RA 10912
R.A. 10912 - Continuing Professional Development Act of 2016
R.A. 10912 - This also known as the Continuing Professional Development Act of 2016, which requires all professionals performing regulated professions under PRC comply with the CPD requirements for the renewal of their professional identification card (PIC). This is also the law that created the CPD Council.
R.A. No. 10912 lapsed into law on July 21, 2016, and took effect on August 26, 2016, following its publication.
R.A. No. 10912, unlike other medical technology laws, became a law without the signature of the President of the Philippines.
Under the Constitution, a bill will become law if not vetoed by the President within 30 days, and shall lapse into law as if he had signed it.
CPD - The term "continuing professional development"
refers to inculcation of advanced knowledge, skills, and ethical values in post-licensure specialization or an practice, self-inter- or multidisciplinary field of study,
for assimilation into professional directed research, and/or lifelong learning
Lifelong learning - refers for learning activities undertaken throughout one's life for the development of the competencies and qualifications of the professional.
Self-directed learning
constitutes learning activities such as online training, local/ international seminars, non-degree courses, institution/company-sponsored training programs, and the like.
These pursuits do not undergo CPD accreditation but may be applied for and awarded CPD units by the respective CPD Council.
What is the nature of CPD?
The CPD is a mandatory requirement for the renewal of the professional identification cards (PIC) of all registered and licensed professionals under the regulation of the PRC, including RMTs and MLTS.
What is a CPD Credit Unit?
A CPD credit unit (CU) refers to the value of an amount of learning that can be transferred to a qualification achieved from formal, informal, or non-formal learning setting including professional work experience wherein credits can be accumulated to predetermined levels for the award of a qualification.
The CPD CUs are mandatory for the renewal of a professional identification card (PIC) per compliance period of three years.
Guidelines in earning CPD CUs
Generally, a maximum of one CU per hour of activity may be given.
Full credit units are given for attendance and completion of assessment.
a. For Certificate of Attendance: 50% of the full credit units is given for attendance/participation.
b. For Certificate of Completion: Full credit units is given for attendance/ participation and completion of pre- and post-test.
Programs under the professional track, i.e., conferences, workshops, etc., may be given a maximum of 20 credit units only for activity of three or more days.
Programs under the academic track, i.e., Master's or Doctorate degree or its equivalent, may be given credit units as the specific course is completed, the sum total of which shall not exceed the allowable full credit units for the compliance period upon completion of the degree.
The maximum creditable units for self-directed and/or lifelong learning are as follows:
Registered medical technologists (RMTs): 15 Cus
Medical laboratory technicians (MLTs): 10 CUS
This, however, does not apply to RMTs/MLTs working overseas during the compliance period.
Applications for accreditation of self-directed and/or lifelong learning should be filed no later than five years after completion of the degree or program.
Certificates of Attendance/Completion of CPD activities under the professional track or other CPD activities issued to participants by the accredited CPD providers shall include the corresponding CPD units.
What happens if a medical technologist accumulates more than the required CPD credit units?
The excess credit units cannot be carried over to the next compliance period.
There is no provision under the CPD Act of 2016 and its implementing rules that permits the transfer of excess credit units to the succeeding compliance period.
What is the CPD Council?
The CPD Council refers to a body created to promote and ensure the continuous improvement of professionals, in accordance with national, regional, and international standards of practice.
What is the composition of the CPD Council?
Every CPD Council shall be composed of a chairperson and two members, and shall be under the supervision of the concerned PRB.
CPD Council
The CPD Council for Medical Technology operates under the supervision of the MTB, and is composed of the following:
1. The Chairperson is a member of the MTB (Management Team Board) chosen by the MTB.
2. The First Member is the president or officer of PAMET (being the only authorized professional organization (APO) of all registered medical technologists in the Philippines.)
3. The Second Member is the president or officer of PASMETH (being the national organization of all deans or department chairpersons of schools, colleges, or universities offering a medical technology course.)
Term of office
Chairperson is coterminous with his/her incumbency in the PRB.
The First and Second Members have a term of office of two years.
The Chairperson of the Council has the following functions:
1. To preside meetings of the Council
2. To supervise the activities of the Council
3. To submit Council's annual report to Planning and Monitoring Division not later than January 15 of the succeeding year
4. To sign Certificate of Accreditation (COA) of qualified CPD providers, the Certificate of Accreditation of Program (COAP) and the Certificate of Credit Units (CCU) for self-directed and/or lifelong learning
The functions of the CPD Council are as follows:
1. Ensure the adequate and appropriate provision of CPD programs for their respective profession
2. Evaluate and act on applications for accreditation of CPD providers and their CPD programs
3. Monitor and evaluate the implementation of the CPD programs
4. Assess criteria for accreditation of CPD providers and their CPD programs on a regular basis
5. Develop mechanisms for the validation, accreditation, and recognition of self-directed learning, prior/informal learning, online learning, and other learning processes through professional work experience
6. Conduct researches, studies, and benchmarking for international alignment of the CPD programs
7. Issue operational guidelines, with the approval of the PRC and the PRB concerned
8. Perform such other functions related or incidental to the implementation of the CPD
The CPD Act of 2016 created the CPD council and the CPD Council Secretariat to provide technical, administrative, and operational support to the CPD Councils and the PRBS in the implementation of the CPD programs.
The CPD Council Secretariat shall be headed by an Executive Director who is appointed by the PRC.
The following are the major areas of activities:
a. Ethics
b. Standards of Professional Practice
c. Enhancement of Professional Practice and Technical Competence
d. Environmental Factors Affecting the Profession
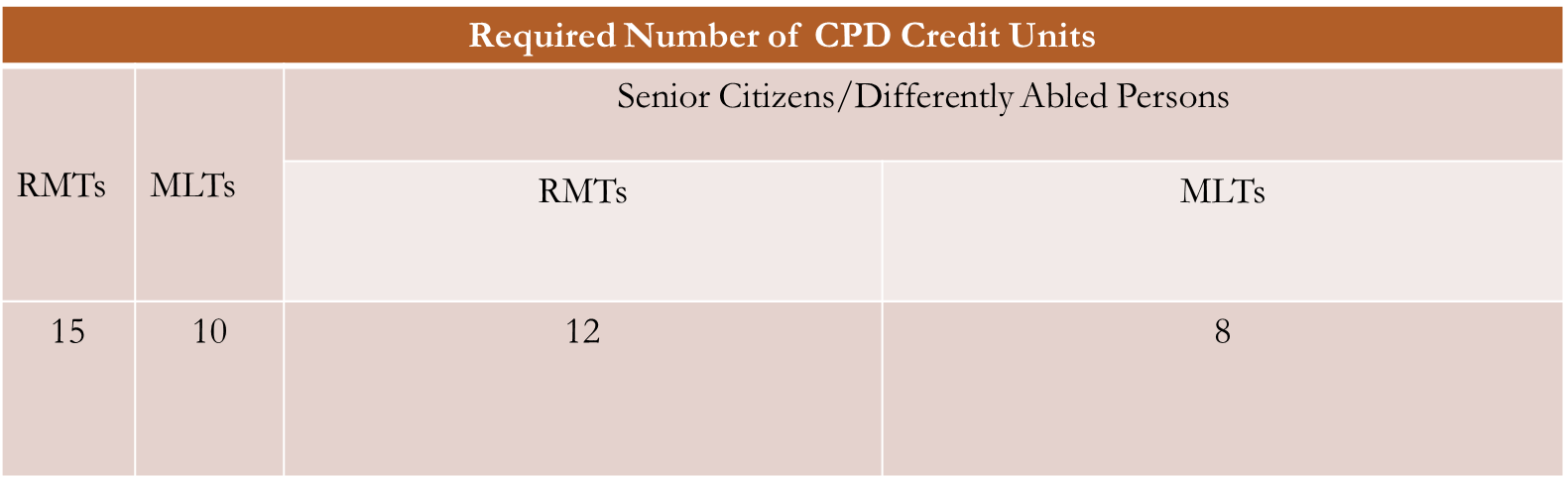
In PRC Resolution No. 2019-1146, Series of 2019, the following provisions for the transition period must be observed:
a. Professionals working overseas shall not be covered by the CPD requirements.
b. Newly licensed professionals shall not be covered by the CPD requirement for the first renewal cycle after obtaining their license.
c. The various CPD Councils shall reduce the required CPD to a minimum, which shall not be more than 15.
In compliance with the aforementioned mandate of the PRC, the PRB of Medical Technology issued PRB of Medical Technology Resolution No. 10 Series of 2019 suspending the compliance of 45 CUs for RMTs and 30 CUs for MLTs for the renewal of PICs during the transition period, requiring only 15 CUs instead.
Thus, during the transition period, the CU requirements for each category in the table below will be
observed.
The CPD Council for medical technology profession use the Dreyfus Model of Skill Acquisition,
the basis of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Comprehensive Guidelines for Public Health Laboratory Professionals of 2015.
The following proficiency tiers and definitions shall be adopted in categorizing CPD activity leading towards career progression and specialization.
Proficiency Tiers in categorizing CPD activities
1. Beginner - One who can demonstrate an elementary level of performance.
Beginners might have gained enough classroom or on-the-job training to note (or to have pointed out to them by a mentor) recurring principles and themes but might not yet be able to apply them consistently.
The beginner might have sufficient subject matter knowledge but has limited experiential knowledge needed to perform a behavior or function without frequent guidance or oversight.
2. Competent - One who has been in the same or similar job and who begins to see their actions within the context of the laboratory's long-range goals and plans.
The competent laboratory scientist develops knowledge and experience to recognize a situation in terms of overall picture or in terms of which aspects are most salient or most important.
The competent worker has the necessary ability to cope with and address many contingencies of laboratory operations, as this person has a feeling of adequacy and is able to perform a task, behavior, or function with a high degree of independence.
3. Proficient - One who understands situations as a whole and perceives their meaning in terms of the laboratory's mission and long-term goals.
The proficient person learns from experience what typical circumstances to expect in a given situation and how plans need to be modified in response to these events.
The proficient laboratory scientist uses established principles to manage the many contingencies of laboratory operations and has developed sufficient mastery to integrate or design a new task, behavior, or function.
4. Expert - One with substantial experience and knowledge, has an intuitive grasp of situations, and focuses on the root of the problem.
The expert operates from a deep understanding of the total situation and integrates system thinking, collaborative relationships, and the resources at their disposal to achieve the laboratory's mission.
The expert laboratory scientist has acquired mastery to design new strategies, policies, tasks, behaviors, and functions that support quality behavior.
What is the nature of CPD programs?
Continuing professional development programs refer to sets of learning activities accredited by the CPD Council such as seminars, workshops, technical lectures, or subject matter meetings; non-degree training lectures and scientific meetings; and modules, tours, and visits, which equip the professionals with advanced knowledge, skills, and values in specialized inter- or multidisciplinary fields of study, self-directed research, and/or lifelong learning.
The activities in CPD programs consist of the following:
Formal learning consists of educational arrangements such as curricular qualifications and teaching-learning requirements that take place in education and training institutions recognized by relevant national authorities and lead to diplomas and qualifications.
Non-formal learning is acquired in addition or alternatively to formal learning and may be structured and made more flexible according to educational and training arrangements.
Informal learning occurs in daily life and is assessed through recognition, validation, and accreditation process and can contribute to a qualification.
Online learning activities are structured or unstructured learning initiatives that use the Internet and other web-based information and communications technology solutions.
Professional work experiences refer to participations that a professional gains while working in a specific field.
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Enumeration:
Function of Chairperson in Council:
1. To preside meetings of the Council
2. To supervise the activities of the Council
3. To submit Council's annual report to Planning and Monitoring Division not later than January 15 of the next year
4. To sign COA, COAP, CCU
The CPD Council has the following functions:
Ensure appropriate provision of CPD programs
Evaluate and act on applications for accreditation of CPD providers and programs.
Monitor the implementation of CPD programs.
assess criteria for accreditation of CPD providers and programs.
Develop mechanisms for validation, accreditation, and recognition of self-directed learning, prior/informal learning, online learning, and other learning processes through work experience.
Conduct research, studies, and benchmarking for international alignment of CPD programs.
Issue operational guidelines with approval from PRC and PRB.
Perform other functions related to the implementation of CPD.
The following are the major areas of activities:
a. Ethics
b. Standards of Professional Practice
c. Enhancement of Professional Practice and Technical Competence
d. Environmental Factors Affecting the Profession
PRC Resolution No. 2019-1146 outlines following provisions:
a. Professionals working overseas are exempt from CPD requirements.
b. Newly licensed professionals are exempt from CPD requirements for their first license renewal.
c. CPD Councils will minimize the required CPD to a maximum of 15 units.
CPD programs include the following activities:
Formal learning: This includes education and training in recognized institutions, leading to diplomas and qualifications.
Non-formal learning: Additional or alternative learning that can be structured and flexible.
Informal learning: Learning that happens in daily life, assessed through recognition and validation, and can contribute to a qualification.
Online learning: Structured or unstructured learning using the Internet and other web-based technology.
Professional work experiences: Gaining experience in a specific field while working.