AP Human Geography Unit 6 Exam Review
Cities Across the World
Urban is the built-up city or town & its surrounding environment
Urbanization refers to population shifts from rural to urban areas & people’s adaptation to these changes
Due to expansion of urban areas, known as urban sprawl, many modern challenges have arisen
Suburbs are a largely residential are adjacent to an urban area
Process of suburbanization involves people moving, from cities, to residential area on the outskirts of cities
Four causes leading to the suburbanization of the U.S. after WWII:
Economic expansion
Greater purchasing power for families
Growth of a car-centered lifestyle
Gov’t’s construction of a vast system of new highways
New forms of land use:
Boomburbs: rapidly growing, sprawling city of 100,000 or more on the edge of a major metropolitan area
Edge City: cities that are located at the edge of cities and have economic activity despite their location away from the CBD
Large node of office and retail activities on the edge of an urban area
Counter urbanization: increase in rural populations resulting form the out-migration of city residents
Exburbs: district outside a city, especially a prosperous area beyond the suburbs
Developed in the 1950s when people commuted into the city
Megacities are very large urban centers around the globe that have a population of greater than 10 million people
World’s largest cities & typically have more than 10 million people
Influence due to size of population, also their political, economic & cultural power
Metacities are a large cluster of Megacities that have a population of greater than 20 million people
Connected through transportation systems and infrastructure
Form one very large economic center
Cities and Globalization
Type of City | Characteristics | Examples |
|---|---|---|
World City | Dominant City in Terms of Economic Standing | New York, London, Tokyo |
Megalopolis | An extended Conurban Area, Consisting of Several Cities | BosNYwash (the Area from BOSTON to NEW YORK to WASHINGTON DC) |
Alpha City | Primary Regional Nodes in the Global Economy (Similar to World Cities) | New York, London, Hong Kong, Sydney |
Beta City | Secondary Regional Nodes in the Global Economy (One Step Down from Alpha) | Washington DC, Dallas, Berlin, Wuhan |
Gamma City | Tertiary Regional Nodes in the Global Economy (One Step Down from Beta) | Cleveland, St. Petersburg, Austin, St. Louis |
The Size and Distribution of Cities
Problems with the Rank Size Rule
Some countries have some cities that fit in the rank size rule but other cities populations in the top 10
In the U.S.,
1. NYC is largest
2. Los Angeles
3. Chicago
4. Houston
5. Phoenix
6. Philadelphia, etc.
In the USA, the top 5 cities fit in the Rank Size Rule, but cities 6-10 do NOT
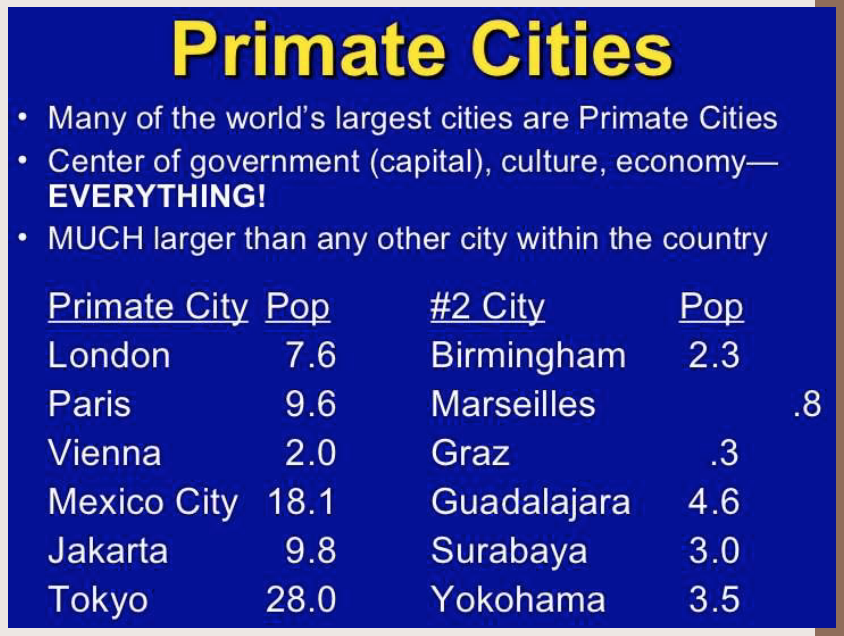
Largest city in an urban system is more than twice as large as the next largest city makes a primate city
Usually social, political or economic hub
U.K. (Developed) & Mexico (Developing) Country follow the primate city model
Gravity Model shows that interaction between locations is proportional to the multiplication of the two populations divided by the distance between them squared (though it is mostly used for migration)
Central Place Theory
Walter Christaller, German geographer, first developed the Central Place Theory
Explaining the reasons behind the distribution patterns, size, & number of cities or towns across the globe
Serving as the framework for both historical & locational patterns today.
Explaining the identification of most profitable locations
Threshold is the size of population necessary for any particular services to exist & remain profitable
Convenience stores & gas station are services that have very low thresholds
Restaurants, hospitals, high schools & department stores are services that have a higher threshold
Range is the distance people will travel to obtain specific goods & services
Higher order services people are willing to travel farther
Lower order or basic services people are less likely willing to travel
Fast food or basic needs
Urban Sustainability
New Urbanism is a counter to urban sprawl
Urban Sprawl is unrestricted growth of housing, commercial developments & roads over large expanses of land, with little concern for urban planning
Urban Sprawl came about in the automobile era from Detroit, MI
Before this era, cities were built in walking-distances & there was less development
When the automobile was invented, cities grew "up" & the city itself instead grew "out"
Green Belts are a ring of well-maintained parks circling the Urban City Center also known as a Belt-line
London England attempted to slow growth
Includes running & biking paths
Tends to incorporate many tunnels & small gardens
Limit or slow down the sprawl of urban areas
Limit pollution & use of mass transit with paths to take around the city
Famous & large green belt is located in the city of Atlanta circling the MLK, Midtown & Downtown Neighborhoods
Having nice running & biking paths
Crosses through many small farmers markets & Atlanta Botanical Garden
Challenges of Urban Changes
Problems
Redlining is denying people of certain races/ethnicities loans within particular areas
Blockbusting is a racially discriminatory practice of pressuring a party to sell a home to families of a minority race or ethnic background
Using fear tactics to cause others in the neighborhood to sell their homes at low prices
Consequence: Ethnic composition of neighborhoods changed
Led to White flight or the movement of whites from the city to the suburbs, often as minorities moved in
Gentrification process of rehabilitating old structures in deteriorated areas rather than demolishing the old structures to make new
Changes formerly low‐income areas to middle‐ & high‐income groups
Giving an economic boost to the area
Raises property values
Force out the poorer, often minority groups that settled there during the redlining & blockbusting times
Creating tension between long‐time residents & newcomers
Sometimes, empty or abandoned areas are demolished to the ground