Chapter 20: Antimicrobial Drugs
Spectrum of Antimicrobial Activity
Narrow spectrum antibiotics
Targets specifically gram-negative only or gram-positive only
Broad-spectrum antibiotics
Targets both gram positive and gram-negative
Superinfection - overgrowth of normal microbiota that is resistant to antibiotics
Antibiotics affect normal microbiota which then allows other bacteria or viruses that are not affected by the antibiotics to proliferate and cause an infection.
Action of Antimicrobial drugs
Bactericidal → Kill microbes directly
Bacteriostatic → prevent microbes from growing
Major Action Modes of Antibacterial Drugs
Inhibition of cell wall synthesis
Penicillins prevent the synthesis of peptidoglycan
Inhibition of protein synthesis
Target bacterial 70S ribosomes
Chloramphenicol, erythromycin, streptomycin, tetracyclines
Inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis
interfere with DNA replication and transcription
Rifamycin, quinolones (nalidixic acid) & fluoroquinolones
Injury to plasma membrane
Polypeptide antibiotics change membrane permeability
Ionophore antibiotics: allow for uncontrolled movement of cations
Inhibition to essential metabolite synthesis
inhibits the creation for nucleotides
Anti-metabolites compete with normal substrates for an enzyme
Sulfanilamide competes with para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), stopping the synthesis for folic acid
Antiviral drugs
Entry and fusion inhibitors
Block the receptors on the host cell that bind to the virus
Block fusion of the virus and cell
Uncoating, genome integration, and nucleic acid synthesis inhibitors
Prevent viral uncoating
Inhibit viral DNA integration into the host genome
Nucleoside analogs inhibit RNA/DNA synthesis
Assembly and exit inhibitors
Protease inhibitor - block the cleavage of protein precursors
Exit inhibitors - inhibit neuraminidase, an enzyme required for some viruses to bud from the host cell
Interferons
Produced by viral-infected cells to inhibit further spread of the infection
Imiquimod - promotes interferon production
Antiretrovirals for Treating HIV/AIDS (RNA virus)
Antiretroviral drugs is used to treat HIV infections
AZT - interferes with reverse transcriptase
Resistance to Antimicrobial Drugs
Persister cells - microbes with genetic characteristics allowing for their survival when exposed to an antibiotic
Superbugs - bacteria that are resistant to a large number of antibiotics
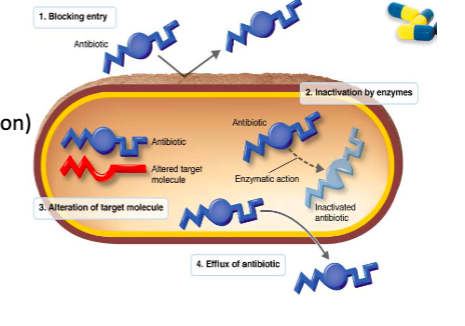
Mechanisms of Resistance
Enzymatic destruction or inactivation of the drug
Prevention of penetration to the target site within the microbe
Alteration of the drug’s target site
Rapid efflux (ejection) of the antibiotic
Variations of the mechanisms of resistance
Antibiotic Misuse
Misuse of antibiotics selects for resistance mutants
Misuse includes:
using outdated or weakened antibiotics
Using antibiotics for the common cold and other inappropriate conditions
Using antibiotics in animal feed
Failing to complete the prescribed regimen
Using someone else’s leftover prescription
Effects of Combination of Drugs
Synergism - the effect of two drugs together is greater than the effect of either alone
Streptomycin & Penicillin
Antagonism - the effect of two drugs together is less than the effect of either alone
Penicillin & Tetracycline