectio of human GAMMA GLOBULIN
- Be able to differentiate your immunoglobulins (IgG, IgE, IgM, IgA….)
HUMORAL IMMUNE SYSTEM – ANTIBODIES
Type of Antibody | |
|---|---|
IgD | Present in plasma Protects against bacterial and viral infections |
IgM | Largest antibody First made to fight a new infection Transferred to nursing infant |
IgG | Makes up 80-85% of plasma antibodies Protects against infection Transferred across placental barrier providing immunity to fetus Transferred to nursing infant |
IgA | Found mainly in body secretions: saliva, tears, mucus, colostrum Transferred to nursing infant |
IgE | Involved in allergic reactions Located in mucosal lining of respiratory and GI tracts |
Which are passed to neonate through breastfeeding
- A, G, E
- What cells are involved in immunity?
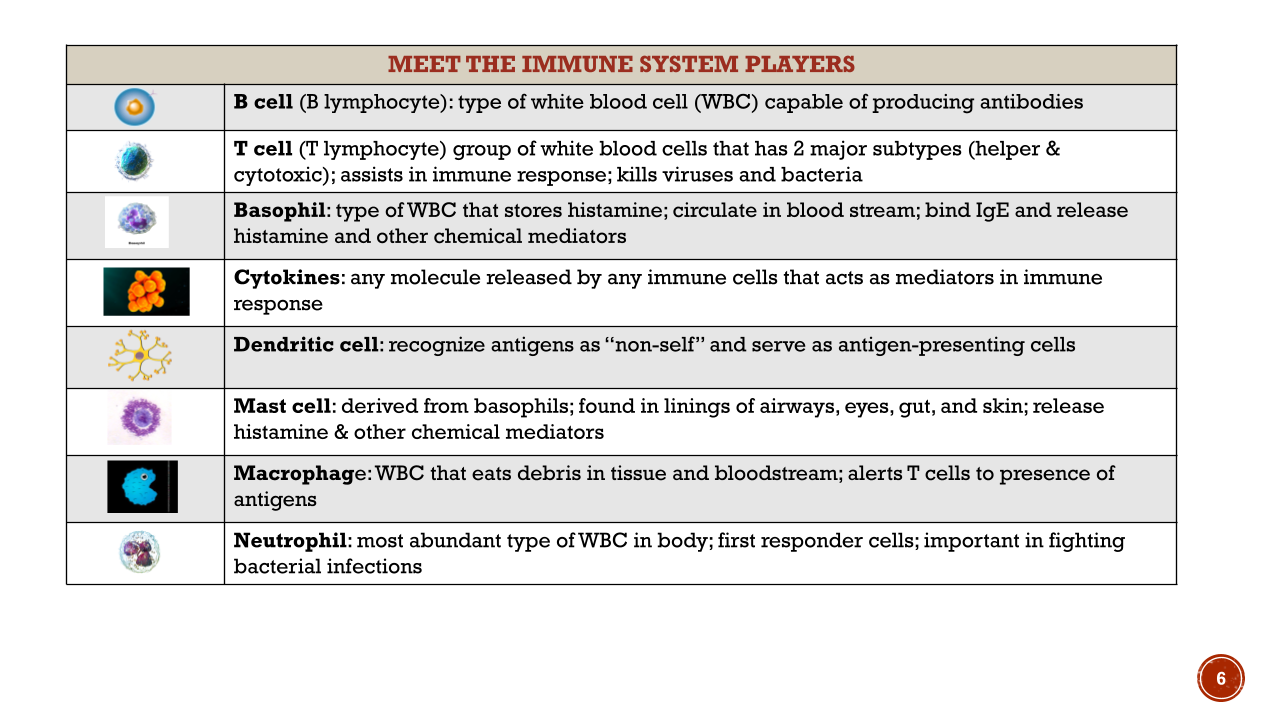
Look at MAST CELLS derived from basophils
Basophils store Histamine
- Understand B cells and T cells and what their roles are
B cells- produce antibodies
T cells: helper and cytoxic
Basopils: store histamine
Dendritic cell : recognize antigens as non-self
Neutrophils: are the most abundant
Memory trick: visualize antibodies as the soldiers produced by your body going to attack and neutrilaze antigens (enimes)
ACQUIRED IMMUNE SYSTEM
On test:
- primary response: 1- 2 weeks before antibody reaches efficacy (desired therapeutic effect)
- Secondary response: more rapid response efficacy in 1-3 days
Immune Response | Primary Cells | Functions | Protection |
|---|---|---|---|
Humoral (antibody-mediated) |
|
| Mainly bacteria |
Cellular (Cell-mediated) |
|
| Viruses, cancer, tumor cells & transplanted cells |
Humoral Response primarily protects against bacteria and viruses
Understand autoimmunity and alloimmunity - teaching on meds for transplant
- Autoimmune: body attacks itself
- Alloimmunity: body rejects transplant
- Immunosupressant - cyclosporine- helps slow downe system say you get a transplant you can this med to the body does not reject
- CYCLOSPORINE
- Adverse effects: kidney damage. Risk for injection
- Do not give with grapefruit, NSAIDs, and avoid crowds
- What do your lymph organs do? - what is lymphadenopathy?
- Lymphadenopathy is the swelling of the noses secondary to autoimmune disease
- Hypersensitivity reaction
- CYCLOSPORINE
Hypersensitivity Reactions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Type | Antigens | Onset | Mechanism | Disorders |
I ** | Pollen, foods, drugs, animal dander | Immediate | IgE binds to mast cells & basophils → releases chemical mediators | Hay Fever, asthma, food allergies, dermatitis/eczema, anaphylaxis |
Type 2: blood transfusion
- What does histamine do? What are signs & symptoms of the presence of histamine?
, histamine & other substances are released from mast cells, basophils, and other cells in response to antigens circulating in the blood. FIght infection
- Vasodilation
- Flushing: face and upper body
- If extensive can cause hypotension
- Increased capillary permeability
- Edema
- Bronchoconstriction
- CNS
- Drowsiness, foggy-headed
- Mucous membranes
- Increased mucous production
- Runny nose, teary eyes
- Peripheral nerves
- Itching, pain
- Do not memorize tasks of every chemical mediator, but know what they are
Chemical mediators: - complement, cytokines, histamine, leukotrienes, prostaglandins
- What does hypersensitivity look like?
Type | Antigens | Onset | Mechanism | Disorders |
|---|---|---|---|---|
I ** | Pollen, foods, drugs, animal dander | Immediate | IgE binds to mast cells & basophils → releases chemical mediators | Hay Fever, asthma, food allergies, dermatitis/eczema, anaphylaxis |
II | May be self or foreign (tissue-specific) | Delayed | IgG or IgM binds to antigen on cell surface → cell lysis & tissue damage | Blood transfusion (foreign), Goodpasture’s syndrome (kidney), Graves’ disease (thyroid) |
III | Fungal, viral, bacterial | Immediate or delayed | IgG or IgM binds to antigen → creates immune complexes → inserts into small blood vessels, joints, & glomeruli → inflammation & tissue damage | Rheumatic fever, rheumatoid arthritis, post-strep glomerulonephritis, type I diabetes mellitus, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) |
IV | Fungal, viral, bacterial, foreign substances: foreign tissue, metals, rubber, plants | Delayed | Cell-mediated: sensitized T cells → attack antigen → inflammatory response | Contact dermatitis, poison ivy, transplant rejection, TB infection, PPD (TB skin test) |
- How do you differentiate and determine anaphylaxis? - what is treatment?
Defining characteristics
-hypotension
-laryngeal edema
-bronchospasm
Severity depends on the level of response: local or systemic
Reaction is immediate & can be life-threatening
Itching, erythema, headache
Vomiting, abdominal cramps, diarrhea
Contraction of respiratory bronchioles
Laryngeal edema
Vascular collapse
**If you use an EpiPen, call 911!!!
Even if the patient seems better.
- In a reaction, if there is any respiratory/breathing symptom what is treatment?
EPIPEN
- What are side effects of antihistamine drugs?
Sedation! Especially with first gen
- Differentiate between 1st and 2nd generation antihistamines
ANTIHISTAMINES: FIRST GENERATION- benodryl
- Mechanism of action
- Compete with histamine for H1 receptors in tissues → block the actions of histamine
- Not bullies
- Give before (prophylactic) or early in allergic response
- Compete with histamine for H1 receptors in tissues → block the actions of histamine
- Can bind to (wet) muscarinic receptors → anticholinergic (dry) effects
- Drying of mucous membranes , DRY mouth
ANTIHISTAMINES: 2ND GENERATION
- Mechanism of action
- Similar to1st generation
- do not cross/minimally cross the blood-brain barrier → much less sedation
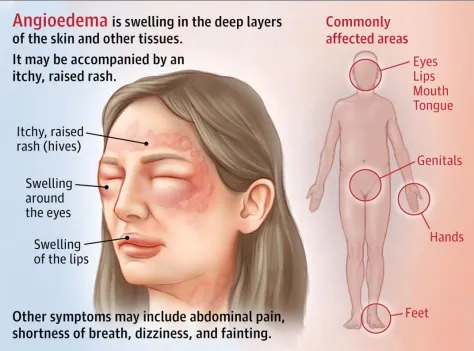
What is angioedema?
With immunosuppression, what are our worries?
- Getting sick
5mm TB test
Know T cells, B cells, cytokines, macrophages
Adreergic, IGG and IGM,
Drugs,: tetro-teeth
Asprin- can thin the blood you do not combine anticoag like warfarin and heparin bc too much bleedign
Celebox(NSAID) increased risk of MI and stroke
Tylenol is metabolized by LIVER and does no thave antiinflamator effects
Prednisone (glucocorticoids) is a steroid and adverse effects include hypergylcemia, PUD, and suceptibility to infection TAPER off
- Infections
- KNOW your antibiotics - their side effects specific to each, and indications or what to avoid when on them.
- Know how to prevent side effects for vancomycin
60-90 min slow rate
- Understand an infection workup and how to prioritize those tasks
- What do you do when you suspect an allergy to an IV drug?
STOP INFUSION CALL DR
- Know about interpreting TB tests
- Tuberculin skin test (TST)
- Positive if ≥15 mm induration in low-risk individuals
- Immune compromised-may not respond as well to PPD
- Reactions ≥5 mm considered positive
- Know about active vs latent TB
- Milary TB is organisms spread via bloodstream
- Understand HIV testing
Transmision is throught blood, semen, vaginal secretions and breast milk. It targets and kills T cells
Transmision is more likley when viral load is high
- Viremia: large viral levels in blood for 2-3 weeks
- Pathophysiology of GIV damage to CD4 and T cels (T helper cells_
- When T helper cells drop to <500 NORMAL IS 800-1200
A diagnosis of AIDS cannot be made until the HIV-infected patient meets criteria established by the CDC.
AIDS is characterized by:
- Severe immune system suppression and CD4+ T-cell counts < 200 cells/μL
- An opportunistic infection
- An opportunistic cancer
- Wasting syndrome (loss of 10% or more of ideal body mass)
- AIDS dementia complex (ADC).
- Understand the importance of T& CD4 cells in HIV
- Symptomatic infection when CD4+ T cekks trioto 200-500 normal is 800-1200
- Know diff b/w AIDS and HIV Cd4ct Helper T cells reduse risk of spreading and getting
- Understand the goal of HIV treatment with ART
- Understand the importance of T& CD4 cells in HIV
Treated with antireoviral therpay for mothers to decrease viral load
Cd4+ normal range is 800-1200 cells
Nursing implications for Penicillin
- Give IM
- Give IV to not add or mix another drug
Cephalexan
- give PO
Vancomyacin
- Used fro serious infections such as C DIFF and MRSA can get Red Mans syndrome so you need to administer IV drug slowly over 60-90 min
Tetracycline: no dary products causes teeth color change
Levofloxacin - tendonitis and tendon rupture
- Adrenergic/Cholinergic
- Understand selectivity and its relationship to dosing
- Know your beta 1, beta 2, and alpha functions
- Know your muscarinic functions
Cholinergic Drugs (weT)
- Agents that influence the activity of cholinergic receptors
- The Receptors:
- Nicotinic N
- Nicotinic M
- Muscarinic - THIS is where our focus lies.
- cause contraction of ciliary eye muscles, decreased heart rate, constriction of bronchi, voiding, increased intestinal tone & motility, sweating, vasodilation
Muscarininc Agonist: Bethanechol
- Nurisng considerations : take on empty stomach
- Overdose: treat with atropine
- Increases peeing
- Rest and digest: wet response causes bradycardia
ATROPINE- drys em up so its a muscarininc antagonist
Epinephrine- activates ALL ADRENERGIC receptors
Beta 2 agonist is Albutteroll used for Asthma
Alpha 1: pupil dilation Increase BP
Alpha 2: norepinephrine release
Beta 1: increase HR
Beta 2: dilation of bronchioles
Prozasosis: 1st dose effect experience hyposttit