Science 9- Unit 2
Particle Theory of Matter:
All matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms
All particles in substances are identical
All particles are in motion and change with temperature
All particles have space in between them
All particles have attractive forces
Colloids: Tiny particles
Solids have a definite shape and volume because the particles in a solid can only move a little bit. All they can do is vibrate.
Liquids take the shape of their container because the particles can move more freely then they can in solids. A liquids particles are held together by strong attractions to each other, so it has a definite volume. These particles move from one area to another.
Gases always fill whatever container they are put in. Since gases have very little attraction, the particles are quite far apart. These particles are constantly moving everywhere.
Chemical properties: How something interacts with another substance Observed through chemical reaction.
Physical properties
A physical property is a property of a system that is measurable
There are 10 different ways to measure physical properties. They are
State ( type of motion it has, solid, liquid, or gas)
Color, size and shape
Malleability (how much it can bend without breaking)
Ductility (how well it stretches)
Hardness
Toughness
Melting point
Boiling point
Solubility (how well it breaks apart in water)
Conductivity (how well it conducts electricity)
Exothermic= releases energy Endothermic= Takes in energy
Qualitive properties: Physical properties that can be described with words
Quantitative properties: Physical properties that can be described with numbers
WHMIS: Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System. This is involved in this like flammability, exploding substances, corrosion, biohazards, chronic toxicity, even death
Density
Density is how much mass a substance has per volume.
Formula: density= mass/volume
Formula: mass= density x volume
Formula: volume= mass/density
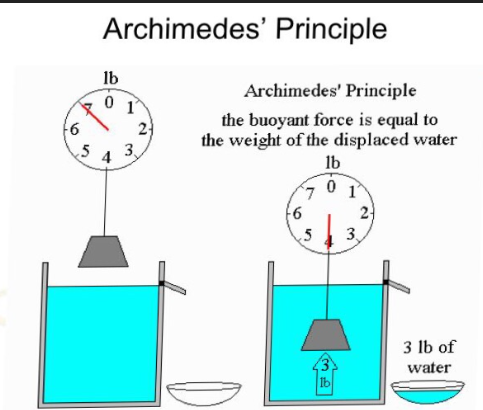
Buoyancy: Archimedes Principle
Chemical Properties
a chemical property is how a substance reacts. a chemical change means that the identity of a substance has changed
chemical properties include toxicity, reactivity, combustibility, and stability
A reaction rate is how fast or slow a reaction occurs, based on how much product or reactant is used in a specific amount of time
LD50 is a standard measure to determine if a substance is toxic or not
Combustibility: a measure of how readily a substance reacts with oxygen to produce fire
Stability is not the opposite of reactivity. It does not change form quickly when left alone
Catalyst: a substance that speeds up the rate of a reaction without being used up or changed itself.
Indicators that a chemical change has occurred: Bubbles, temperature change, color change, odor change, precipitate forms ( solid that forms when 2 liquids are mixed)
Chemical reaction- when atoms of 2 or more substances are rearranged to form new substances
Reactants go in, Reaction is the outcome
Photosynthesis= reactant 1 + reactant 2= product 1 + product 2
Photosynthesis= Sunlight+ Co2+ H20+water= O2 and Glucose (C6H206)
There are 2 kinds of equations, chemical and word equations
Word equations= Chemical reactions are written using the names of the substances
Ex: Silver+ Nitrogen= Silver Nitride
Chemical equations= Chemical reactions that use chemical formulas to represent the substances
Ex: Silver Nitride AGs + N2g= AG3N
Prefixes: Mono 1, Di 2, Tri 3, Tetra 4, Penta 5, Hexa 6, Hepta 7, Octa 8, Nena 9, Decca 10
Roman numerals: use when an element has more than 1 change ex: 1= II
There are 7 elements that are naturally diatomic. This means that when they are all by themselves, there are actually 2 of them stuck together rather than 1. These elements are nitrogen, (n2) oxygen( o2), fluorine (f2), hydrogen, (h2) bromine (br2), iodine, (i2) and chlorine (cL2)
Combustion- when oxygen reacts with a carbon fuel such as gasoline
Corrosion- when oxygen reacts with metal over time
Photosynthesis- How plants convert Co2 and o2 into glucose and energy
Cellular respiration= oxygen, glucose, water, energy, carbon dioxide
Types of Matter
Conservation of mass= Matter can’t be created or destroyed. It is also a closed system
Matter can be classified as either a pure substance or a mixture.
Pure substances: Elements (Sodium, Oxygen, Nitrogen) Compounds (Water, Table Salt, Sugar) Made of 1 element.
Mixtures: Solutions (Coffee, Milk, Air. Contains more than 1 type of substance throughout) Made up of 2 elements
Mechanical mixtures (Orange juice with pulp, Contains more that 1 type of substance, not the same throughout)
Homogenous Mixture: Looks like one substance but is made of many
Heterogeneous Mixture: Looks like there are 2 or more parts to a mixture.
Subatomic Particles: Particles that are within an atom; such as electrons, neutrons, and protons
The periodic table of elements
This system was invented by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev.
The periodic table is organizes atoms into groups (columns) and periods (rows). The last digit of the group number tells you how many valence (outer) electrons the atom has. The period number tells you how many energy levels (shells) the atom has. The elements are listed in increasing order of proton number (atomic number)
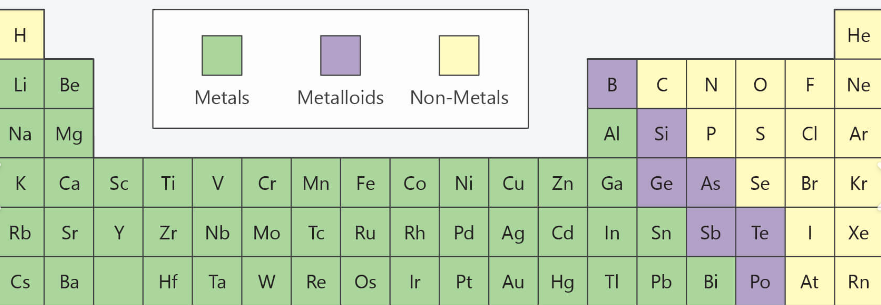
Metalloids are elements that share a mixture of metals and non metal mixture.
Metals are located on the left hand side of the staircase. They are shiny.
Non metals are located on the right hand side of the staircase. They are brittle and they tend to be gases
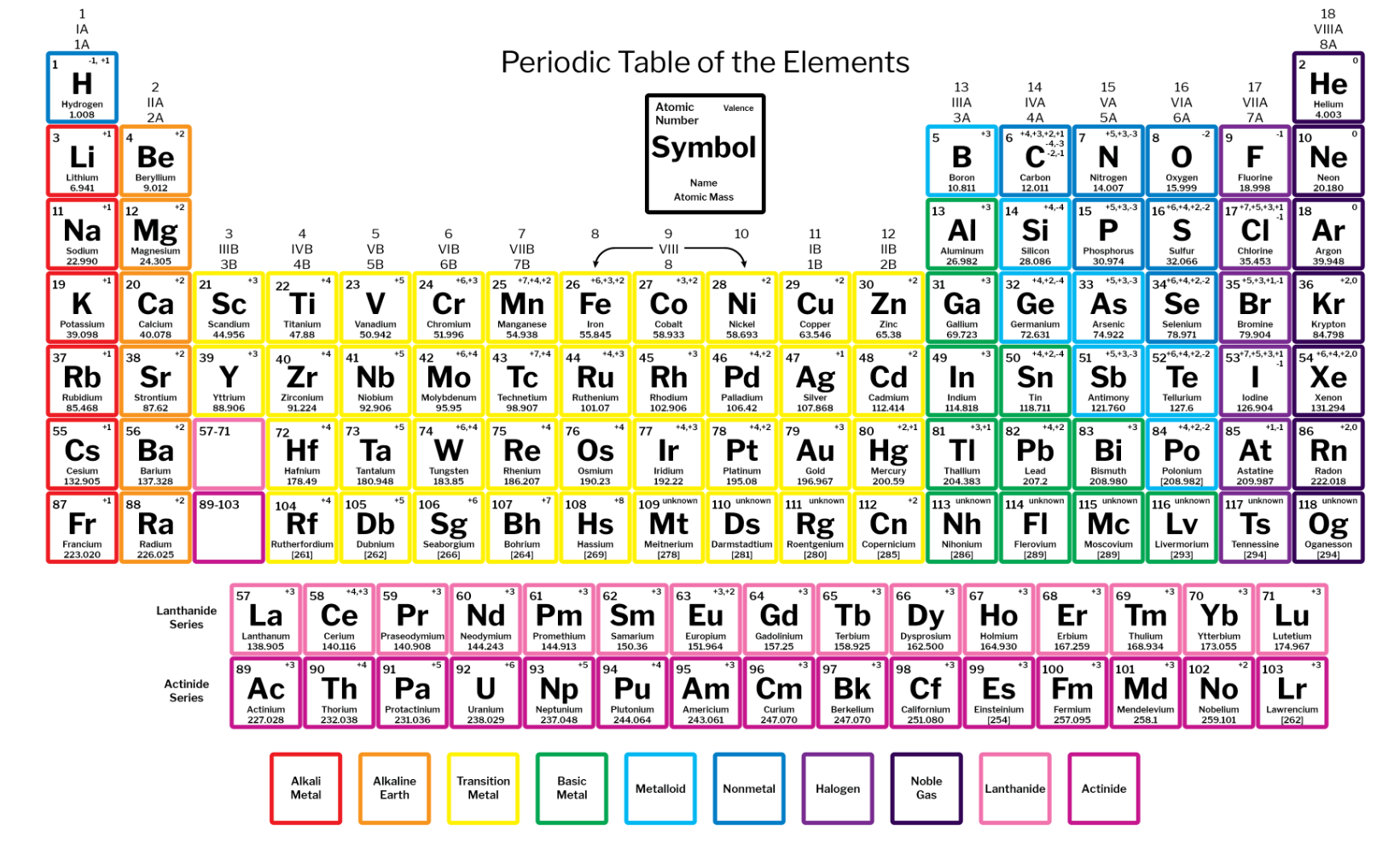
The red column is the alkali metals. They are very reactive with air and water. They are the most reactive metals
The orange column is the alkaline earth metals. They are less reactive than alkali metals. They easily react with oxygen
The purple column is the halogens. They are the most reactive non metal, They react very easily with the 1st and 2nd column (group)
The dark purple column is called the noble gases. They are very unreactive, but are also very stable.
Each group is made up of elements that are in the same family that share similar properties.
The mass increases from left to right along a period.

On an element, there is also a charge symbol.
Symbol is always 1 capital letter or 1 capital and 1 lowercase letter
We can find and calculate the number of subatomic particles an element has.
#protons= p+ = atomic #
#electrons= e- = atomic #
#newtons= n°= atomic mass- atomic number. Round to whole #
Ionic compounds
Ionic compounds always contain a metal and a non-metal , so they are always on opposite sides of the staircase.
Metals always want to lose electrons
Non metals want to gain electrons
You can discover their charges on the periodic table!
Charges are always written as number first, then their sign.
Balancing the charges
Look up each element and write each symbol with its charge, writing the positive ion first and the negative ion second
Check to see if the total positive charge is equal to the total negative charge
Add more of own or both ions until the total charges are unequal
Write your chemical formula, making sure the positive ion is first and the negative ion is second, using subscripts to show how many of each ion you needed
Ex: Na 1+ Cl 1-
Na, Cl 1s are invisible
NaCl
To cross your changes (always put in lowest terms)
Look up each element and write each symbol with its charge writing the positive ion first and the negative ion second
Draw arrows showing that the charge on one ion becomes the subscript on the other ion
Write your chemical formula making sure that your charges have become subscripts and that you don’t write the + or - signs anymore
CHECK that your subscripts are in the lowest terms possible
Ex: : Na 1+ Cl 1-
Na, Cl ones are invisible
NaCl
The Lewis dot diagram
Steps
Count all the valence electrons
Determine the central atom (the odd atom out)
Draw single bonds to the central atom
Put all the remaining Valence electrons on atoms as 1 part
Turn ion pairs into double or triple bonds to give every atom an octlet
Valence electrons
In an atom, electrons move in orbitals around a nucleus
Valence electrons are special electrons that are the ones in the outermost shell and are available for bonding
Not all electrons are valence electrons
You can find out the number of valence electrons of a atom by looking at what column the atom falls under in the periodic table. Ex: Oxygen is in the 3rd column, so it has 6 valence electrons
Helium is an exception of this! It only has 2 valence electrons
To break you bonds: needs energy, When bonds form, energy is released.