AGGREGATE DEMAND
Aggregate demand refers to the total of all demands or expenditures made in the economy at any given price over a given period of time. it is also known as the total level of spending in the economy at any given price.
the components of AD:
AD = C + I + G + ( X - M )
consumption : consumption refers to the spending by households on goods and services. it makes up about 60% of AD
investment : the spending by firms on the investment of capital goods, such as equipment and buildings. it makes up about 15-20% of AD
government spending : the spending on provision of goods and services by the government. generally public and merit goods. it makes up about 18-20% of GDP
net trade : exports minus imports. foreigner spend money on goods produced in the domestic country which is included in national expenditure , however , the spending on goods from abroad is deducted. it makes up about 5% of AD
The AD curve shows the relationship between price levels and the level of real expenditure in the economy.
price level is the average level of prices in the economy
real output must equal real expenditure and real income made in the economy
The AD curve slopes downwards because the higher the price level , the fewer products will be demanded in the economy.
THE FOUR REASONS BEHIND THE AD CURVE BEING DOWNWARDS SLOPING :
income effect : As a rise in prices is not matched straight away by a rise in income, people have lower real incomes so can afford to buy less, leading to a contraction in demand.
substitution effect : If prices in the UK rise, less foreigners will want to buy British
exports and more UK residents will want to buy imported foreign goods because they are cheaper. The rise in imports and fall of exports will decrease net exports so AD will contract.
real balance effect : A rise in prices will mean that the amount people have saved
up will no longer be worth as much and so will offer less security. As a result, they will want to save more and so reduce their spending, causing a contraction in AD. ( fall in purchasing power )
interest rate effect : Rising prices mean firms have to pay their workers more and so there is higher demand for money. If supply stays the same, then the ‘price of money i.e. interest rates will rise because of this higher demand. Higher interest rates mean that more people will save and less will borrow and will also mean that businesses invest less, so AD will contract.
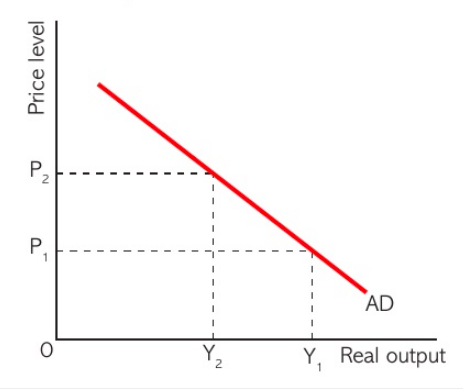
MOVEMENT ALONG THE DEMAND CURVE :
consumption : when prices increase , consumers may need more money to maintain their living standards therefore the demand for borrowing rises which pushes up interest rate resulting in a fall in the quantity of output demanded
investment : when prices rise , it leads to an increase in interest rates. thus , new investment projects become less profitable which lowers the investment in the economy , leading to a decrease in national expenditure
exports and imports : a higher price will mean that foreign firms will compete easier , so exports will fall and at the same time imports will rise as its more affordable to consumers. as a result there will be a possible trade deficit
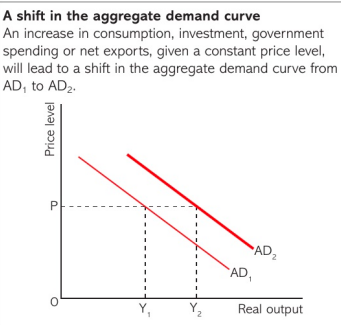
SHIFT IN THE AD CURVE :
consumption : a number of factors may increase consumer spending at any given level of price such as a decrease in unemployment , lower interest rates , a substantial rise in stock market prices , increase in consumer wealth , reduction in saving rates or fall in income tax
investment : many factors can increase investment spending at any given level of pricing including increase in business confidence , fall in interest rates or a fall in corporate taxation in the economy , which would act as an incentive to invest more as it would cost less
government spending : the government could change their fiscal policy
exports and imports : a number of factors may influence the amount of goods exported or imported such as a rise in exchange rate which would decrease exports and increase imports , resulting in AD curve to shift leftwards and vice versa. the quality of goods will also effect exports