Unit 2: (The Demographic Transition Model)
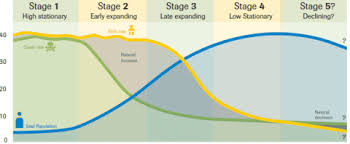
Stage 1:
High CBR
High CDR
Low NIR
No country in the world today
Stage 2:
High CBR
Falling CDR
High NIR
Started by the Industrial Revolution
Stage 3:
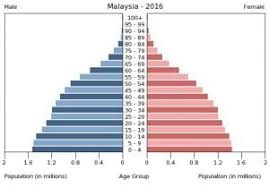
Starts with more urbanization
Falling CBR
Lower CDR
Moderate NIR
India
Stage 4:
Women get more opportunities
Low CBR
Low CDR
Low/ No NIR
Most developed countries today fall in Stage 4
US, UK, AUS, West EU
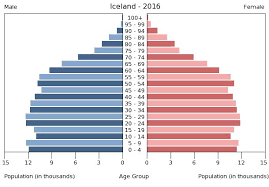
Stage 5:
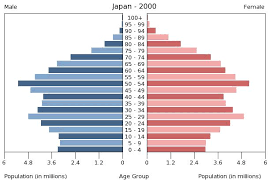
Low CDR
Low CBR
Negative NIR
Russia, Japan, Belarus, Germany
Dependency/Sex Ratios:
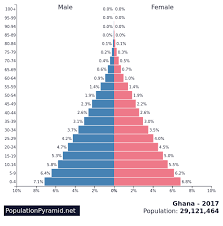
High Youth Dependency Ratio:
Large future workforce
Leads to lack of qualified workforce
puts a strain on carrying capacity
women are typically in home roles
More schooling is required
High Elderly Dependency Ratio:
higher cost for Medicare and other services
possible future labor shortages
Male skewed sex ratio:
Low TFR
Lack of population growth
Increased social tensions