review
Neruons are the ciruts that underline addiction
addiction is pathology in the brain
read chapter readings fillbey
neurons send info- make sure you know how
modles of addiction
Behaviroal psych
operant: movements are reinforced thro rewards (food)
Classical: Stimuli that occur together build learned associations
Habituations: over repeated experance responses are reduced (as something happens over and over we care about it less) (why people keep uping dose)
sensitization: an increased response can be elicited given the right stimulus (if given a shock we get back to hightened response) (matters because addiction relies on stimuli assocated with drug) (for example changing location will increase reposnse to drugs)
Tolerant
withdrawl
critrea DSM
Indidual
Brain disease model
Ventral Tegmental Area- dopamine encodes rewards
Nucleus accumbens- recives dopamine, determines hedonic please and intergrates it into movment plans
Why does it matter how we define addiction
social theory
gentic basis
Blah
Blah
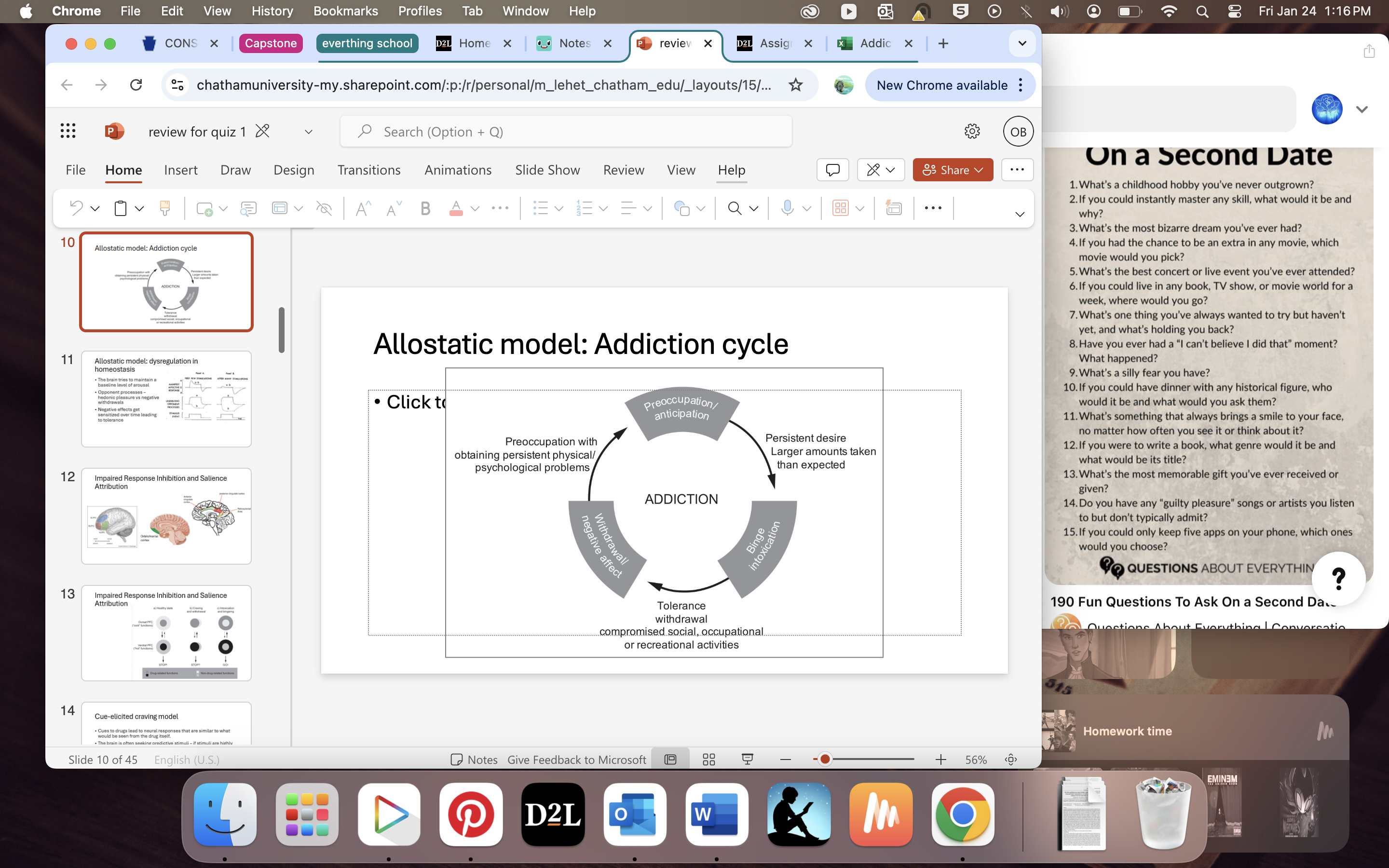
Alloostatic model
brain is trying to maintain basline level of arrousal
oppenent processes- hedonic pleasure vs neg withdrawls (crash after caffine)
Neg effect gets senstized over time
Impaired response inhibition and salience
regulatory stuff is at odds with emotional drives, but in a normal brain the normal regulatry drives influcances behaviors more than emotions
as addiction takes over emotional dives start to take over
as it moves to true addiction sets in those normals really discrease and effect normal function
cue elicited craving model
cues to drugs lead to neural responses that are simliar to what would be seem from the drug itself
the brain is often seeking predective stimuli- if stimuli are highly predective of s very rewarding things (drugs) then the resposne will be enhances
condition associations lead to emotional, motivational and movment planning proportanate to the value (reward) of the assocated stumli
things we do before drug use gets programed as a dompamine cue and will possible cause cravings (putting on shoes to go get drugs now everytime you put on shoes you get a small craving to get drugs, even if only 30% of the time you put on shoes to get drugs)
Types of channles
These are types of openings that allow the inside and the outside of the cellto exchange stuff across the cell membraine
ions- lets specific ions (NA+, Ca+2, Cl-, K+) flow across cell mem
Gatted cahnnles need an ion or nerutransmiter to open them
DNA→ RNA → amino acids → functional proteins → vessicles → changes in cell
may not be on test but know how DNA gets turned into changes into cell
Zinc fingers and epigentics
How DNA can have certain areas blocked or turns into proteins more
what the protein turns into depends on what part of the DNA gets transcribed
some parts of gentic codes are deactiveated by these while other parts are emphased and get turned into proteins
happens in nucleus
can happen cause of stress, diet, drugs, and ect
where do these receptors enzymes and proteins come from
DNA and one area gets copied into RNA and then gets turned into amino acids
the amino acids get repackaged over and over again till the protiens are doing what they need to do in the body
Variety in protein assembly leads to variety of function
Gabba receptor can be made of multiple differnt parts in differnt ways, depending on what protens get folded together will effect shape and what it does'
basicly depending on what proteins are folded it changes the function of said amino acid
G- protein coupled receptors
do lots of things
change what genes get turned into proteins
Basic process of neural transmistion
Chemical → elcetrical → chemical
Cell 1 realeses nerotransmiter → cell 2 ligand gated ion channles are opened by the neurotranmiter, post synaptic potentials, action potentals, vessicles fusion, (slide 22 review) (VERY IMPORTANT!!!!!)
Steps of chemical messaging
reception- nerotransmiters being recived
intergation- ions join the cells and info gets encoded
electrical switch
signal prpagation
signal transduction into chem messengars
Dendrites
integrate imputs from lots of othe neruons
if. excitory (pos charges from ions that come in)
if excitory enough that they push the cell past the threshold and cause action potential
synaptic cleft
ligengated ion channels,
Action potenional
voltage gated channles are for action potential- not on dendrites tho
its the same every time
sodium ions go in & ions go outt, membrane potential changes as they flow in & flow out
Action potential
membrane potential
potasium
repolarization
hyperpolarazation is below normal
sodium that comes in from depolarizatison spreads out within cell (food coloring and H2O)
Mylinzation
stops flow of ions
and gets turned into energy then back into ions
Synapse
once the action potential reaches the synaptic button (bouton, terminal, synapse)
Action potential reach synapse
calicium is important
LTP
glutamate channles are AMPA channles and NMDA channles
1st activation is AMPA, 2nd is both
sporatic means that these channles feel and cause LDP