Photosynthesis LIKE CELLULAR RESPIRATION BUT IN REVERSE
Photosynthesis
• Energy within light is captured and used to synthesize carbohydrates
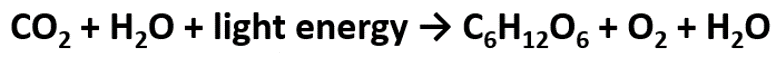
• CO2 is reduced
• H2O is oxidized
• Energy from light drives this endergonic reaction
Two stages of photosynthesis
Light reactions
◦ Use light energy
◦ Take place in thylakoid membranes
◦ Produce ATP, NADPH and O2
Calvin cycle
◦Occurs in stroma
◦Uses ATP and NADPH to incorporate CO2 into carbohydrate
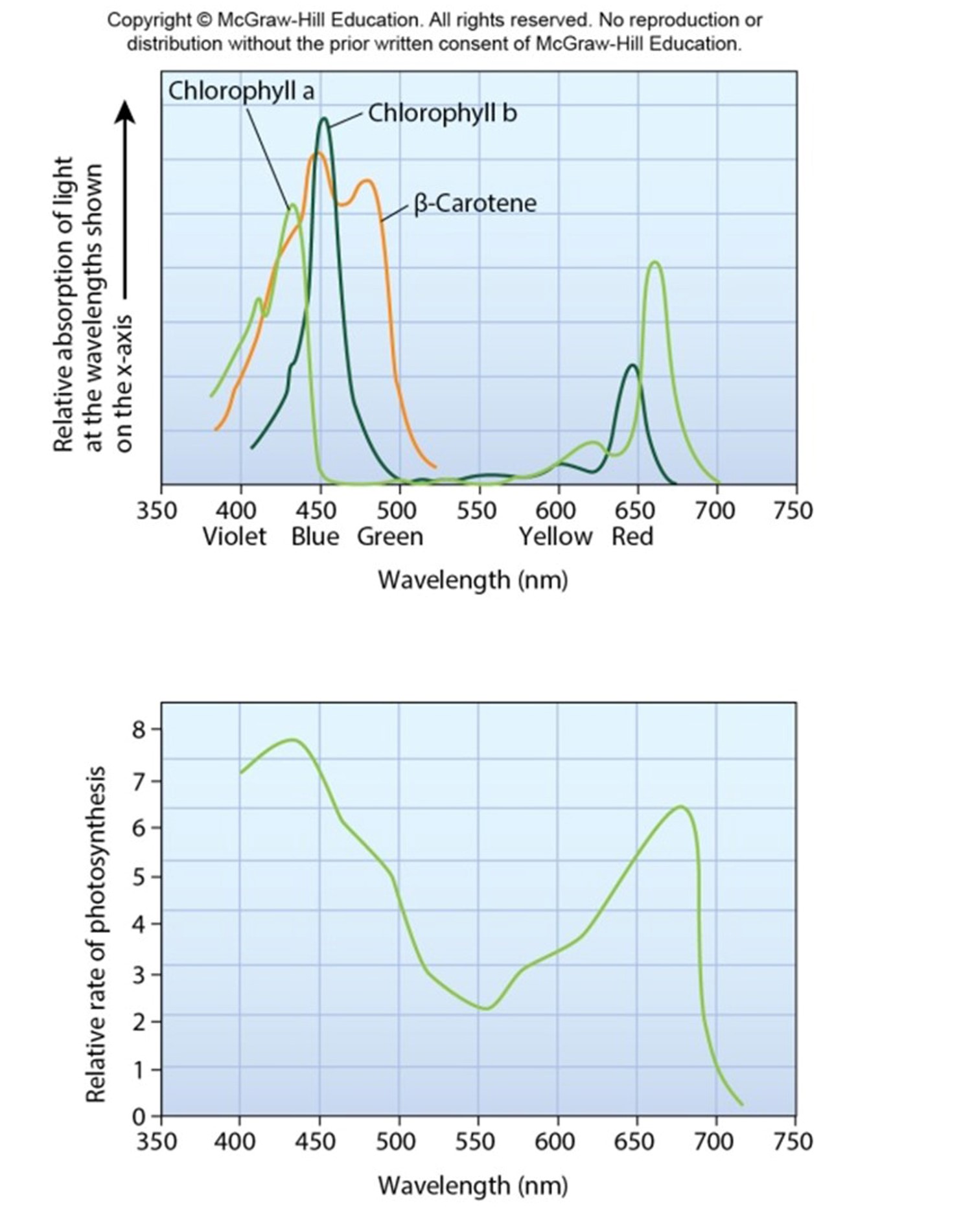
Absorption versus action spectrum
Absorption spectrum
◦ Wavelengths that are absorbed by different pigments
Action spectrum
◦ Rate of photosynthesis by whole plant at specific wavelengths
a) Absorption spectra
b) Action spectrum
Photosystems I and II 1
Thylakoid membranes of chloroplast contain two distinct complexes of molecules
◦ Photosystem I (PSI) – discovered first
◦ Photosystem II (PSII) – first step in photosynthesis
Light excites pigment molecules in both PSII and PSI
Formation of ATP in chloroplasts
ATP synthesis in chloroplasts
◦ Achieved by chemiosmotic mechanism called photophosphorylation
◦ Driven by flow of from thylakoid lumen into stroma via ATP synthase
gradient generated three ways:
• 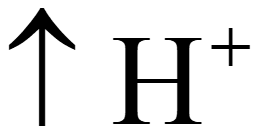 in thylakoid lumen by splitting of water
in thylakoid lumen by splitting of water
• 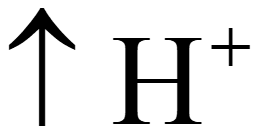 by ETC pumping into lumen
by ETC pumping into lumen
• 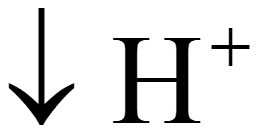 in stroma from formation of NADPH
in stroma from formation of NADPH
Three chemical products
Oxygen, O2
◦ Produced in thylakoid lumen by oxidation of H2O by PSII
◦ Two electrons transferred to molecules
NADPH
◦Produced in the stroma from high-energy electrons that start in PSII and are boosted in PSI
ATP
◦ Produced in stroma by ATP synthase using the electrochemical gradient
Synthesizing Carbohydrates via the Calvin Cycle
CO2 incorporated into carbohydrates
◦ Precursors to other organic molecules
◦ Energy storage
Requires massive input of energy
Calvin cycle
Phase 1 – Carbon fixation
C02 → RuBP
Rubisco → enzyme
Phase 2 – Reduction and carbohydrate production
Stabilizing
Phase 3 – Regeneration of RuBP
Continues the cycle
Variations in Photosynthesis
Environmental conditions can influence both the efficiency and way the Calvin cycle works
◦ Light intensity
◦ Temperature
◦ Water availability
Photorespiration
• More likely in hot and dry environments
• Favored when CO2 low and O2 high
C4 plants
• Evolved a mechanism to minimize respiration
• Leaves have two-cell layer organization
◦ Mesophyll cells
◦ Bundle-sheath cells
Which is better – C3 or C4?
• It depends on the environment
• In warm dry climates plants conserve water and prevent photorespiration
• In cooler climates, plants use less energy to fix CO2
• 90% of plants are C3
CAM plants
• Some plants separate processes using time
• Crassulacean Acid Metabolism
• CAM plants open their stomata at night