FW 404 Forest Stand Improvement [FSI] 9/11
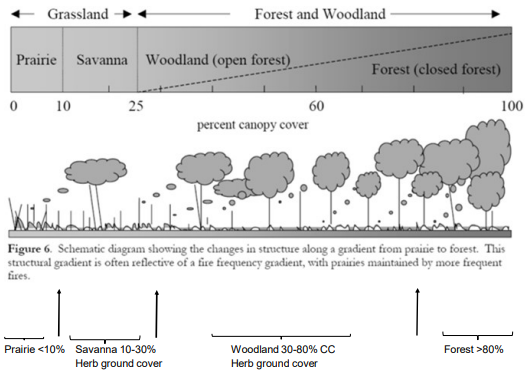
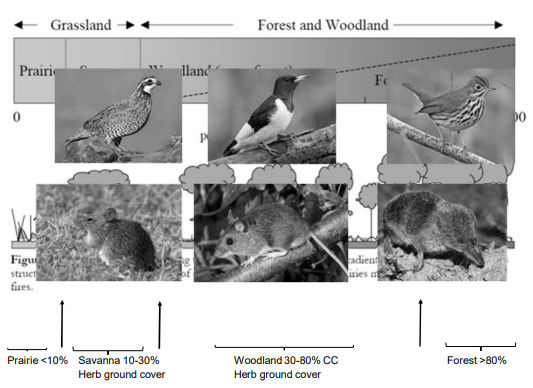
Poor Vertical Structure and Plant Richness
Where quail go to die

Umstead is not natural. Used to be cotton fields, even if it’s not really managed today. Naturally regenerated maybe.
Use the baseball technique
Do quail go to die at this place?
Question: Can you see a ball from 10 feet away on the ground? If not, too little ground cover.
Pre-commercial thin (PCT)
Done early in stand development
when, or just before, crowns close
before trees commercial
cost to landowner
Concentrate growth on crop trees
shift composition
Prolong time to crown closure
increase plant richness and structure
$200+ per acre for pre-commercial thinning
Ultimate wildlife benefit: prolonging canopy closure to allow light over canopy to reach the ground
too dense: too much shade, nothing to eat for animals
too many trees cut: too much fuel potential, wildfire risk
Commercial Thinning
Concentrate growth on crop trees
Trees in marketable size class
More sunlight on the forest floor
Stocking charts for many species
Generally <70% canopy cover
< 70 ft per acre BA for wildlife in pines
< 50 ft per acre BA for northern bobwhite
Greater BA where site index is greater
Site index = the height of the dominant trees in an even-aged stand at a specific/base age
Improvement/Retention Cuts
Typically in older age stands
Often ecological over economical
Remove undesirable trees (girdled, sprayed, or cut) (girdle cuts off blood vessels from tree to kill it)
poorly formed individuals
non-commercial species
low wildlife value
Recover from high-grading
Variable retention replicates natural disturbances like tornadoes
Improvement cutting

Before/After Thinning
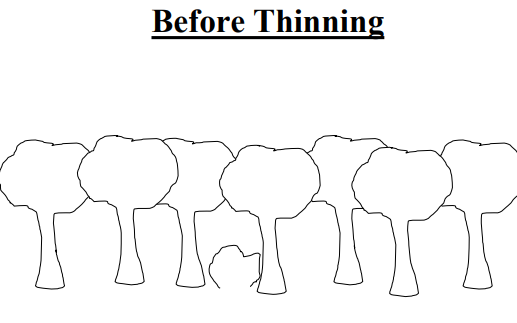

The trees are the same below but now different ages/heights
Long After Thinning without Fire
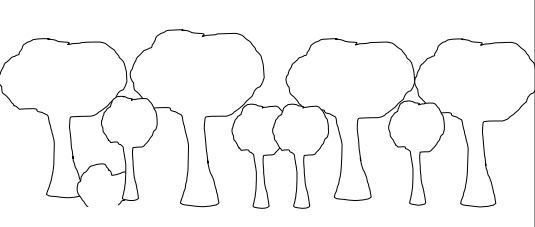
Looks like shelterwood. Intermediate light. Midstory hardwood encroachment: when hardwoods creep into midstory and compete for light. Managers should want to avoid this.
Thinning Effects on Vegetation
Open, diverse structure
Growth of understory woody and herbs
Benefits:
understory birds and quail
small mammals
white-tailed deer
wild turkey
woodland birds (like nuthatch)
good species for stewardship plan (brown-headed nuthatch)
some bats (less clutter for foraging)
more active in forests with trees spread apart, canopy more open
Prescribed Fire After Thinning
Clears leaf litter after germination
Limits midstory growth
Improves browse nutrition
Promotes desirable frobs
Stimulates fruiting
Woody shrubs fruit more prolifically 2-5 years after fire
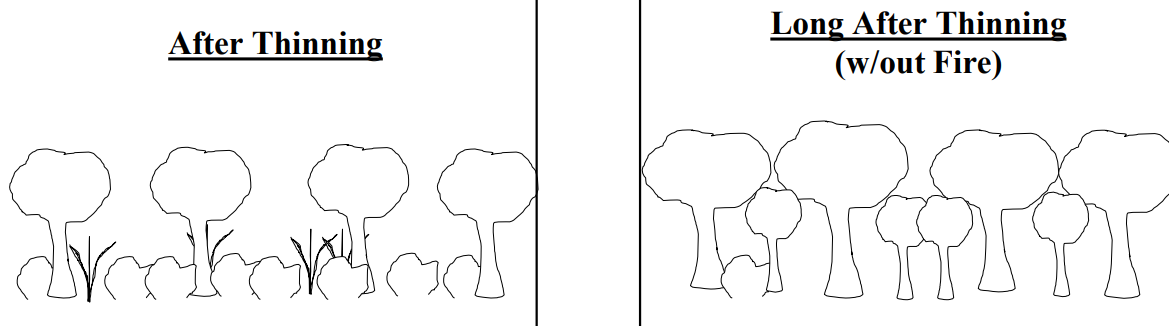
Thin AND Burn!

Too little light and too much litter
Nothing can grow under litter layer in second photo
Restoration with Thinning (and Burning)
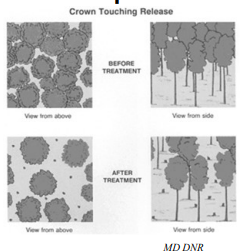
Mid-rotation Herbicide Release
Broadcast application
Controls mid-story hardwood in pine
Increase growth of crop trees
Increases shrub-herb in understory
Arsenal (Imazapur) releases legumes
Best if followed by prescribed fire
to get rid of leaf litter, which can’t be removed with herbicide
promotes growth of forbs
Crop Tree Management
Focus on individual trees, not stand
Choose trees based on:
species’ commercial value
species’ wildlife value
individual characteristics
straightness
crown size
mast production
leave cavity trees

Crop Tree Management
Inject or girdle competitors
Remove only crowns near crop trees
Use on best sites
CTM Benefits to Wildlife
Favor desirable species
“wildlife thinning”
increase acorn/mast production
increase understory
generate snags
CTM increases crown size and therefore acorn production
some oaks not very good at making acorns
large crowns make more acorns
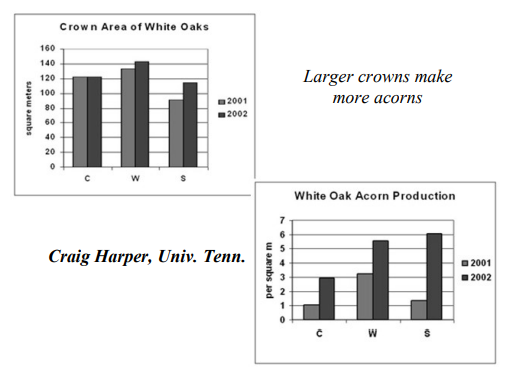
Control = acorn production increased due to being an up year vs down year
2001 vs 2002
Fertilization
Success varies by soil, rate, etc
“More acorns”? “sweeter acorn”?
May decrease acorn production!
Crowns must have room to grow
CTR more efficient
Better FSI
Lower canopy cover and more sunlight
thin on frequent intervals
follow with prescribed fire
leave select mast trees
leave snags
don’t high grade