Bio- 2B
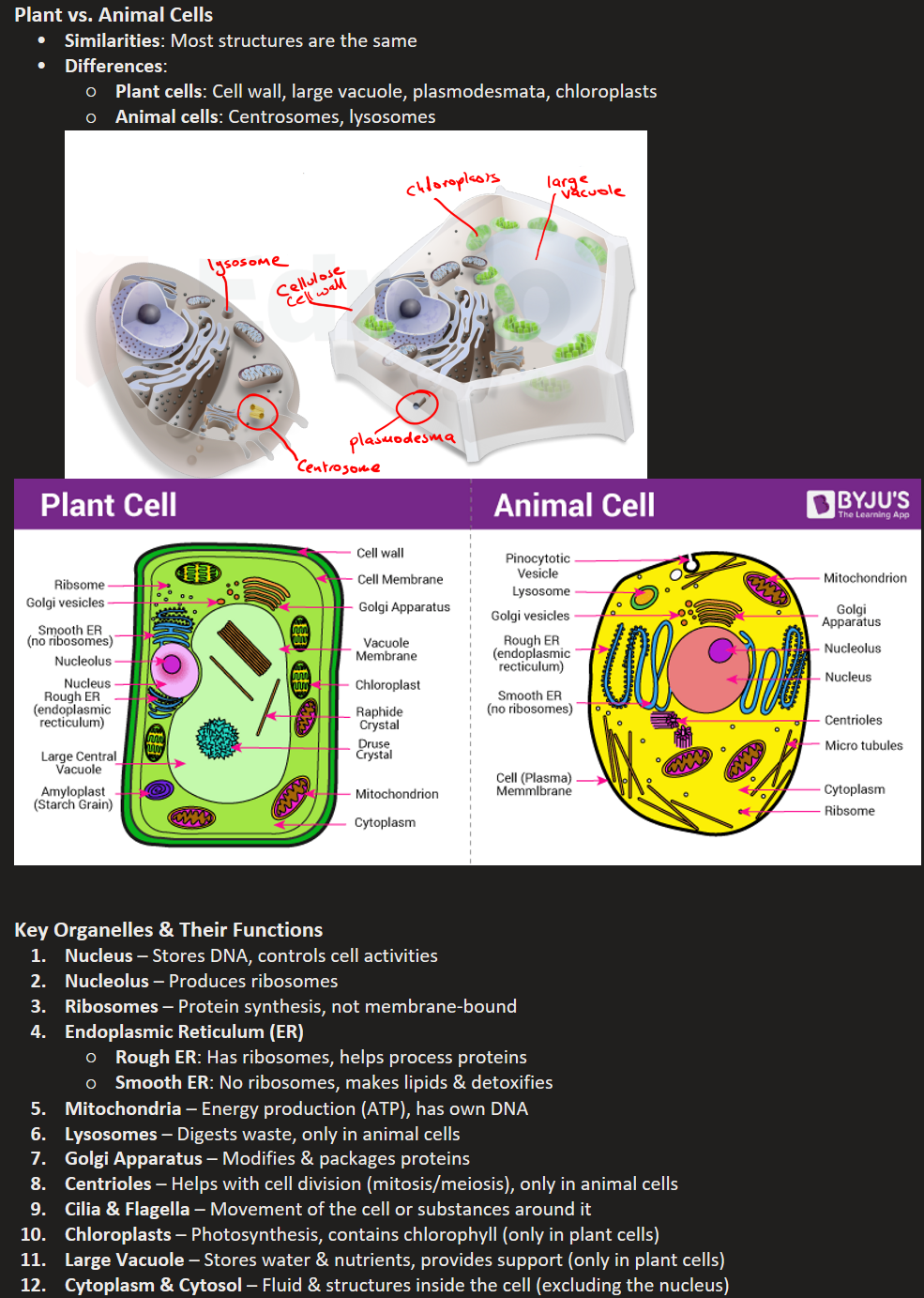
Plant vs. Animal Cells
Similarities: Most structures are the same
Differences:
Plant cells: Cell wall, large vacuole, plasmodesmata, chloroplasts
Animal cells: Centrosomes, lysosomes
Key Organelles & Their Functions
Nucleus – Stores DNA, controls cell activities
Nucleolus – Produces ribosomes
Ribosomes – Protein synthesis, not membrane-bound
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Rough ER: Has ribosomes, helps process proteins
Smooth ER: No ribosomes, makes lipids & detoxifies
Mitochondria – Energy production (ATP), has own DNA
Lysosomes – Digests waste, only in animal cells
Golgi Apparatus – Modifies & packages proteins
Centrioles – Helps with cell division (mitosis/meiosis), only in animal cells
Cilia & Flagella – Movement of the cell or substances around it
Chloroplasts – Photosynthesis, contains chlorophyll (only in plant cells)
Large Vacuole – Stores water & nutrients, provides support (only in plant cells)
Cytoplasm & Cytosol – Fluid & structures inside the cell (excluding the nucleus)