MODULE 1 TOPIC 3: ECONOMIZING PROBLEM
Land - refers to all resources
Resources and their categories
Physical resources - in relation to capital:
investment (economics)- spending on capital goods
2 types of investments:
financial capital
real capital (tangible) / physical assets
Dati land, capital, labor lang. now with entrepreneurial ability na.
Labor - mental and physical talents / skills of men and women usable in production
entrep ability - mental and physical talents / skills of men and women to run/operate the business
Relative scarcity - the resources are scarce, therefore the g/s produced out of these scarce resources are also scarce
RESOURCE PAYMENTS
Property resources
land - rent (rent bc the land isn’t owned privately)
capital - interest
Human resources
labor - wages
entrepreneur - profit & loss
Efficiency - getting the most from available resources
full employment - using available resources (quantity)
full production - using resources that contribute most to production (quality)
Efficiency concepts
allocative - goods and services are demanded by society - willing to pay, demanded (e.g. milktea, jewelry)
productive - producing at least cost possible way (minimum cost)
tatapusin muna ppf bago mag graded quiz
SELF-STUDY SESSION:
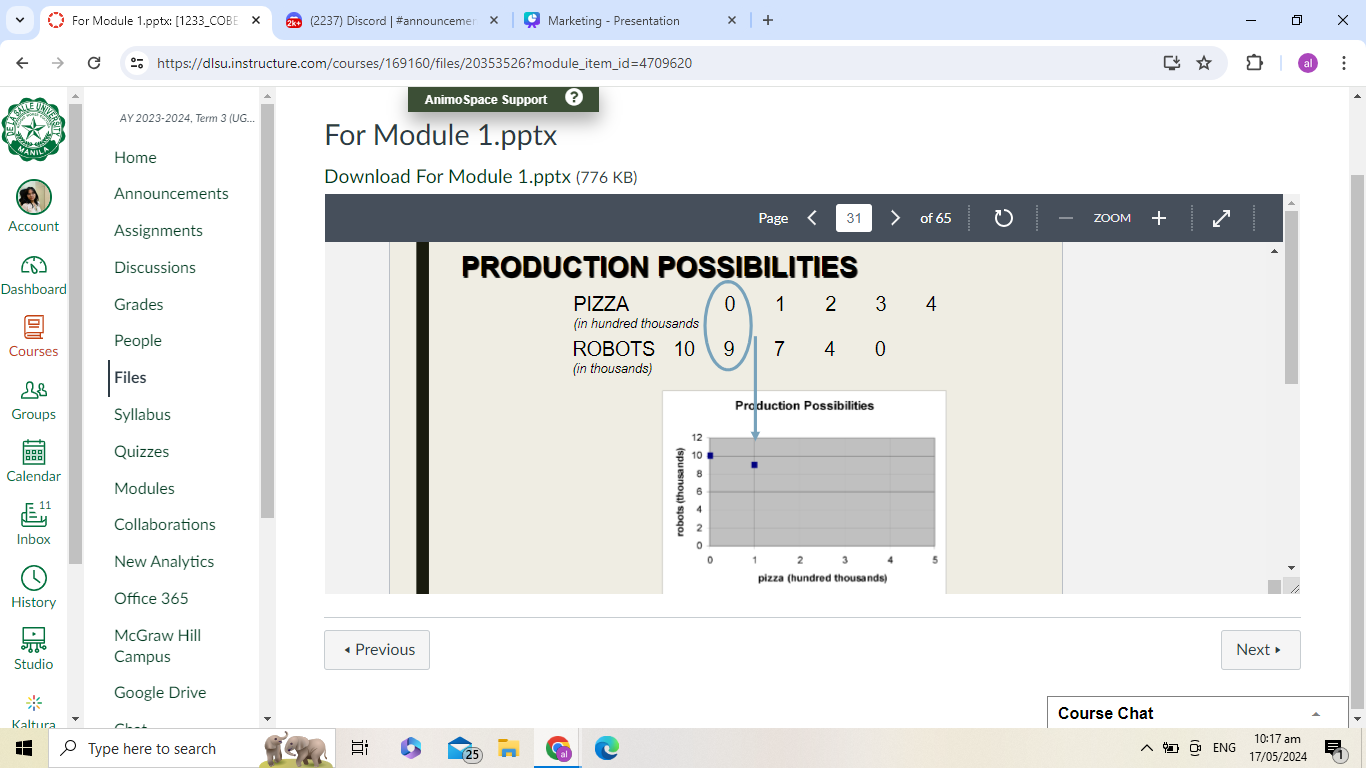
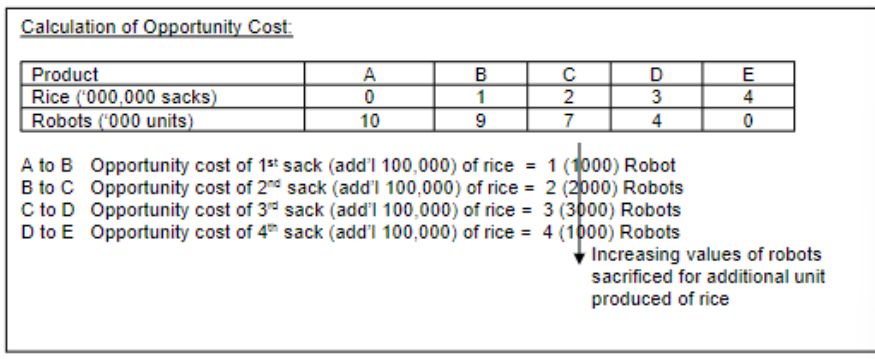
Production Possibilities Curve (PPC) - a model depicting limit to what an economy can produce; reveals that goods and services have opportunity cost
For some reason, -1 yung values ng sa pizza
Production possibilities curve
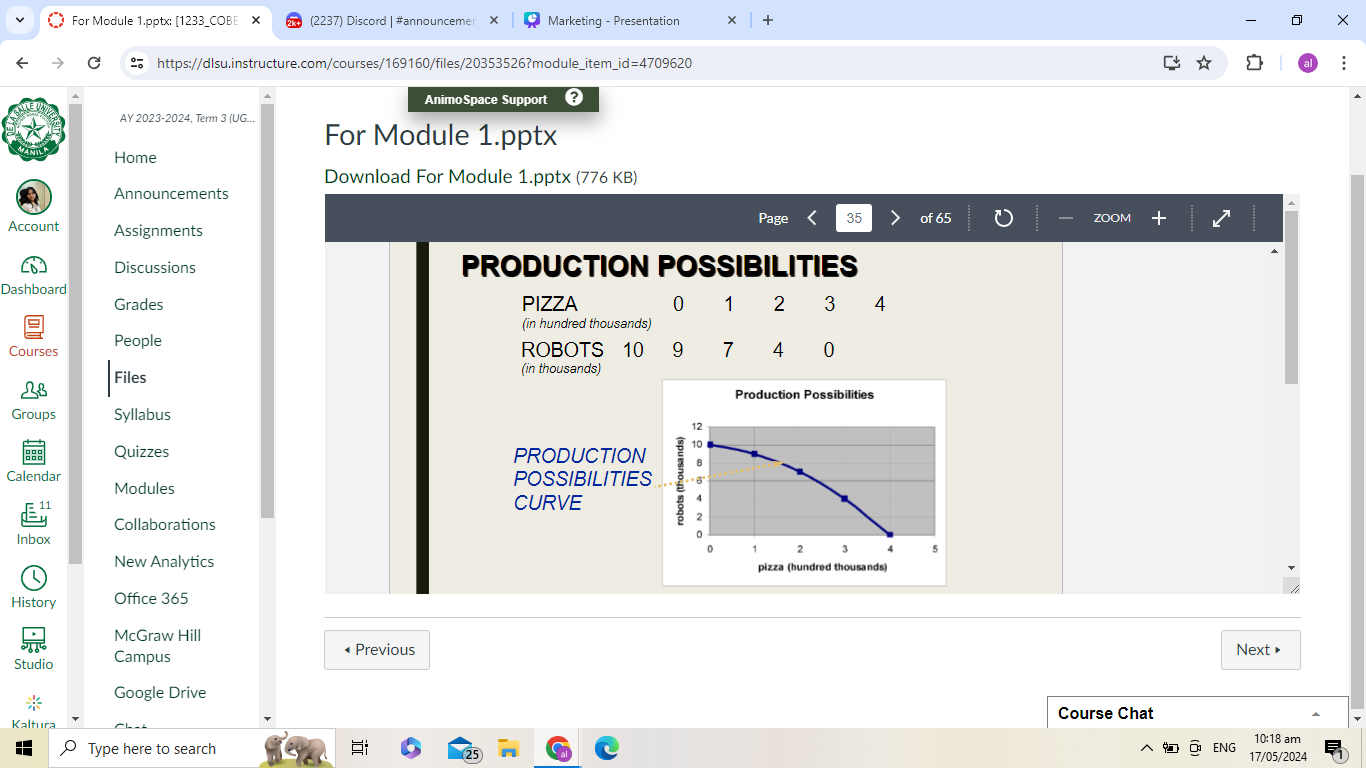
the production possibilities curve (frontier) marks the boundary between attainable & unattainable production levels
Law of Increasing Opportunity Costs:
as we make more pizzas, the # of robots we have to give
up (per pizza) increases (as we make more we give up more of the other)so production possibilities curve gets steeper and
steeper
LAW OF INCREASING OPPORTUNITY COSTS
a graph of production possibilities curve will be concave - bowed out from origin
Economic Growth: a rightward shift of the production
possibilities curve caused by....Increases in resource supplies
Advances in technology
Use of specialized inputs (e.g., hybrid rice)
Engage in international specialization and trade
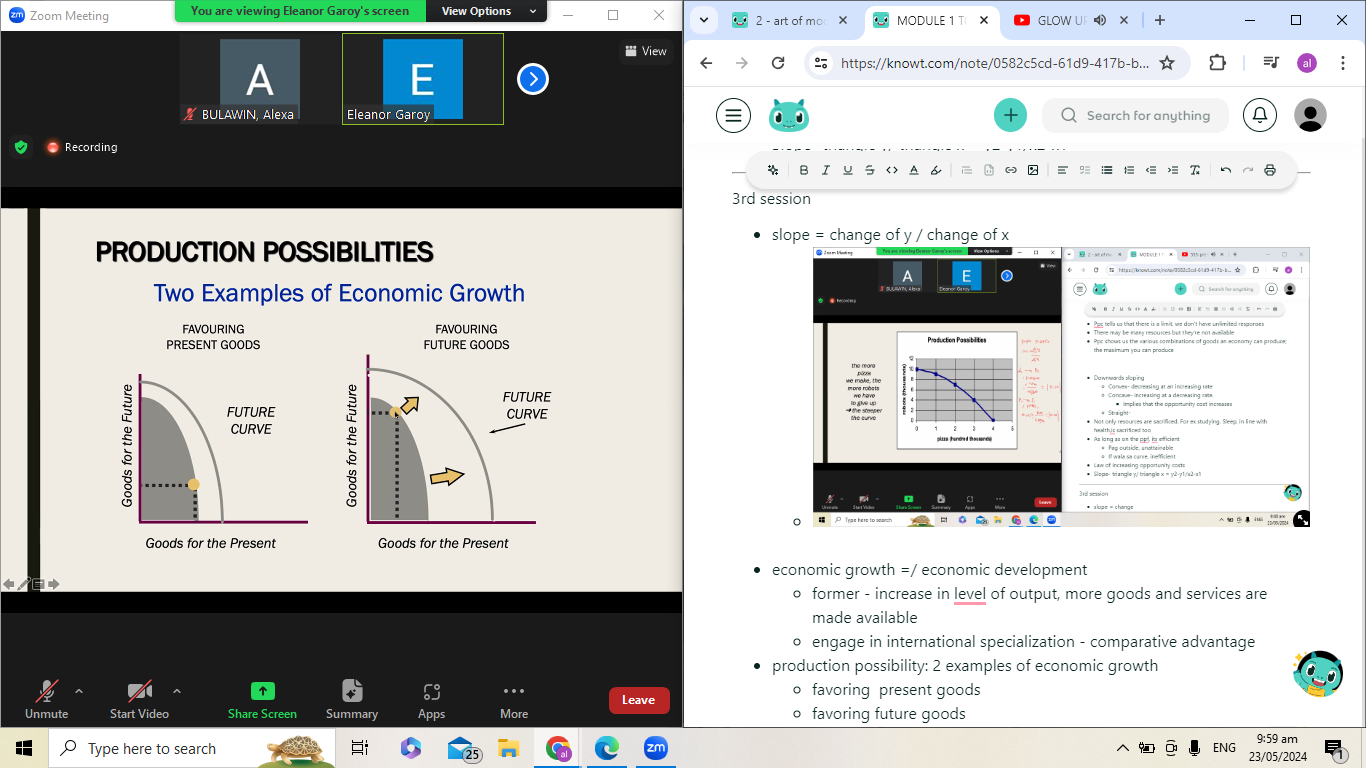
2 examples of economic growth
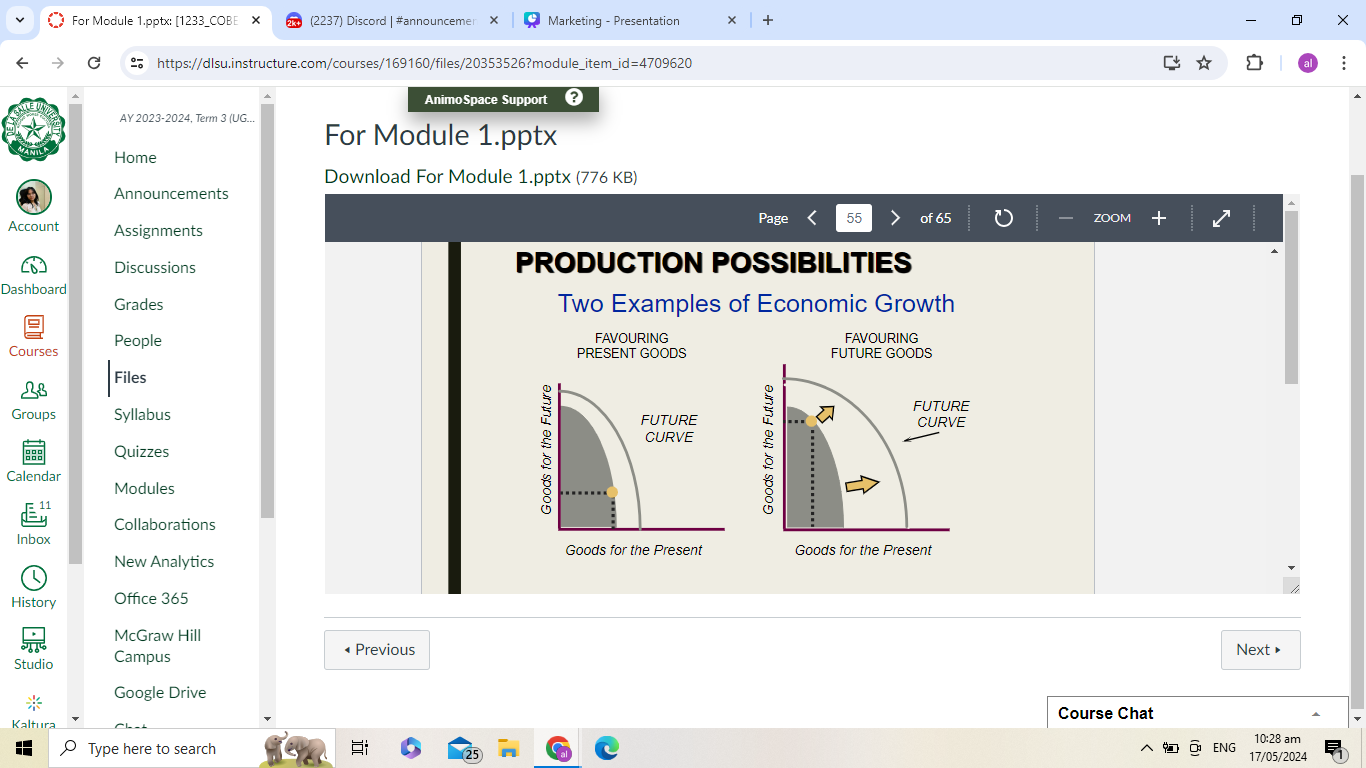
favoring present goods
favoring future goods
Economic system types
traditional
command/planned
market system- dominant economic system used by many nations in
the world1. Private ownership of resources
2. Freedom of choice and enterprise
3. ...
mixed system - Philippines, market + government intervention
1. Allocation Function
2. Stabilization Function
3. Redistribution Function
SYNCH SESSION NOTES
Assumptions in the pp curve
X and y are goods not variables
Labor must be of the right scale/skill
Available resources “fixed”
Technology is assumed to be fixed
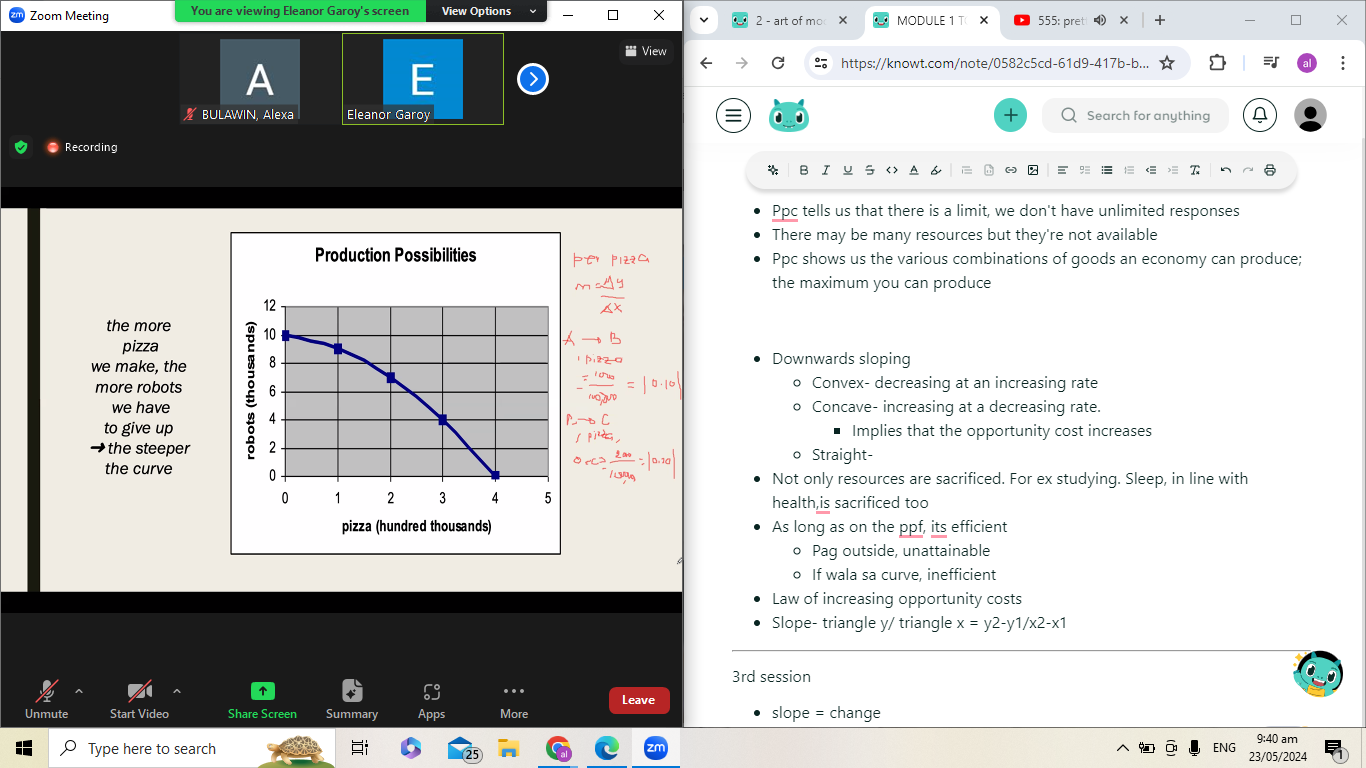
Ppc tells us that there is a limit, we don't have unlimited responses
There may be many resources but they're not available
Ppc shows us the various combinations of goods an economy can produce; the maximum you can produce
Downwards sloping
Convex- decreasing at an increasing rate
Concave- increasing at a decreasing rate.
Implies that the opportunity cost increases
Straight-
Not only resources are sacrificed. For ex studying. Sleep, in line with health,is sacrificed too
As long as on the ppf, its efficient
Pag outside, unattainable
If wala sa curve, inefficient
Law of increasing opportunity costs
Slope- triangle y/ triangle x = y2-y1/x2-x1
3rd session
slope = change of y / change of x
economic growth =/ economic development
former - increase in level of output, more goods and services are made available
engage in international specialization - comparative advantage
production possibility: 2 examples of economic growth
favoring present goods
favoring future goods
GDP - measure of your output
Market system: operation - used by many systems, capitalism
private ownership
freedom of choice and enterprise
self interest
competition - “free enterprise economic system”
systems of markets and prices - every buyer and seller is a price-seller
price - language in a market economy, coordinate goods and services according to price
market - a mechanism which brings buyers and sellers 2 kinds:
input market
product market
Adam smith
invisible hand - laissez faire
a market will not exist if there are no buyers - demand and supply
role of the government in a market system
providing legal structure
maintaining competition
redistributing income
price controls - government has this
taxation - progressive taxation
higher income - lower taxes = other countries adopt this: regressive tax system
reallocating resources
externalities - affected by another party’s activity
if a market system creates negative externalities, that is when we should seek the government
positive - education
negative - pollution
promotes stability
inflation
unemployment
mixed economic system - socialism; heavy on government intervention
not all production is profitable
whatever leaks out sa circular flow , it goes back in - irl di siya nangyayari bc kulang tayo savings, imports are greater than exports
this is how government comes in the picture
F2F DISCUSSION
market demand curve- downward sloping; indicates indirect relationship
Law of demand
as price decreases, quantity demanded increases
common sense
income effect and substitution effect
law of diminishing marginal utility
utility - satisfaction
marginal - change / add 1 extra
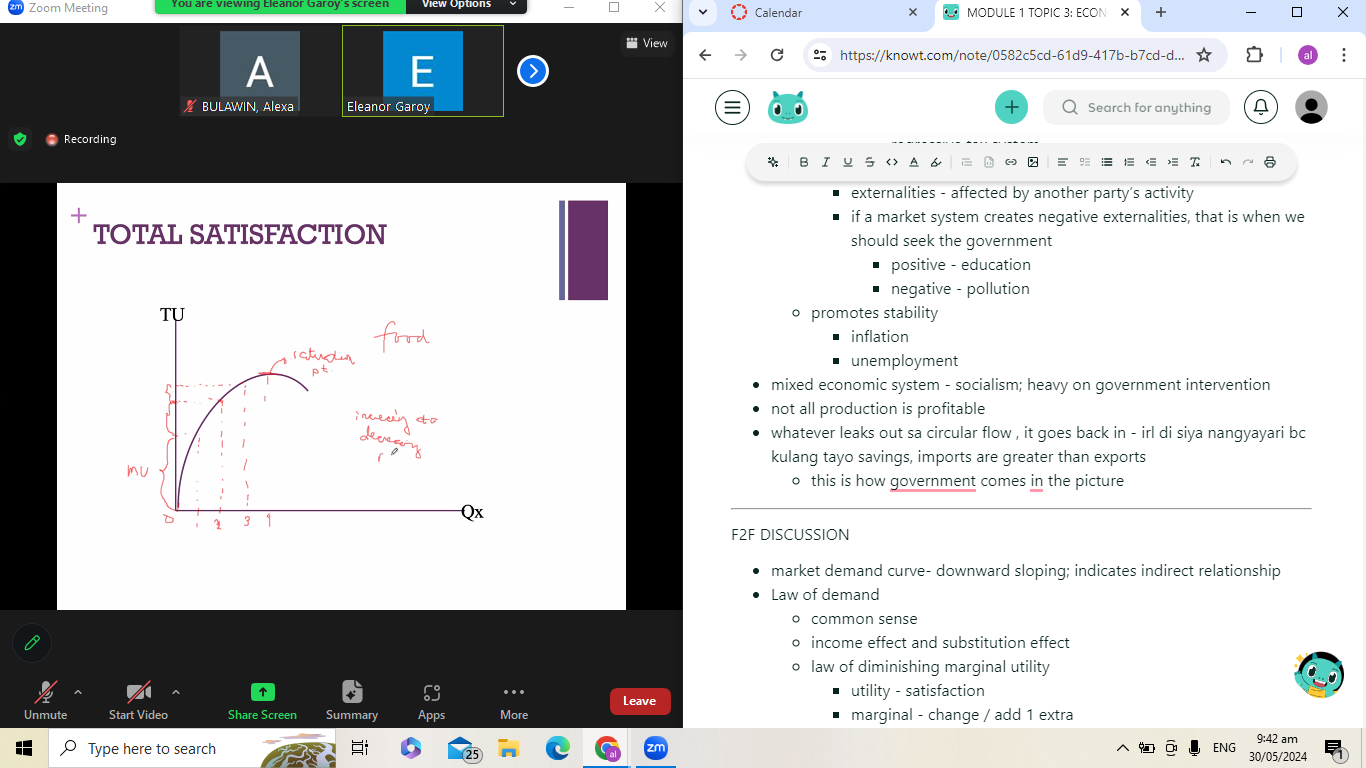 increasing at a decreasing rate
increasing at a decreasing rateas a person consumes more of an item or product, the satisfaction (utility) they derive from the product wanes
water-diamond paradox - the paradox of value is the apparent contradiction that diamonds are more valuable than water, even though water is needed for life
stumped adam smith
law of marginal utility explains this - mabilis magkaron ng falling marginal utility
law of supply and demand
Application of LDMU in business
fast-food restaurants - have to come up w strategies on how to offer products kasi nadidisasatisfy mga tao
combined meals
offering products in packages or sets
clothing, shoes, apparels
bulk purchases
limited edition clothes
partnering w bloggers who give discount codes
bundle discounts
individual demand vs market demand
market demand - summation of individual demands
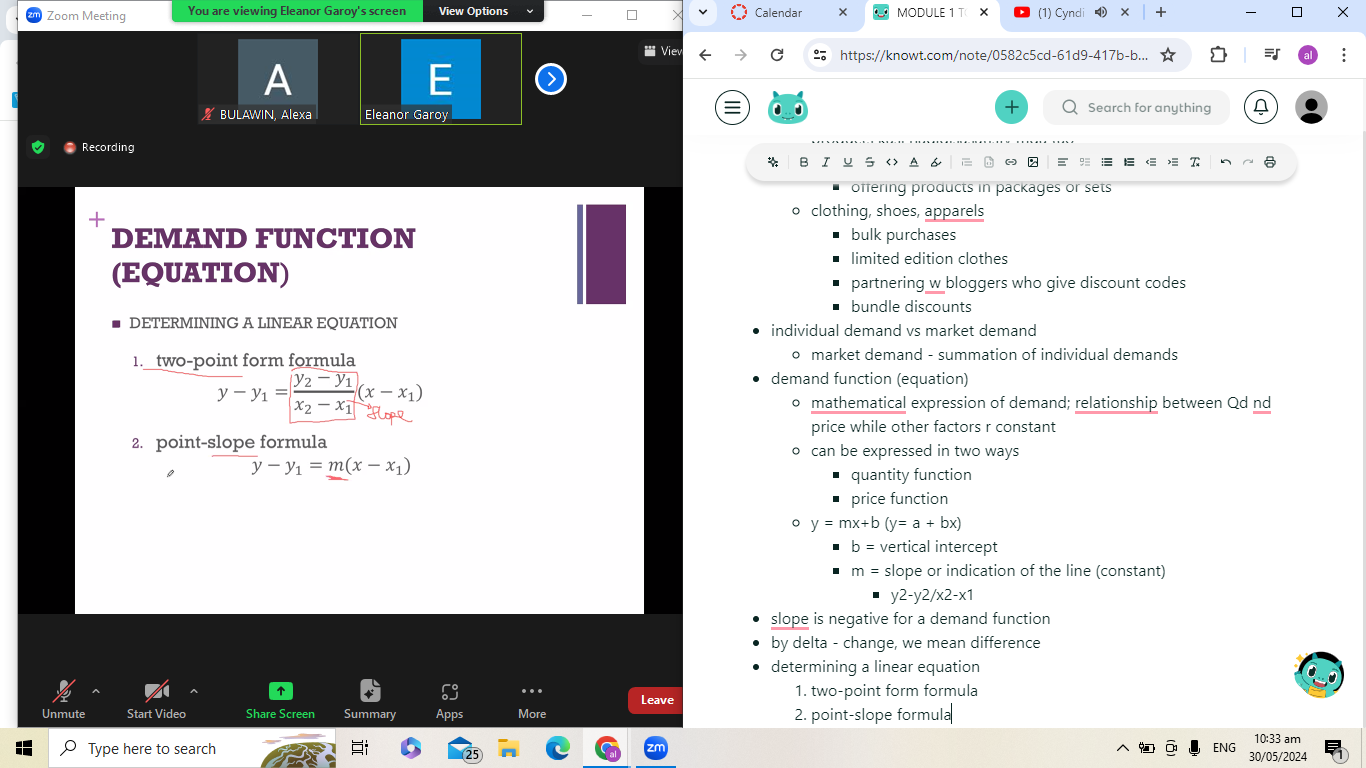
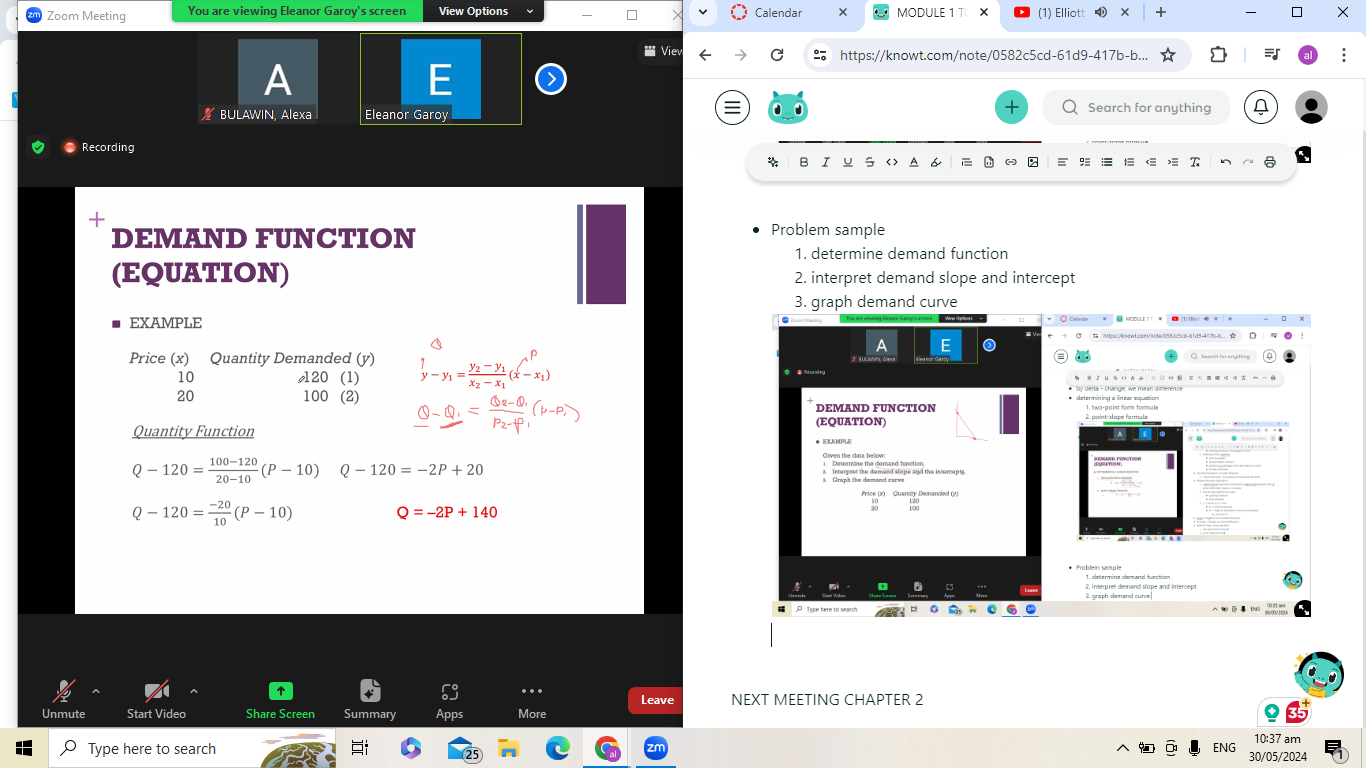
demand function (equation)
mathematical expression of demand; relationship between Qd nd price while other factors r constant
can be expressed in two ways
quantity function
price function
y = mx+b (y= a + bx)
b = vertical intercept
m = slope or indication of the line (constant)
y2-y2/x2-x1
slope is negative for a demand function
by delta - change, we mean difference
determining a linear equation
two-point form formula
point-slope formula
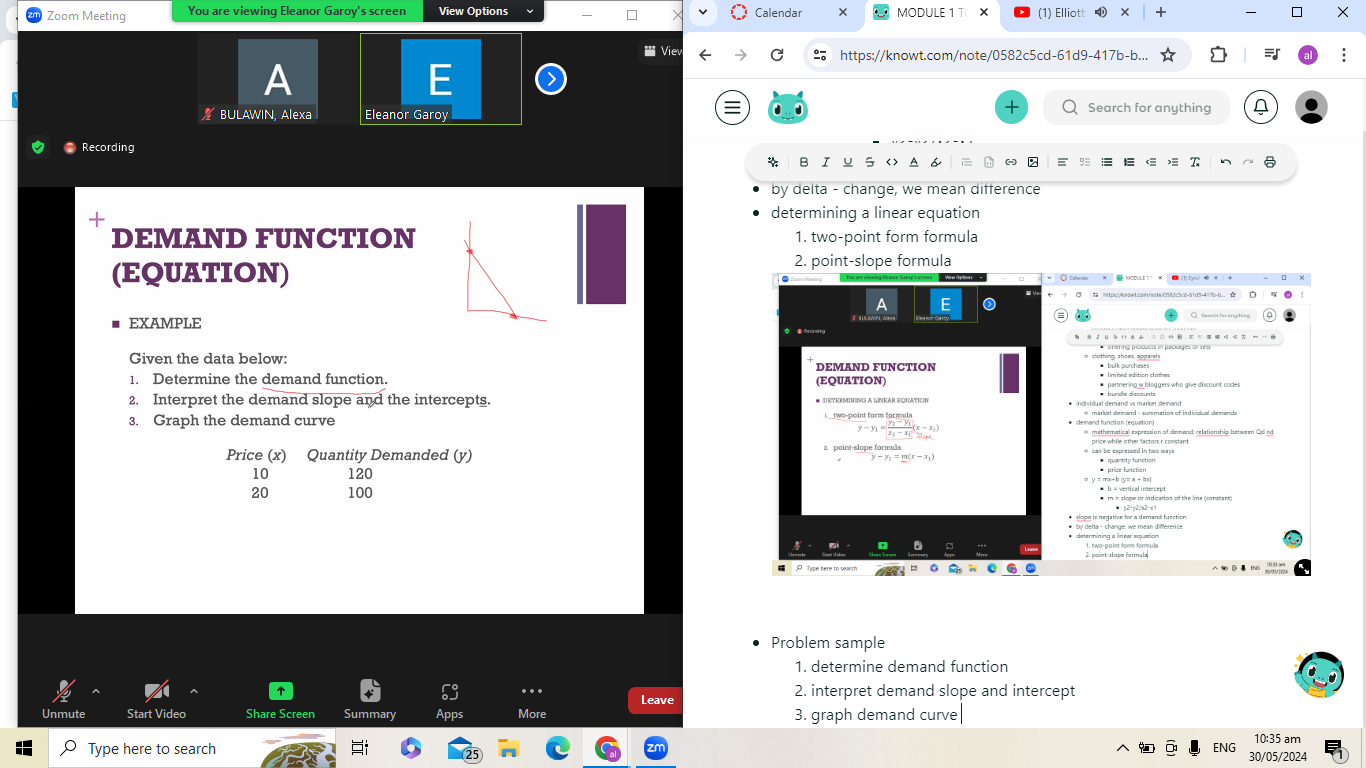
Problem sample
determine demand function
interpret demand slope and intercept
graph demand curve
NEXT MEETING CHAPTER 2
NOTES WHILE STUDYING FOR EXAM:


Economic growth requires:
1. Increases in resource supplies
2. Advances in technology
3. Use of specialized inputs (e.g., hybrid rice)
4. Engage in international specialization and trade
Economic systems differ as to (1) who owns the factors of production and (2)
the method used to motivate, coordinate, and direct economic activity. Economic
systems have two polar extremes: the command system and the market system
Characteristics of PPC:
downsloping
concave
Characteristics of Market System:
Private Ownership of Property Resources
Freedom of Enterprise and Choice
Self-Interest
Competition
Markets and Prices
Technology and Capital Goods
Specialization
Use of Money
Active, but Limited Government: “Laissez Faire” (Leave it Alone) Ideology
The economic functions of government:
providing the legal structure
maintaining competition
regulation
antitrust - involving laws or actions that are intended to make business competition fair and to prevent any company from being a monopoly
redistributing income
transfer payments
market intervention
taxation
reallocating resources
Market failure occurs when the competitive market system (1) produces the
“wrong” amounts of certain goods and services or (2) fails to allocate any
resources whatsoever to the production of certain goods and services whose
output is economically justified.externalities
public goods and services - free-rider prob
promoting stability
inflation
unemployment
 Knowt
Knowt