6.3.2(b) interactions between populations
spec points
interactions between populations
To include predator-prey relationships considering the effects on both predator and prey populations AND interspecific and intraspecific competition.
competition for
mates/pollinators
food/sunlight
territory/space
dominance
water
what is competition?
When two or more individuals share any resource that is insufficient to satisfy all of their requirements fully, then competition results.
(e.g light, food, space)
interspecific vs intraspecific
interspecific: different species
intraspecific: within species
interspecific
Individuals competing for resources who are different species. One population size will grow, and the other shrink.
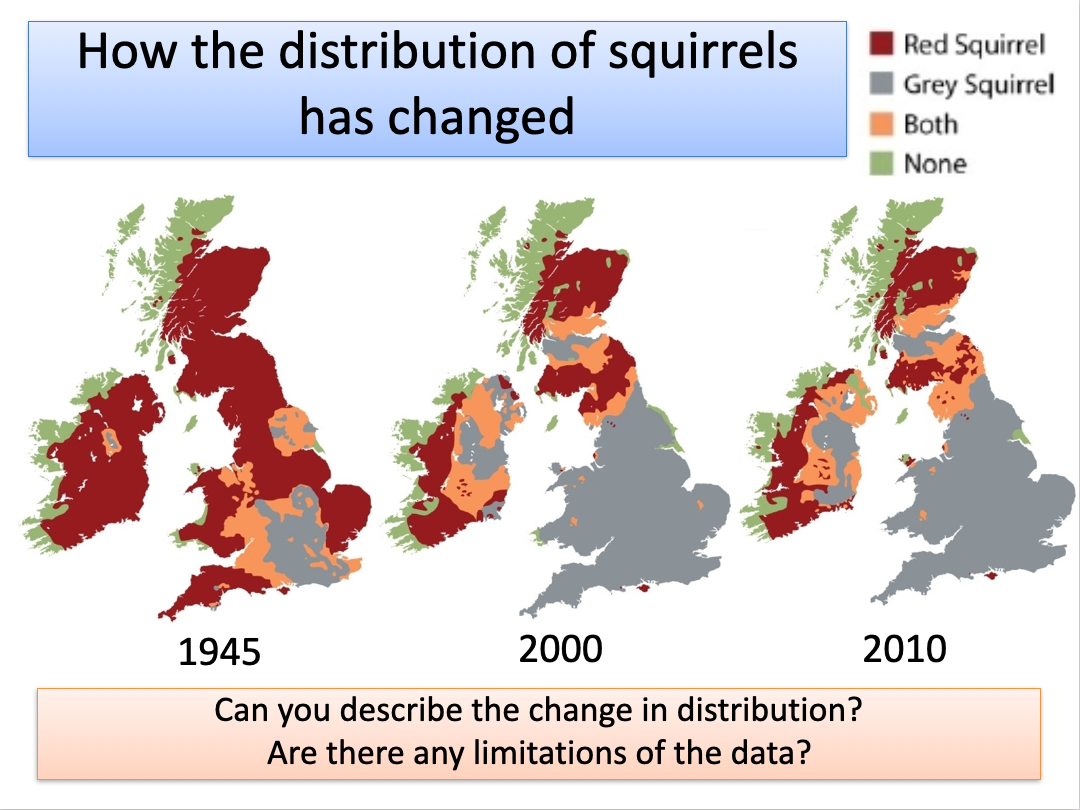
squirrels
Grey squirrel (Sciurus carolinensis) was introduced to Britain over 100 years ago and has been out competing the red squirrel (Sciurus vulgaris)
INTERSPECIFIC
ecological niche
habitat that an organism lives in and also it’s role in that habitat (what it eats)
e.g. ladybirds live on trees and eat greenfly
Carl Gauss (1934)
Grew two species of paramecium. First separately, then together
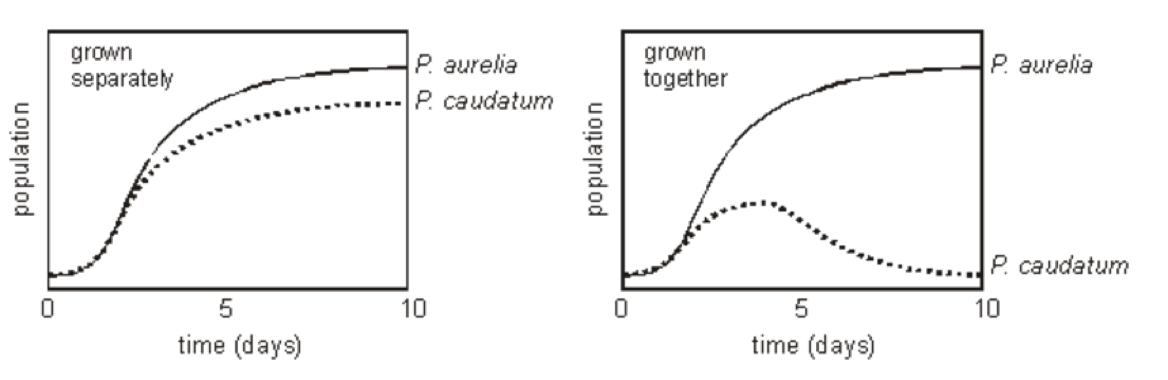
What do the graphs show and how can you explain this?
When together there is greater competition for food. The P.caudatum are out competed by the P. aurelia.
The more overlap between two species’ niche, the more intense the competition.
If they have the same niche then one species is out-competed by the other.
Two species cannot occupy the same niche.
intraspecific
Individuals competing for resources who are the same species.
Availability of the resources will determine the size of that population.
The larger the availability of resources, the larger the population.
competing for water
eventually water dries up
competing for food
intraspecific competition
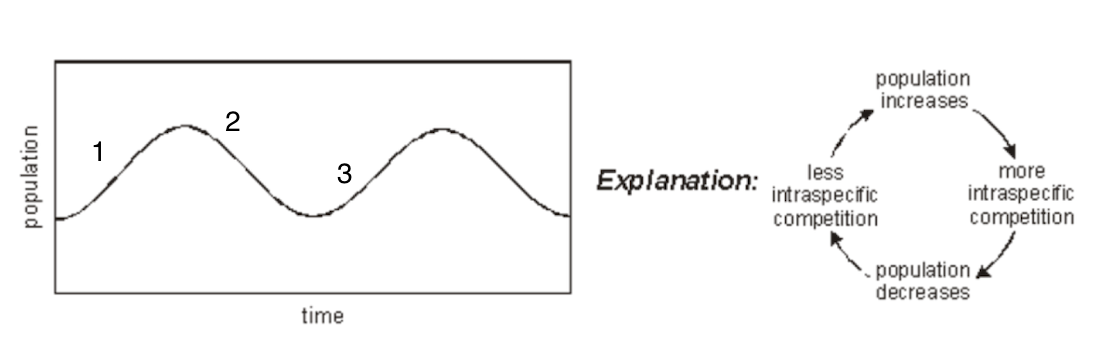
Describe the graph at each stage:
Lots of resources, all organisms have enough to survive and reproduce – population size increases
Resources now limited, not enough for all to survive, population decreases in size
Smaller population means less competition, can survive and reproduce. Population grows
Can this be linked to natural selection?
predator-prey relationships
lady birds and aphids
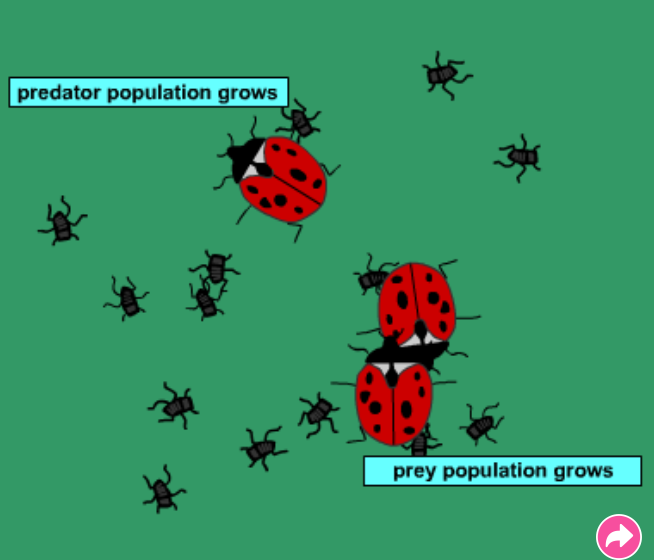
describe + explain stages 1-4 on graph
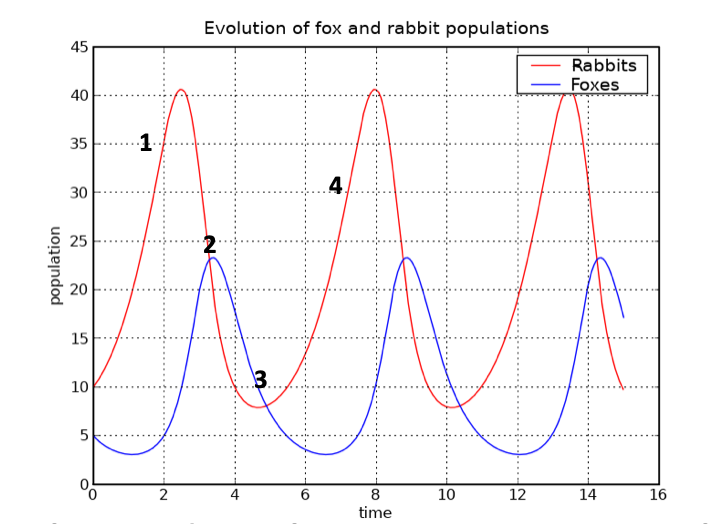
Increase in rabbits means the population of the foxes grows. More food available = survive = reproduce
High number of foxes means a decline in the rabbit population
Less rabbits mean that there is less food for foxes so the number of foxes decreases
Less foxes mean that less rabbits get eaten and numbers can increase. Cycle starts over!
There are many other factors that determine the size of these populations can you list them?
Environmental Factors
Availability of food and water resources.
Changes in habitat or vegetation.
Weather conditions (e.g., droughts or extreme winters).
Disease
Inter/Intraspecific Competition
Migration
Human Influence:
Hunting or trapping of foxes or rabbits.
Changes due to urbanization or farming.
Genetic Factors/variations
Predator-Prey Dynamics